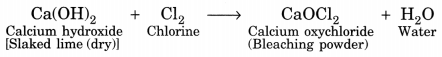
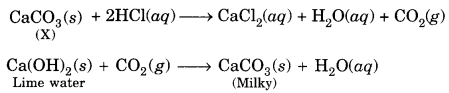
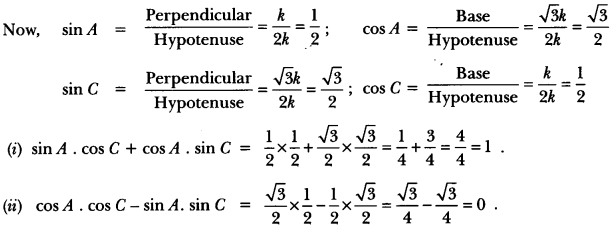
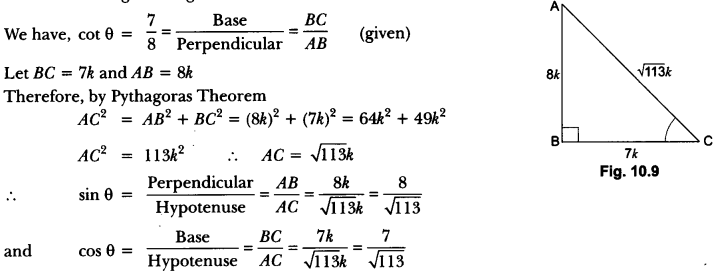
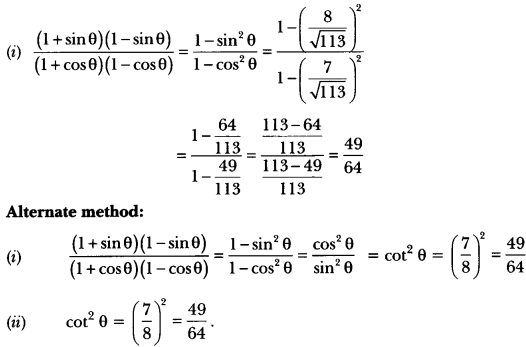
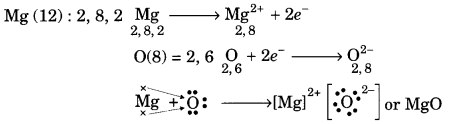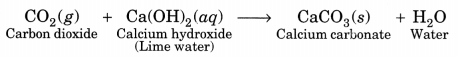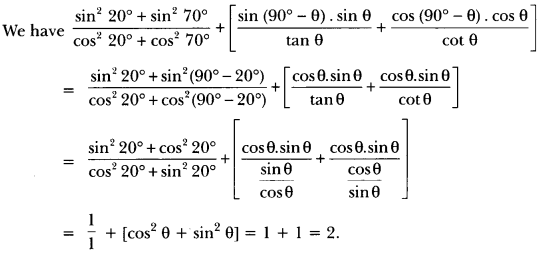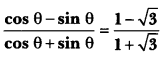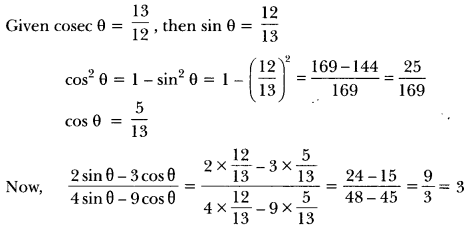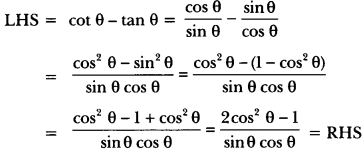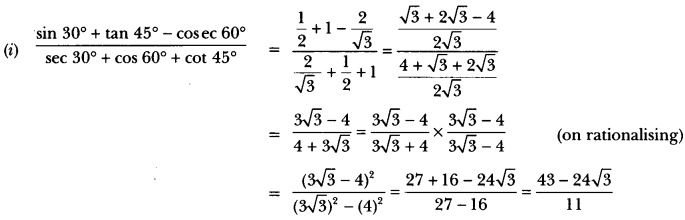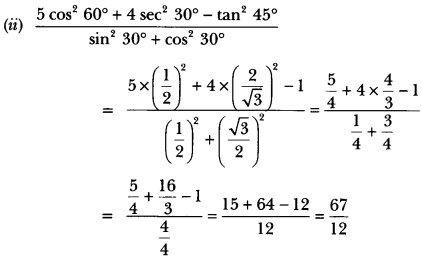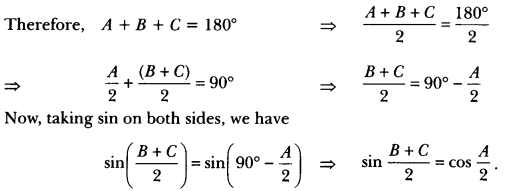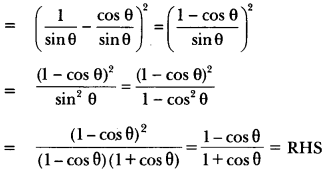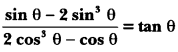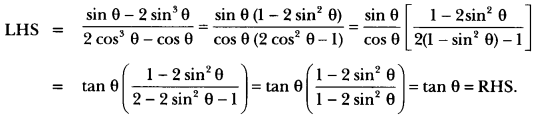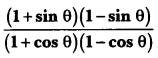Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 10 History Chapter 7 Extra Questions and Answers Print Culture and the Modern World Pdf free download. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-10-social-science/
Print Culture and the Modern World Class 10 Extra Questions History Chapter 7
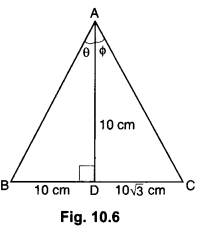
Class 10 History Chapter 7 Questions And Answers Question 1.
What is calligraphy?
Answer:
Calligraphy is the art of beautiful and stylised writings.
Print Culture And The Modern World Extra Questions Question 2.
Where did the earliest print technology develop in the world?
Answer:
The earliest print technology developed in China, Japan and Korea; it was, their, hand printing, around 594 AD.
Print Culture And The Modern World Class 10 Important Questions And Answers Question 3.
Name the explorer who brought with him the print technology to Italy.
Answer:
Marco Polo, in 1295.
Print Culture And The Modern World Question Answers Pdf Question 4.
Who had developed the first known printing press and when?
Answer:
Johann Gutenberg, in 1430.
Class 10 History Print Culture And Modern World Notes Question 5.
Who was Martin Luther?
Answer:
Martin Luther was a Protestant reformer. He wrote Ninety Five Thesis in 1517, criticizing the practice and rituals of the Roman Catholic church.
![]()
Print Culture And The Modern World Class 10 Questions And Answers Question 6.
Why was Luther deeply grateful to printing?
Answer:
Printing, for Martin Luther, was one of the greatest gift of God to the people.
Class 10 History Chapter 7 Mcq With Answers Question 7.
Why did the Roman church begin maintaining an Index of Prohibited Books from 1558 onward?
Answer:
The Roman church was troubled by the effects of the popular reading questioning it. So it maintained such an index from 1558 onward.
Class 12 History Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 8.
What were Priliotheque Bleue ?
Answer:
Peilictheque Bleue were low-priced small books in France.
Class 12 History Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 9.
Whose writings, in France, were widely printed and read during the eighteenth century?
Answer:
Voltaire, and Rousseau.
Print Culture And The Modern World Important Questions Question 10.
Name a socialist whose discoveries, when published, influenced scientifically-minded readers.
Answer:
Isaac Newton.
Print Culture Class 10 Important Questions Question 11.
Whose novels, during the mid 18th century, had provided the basis for opposing despotion?
Answer:
Louise Sebastien Mercier’s novels destroyed the basis of despotism. He once proclaimed: “Tremble, therefore, tyrants of the world! Tremble before the virtual writer.
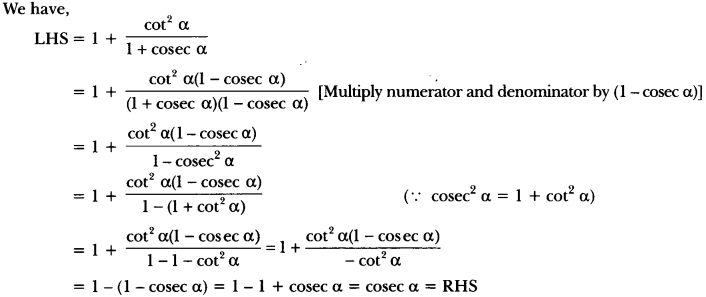
Print Culture And The Modern World Pdf Question 12.
Which magazines were especially meant for women?
Answer:
Penny magazines.
![]()
Ch 7 Science Class 10 Extra Questions Question 13.
How were the earlier manuscripts written in India?
Answer:
The earlier manuscripts were handwritten and in languages such as Sanskrit Persian, Arabic, and also in Vernacular language.
Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions Question 14.
Who brought the printing technology to India?
Answer:
The Portuguese.
Class 6 Science Ch 7 Extra Questions Question 15.
Who brought out the weekly Bengal Gazzette?
Answer:
Gangadhar Bhattacharya, a close associate of Raja Ram Mohan Roy.
Question 16.
When was Tulsidas’s Ramcharitmas brought out in the printed form?
Answer:
In 1810, from Calcutta.
Question 17.
Name the two presses of mid-19lh century India which published religious texts.
Answer:
- Naval Kishore Press (Lucknow).
- Seri Venkateshwar Press (Bombay).
Question 18.
Give two advantages of the print culture.
Answer:
- It stimulates the publication of conflicting opinions among communities;
- It connected communities and people in different parts of India.
Question 19.
Name the book Altaf Husain Ali I wrote in 1874?
Answer:
Majalis Un Nissu (Assemblies of Women).
Question 20.
Which book did Maulana Ashraf Ali write in 1905?
Answer:
Bihishit Zewar (The ornament of Paradise).
Question 21.
Name the first full-length autobiography published in the Bengali language.
Answer:
Amar Jiban by Rashundari Debi.
Question 22.
Who wrote Istri Dharam Vichae?
Answer:
Ram Chaddha.
![]()
Question 23.
What does Battrola signify?
Answer:
Battrala signifies the area developed to the printing of popular books. It is located in central Calcutta.
Question 24.
For what art form is Kitagawa Utamaro known? 1
Answer:
Kitagawa Utamaro, born in Edo in 1753, was widely known for his contributions to an art form called ukiyo (‘pictures of the floating world’) or depiction of ordinary human experiences, especially urban ones. These prints travelled to contemporary US and Europe and influenced artists like Manet; and Van Gogh.
Question 25.
How did print technology travel from China to Italy and later in other parts of Europe?
Answer:
In 1295, Marco Polo, a great explorer, returned to Italy after many years of exploration in China. Marco Polo brought this knowledge back with him. Now Italians began producing books with woodblocks, and soon the technology spread to other parts of Europe, where luxury editions were still handwritten on very expensive vellum, meant for aristocratic circles and rich monastic libraries.
Question 26.
What do you know by the print resolution?
Answer:
Print resolution was not just a development, a new way of producing books; it transformed the lives of people, changing their relationship to information and knowledge, and with institutions and authorities. It influenced popular perceptions and opened up new ways of looking at things.
Question 27.
What is reading mania? Explain.
Answer:
Through the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, literacy rates went up in most parts of Europe. Churches of different denominations set up schools in villages, carrying literacy to peasants and artisans.
By the end of the eighteenth century, in some parts of Europe literacy rates were as high as 60 to 80 per cent. As literacy and schools spread in European countries, there was a virtual reading mania. People wanted books to read and printers produced books in ever-increasing number.
Question 28.
How was the printing press a danger to despotism? What does Mercier say about it?
Answer:
Louis Sebastien Mercier, a novelist in eighteenth-century France, declared: “The printing press is the most powerful engine of progress and public opinion is the force that will sweep despotism away.’ In many of Mercier’s novels, the heroes are transformed by acts of reading.
They devour books, are lost in the world books create, and become enlightened in the process. Convinced of the power of print in bringing enlightenment and destroying the basis of despotism, Mercier proclaimed: Tremble, therefore, tyrants of the world! Treble before the virtual writer.
Question 29.
What do you know about the Grimm Brothers of Germany?
Answer:
The Grimm Brothers in Germany spent years compiling traditional folk tales gathered from peasants. What they collected was edited before the stories were published in a collection in 1812. Anything that was considered unsuitable for children or would appear vulgar to the elites, was not included in the published version.
![]()
Question 30.
‘Women were important readers as well as writers’ Explain.
Answer:
Women became important readers as well as writers Penny magazines were especially meant for women, as were manuals teaching proper behaviour and housekeeping. When novels began to be written in the nineteenth-century women were seen as important readers.
Some of the best-known novelists were women: Jane Austen, the Bronte sisters, George Eliot. Their writings became important in defining a new type of woman: a person with will, strength of personality, determination and the power to think.
Question 31.
How did print come to India? Give a brief account.
Answer:
The printing press first came to Goa with Portuguese missionaries in the mid-sixteenth century. Jesuit priests learnt Konkani and printed several tracts. By 1674, about 50 books had been printed in the Konkani and in Kanara languages: Catholic priests printed the first Tamil book in 1579 at Cochin, and in 1713 the first Malayalam book was printed by them. By 1710, Dutch Protestant missionaries had printed 32 Tamil texts, many of them translations of older works.
Question 32.
Which printed technology appeared in 1820s in India?
Answer:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy published Sambd Kaumudi from 1821 and the Hindu orthodoxy commissioned the Samachar Chandrika to oppose his opinions. From 1822. Iwo Persian newspapers were published, Jam-i-Jahu Nama and Samsul Akhbar. In the same year, a Gujarati newspaper, the Bombay Samachar, made its appearance.
Question 33.
What new visual culture was taking place in late 19th century India?
Answer:
By the end of the nineteenth century, a new visual culture was taking shape. With the setting up of an increasing number of printing presses, visual images could be easily reproduced in multiple copies. Painters like Raja Ravi Verma produced images for mass circulation.
Question 34.
How did the print technology development in China?
Answer:
The earliest kind of print technology was developed in China. This was a system of hand printing. From AD 594 onwards, books in China were printed by rubbing paper – also invented there against the inked surface of ‘Woodblocks. As both sides of the thin, porous sheet could not be printed, the traditional Chinese ‘accordion book’ was folded and stitched at the side. Superbly skilled craftsmen could duplicate, with remarkable accuracy the beauty of calligraphy.
The imperial state in China was, for a very long time, the major producer of printed material. China possessed a huge bureaucratic system which recruited its personnel through civil service examinations Textbooks for this examination were printed in vast numbers under the sponsorship of the imperial state.
From the sixteenth century, the number of examination candidates Went up and that increased the volume of print. By the seventeenth century, as urban culture bloomed in China, the uses of print diversified Print was no longer used just by scholar-officials.
Merchants used print in their everyday life, as they collected trade information. Reading increasingly became a leisure activity. From hand-printing, there began mechanical printing. From China, the print technology moved to Europe through the Silk Route.
Question 35.
Did everyone welcome printed books? Why were some people apprehensive?
Answer:
Printed books were both welcomed as well as unwelcomed. Those who disagreed with established authorities could now print and circulate their ideas. Through the printed message, they could persuade people to think differently and move them to action. This had significance in different spheres of life. Not everyone welcomed the printed book and those who did also had fears about it. Many were apprehensive of the effects that the easier access to the printed word and the wider circulation of books, could have on people’s minds.
It was feared that if there was no control over what was printed and read then rebellious and irreligious thoughts might spread. If that happened the authority of valuable literature would be destroyed. Expressed by religious authorities and monarchs, as well as many writers and artists, this anxiety was the basis of widespread criticism of the new printed literature that had began to circulate.
Question 36.
Why do some historians think that the print culture created the basis for the French Revolution? What are the three types of argument? Explain.
Answer:
Many historians have argued that print culture created the conditions within which French Revolution occurred.
Three types of arguments have been usually put forward.
First: print popularized the ideas of the Enlightenment thinkers. Collectively, their writings provided a critical commentary on tradition, superstition and despotism. They argued for the rule of reason rather than custom and demanded that everything be judged through the application of reason and rationality.
They attacked the sacred authority of the Church and the despotic power of the state, thus eroding the legitimacy of a social order based on tradition. The writings of Voltaire and Rousseau were read widely; and those who read these books saw the world through new eyes, eyes that were questioning critical and rational.
Second: Print created a new culture of dialogue and debate. All values, norms and institutions were re-evaluated and discussed by a public that had become aware of the power of reason and recognised the need to question existing ideas and beliefs Within this public culture, new ideas of social revolution came into being.
Third: by the 1780s there was an outpouring of literature that mocked the royalty and criticised their morality. In the process, it raised questions about the existing social order. Cartoons and caricatures typically suggested that the monarchy remained absorbed only in sensual pleasures while the common people suffered immense hardships.
This literature was circulated underground and led to the growth of hostile sentiments against the monarchy. Indeed, print did not directly shape their minds but it did open the possibility of thinking differently.
![]()
Question 37.
Bring out newer innovations in the print technology since the eighteenth century.
Answer:
By the late eighteenth century, the press came to be made out of metal. Through the nineteenth century, there were a series of further innovations in printing technology. By the mid-nineteenth century, Richard M. Hoe of New York had perfected the power-driven cylindrical press. This was capable of printing 8,000 sheets per hour. This press was particularly useful for printing newspapers. In the late nineteenth century, the offset press was developed which could print up to six colours at a time.
From the turn of the twentieth century, electrically operated presses accelerated printing operations. A series of other developments followed. Methods of feeding paper improved, the quality of plates became better, automatic paper reels and photoelectric controls of the colour register were introduced. The accumulation of several individual mechanical improvements transformed the appearance of printed texts.
Objective Type Questions
1. Choose the most appropriate alternative:
Question 1.
On what model was the Vernacular Press Act (1878) was passed in India?
(a) American Press Laws
(b) French Press Law’s
(c) Irish Press Laws
(d) Australian Press Laws
Answer:
(c) Irish Press Laws
Question 2.
Istri Dharsun Vichar was written by:
(a) Ram Chhddha
(b) Laxman Chaddha
(c) Bharat Chaddha
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Ram Chhddha
Question 3.
Raja Ravi Varma was:
(a) an architect
(b) a doctor
(c) a painter
(d) a novelist.
Answer:
(c) a painter
![]()
Question 4.
Chapbooks were:
(a) low-priced books
(b) high-priced books
(c) cheap books
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) low-priced books
2. Choose true (✓) or false (✗) from the following:
Question 1.
Gutenberg was a French artist.
Answer:
(✗)
Question 2.
Print technology owes its origin to Japan.
Answer:
(✗)
Question 3.
Warren Hastings was the Governor-General of Australia.
Answer:
(✗)
Question 4.
Amar Jiban was the first full-length autobiography written in the Assamese language.
Answer:
(✗).