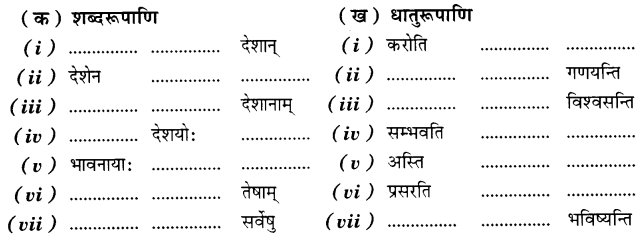
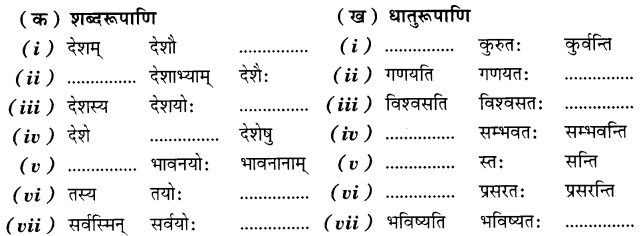
Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 Mother’s Day with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 English with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Mother’s Day Class 11 English MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Online Education MCQ Questions for Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 Mother’s Day with Answers
Mother’s Day Class 11 MCQ Chapter 5 Question 1.
The attitude of Mrs. Pearson’s family changes towards her. Comment.
(a) No
(b) Yes
(c) Maybe
(d) Not clear from the story
Answer
Answer: (b) Yes
Mothers Day MCQ Chapter 5 Class 11 Question 2.
Mrs. Fitzgerald asks Mrs. Pearson to be ___________ with her family.
(a) rude
(b) polite
(c) ignorant
(d) firm
Answer
Answer: (d) firm
Mother’s Day MCQ Chapter 5 Class 11 Question 3.
When do Mrs. Pearson and Mrs. Fitzgerald get back to their original selves?
(a) When Mrs. Pearson’s family gets to know about them
(b) When they both get bored
(c) When the situation goes out of hand
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) When the situation goes out of hand
MCQ Of Mother’s Day Class 11 Chapter 5 Question 4.
“It’s that silly old bag from next door- Mrs. Fitzgerald.” Who said this?
(a) Dorris
(b) Cyril
(c) George
(d) Mrs. Pearson
Answer
Answer: (b) Cyril
MCQ Of Mother’s Day Chapter 5 Class 11 Question 5.
Mrs. Pearson tells George that he is being ___________ at the club.
(a) respected
(b) laughed upon
(c) called names
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
Answer: (d) Both (b) and (c)
Mother’s Day MCQ Questions Chapter 5 Class 11 Question 6.
How does the author describe George Pearson?
(a) Pompous
(b) Solemn
(c) Fifty-ish
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Question 7.
Why was Dorris red-eyed?
(a) Because of an infection
(b) Because of a fight
(c) Because of crying
(d) Because she was getting ready to head out
Answer
Answer: (c) Because of crying
Question 8.
“Buck teeth and half-witted…” Who has been described here?
(a) Cyril Pearson
(b) George Pearson
(c) Charlie Spence
(d) Mrs. Fitzgerald
Answer
Answer: (c) Charlie Spence
Question 9.
What makes Dorris astounded as soon as she enters the house?
(a) The sight of her mother smoking
(b) Because the tea was not ready
(c) Because her mother was not there
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) The sight of her mother smoking
Question 10.
Mrs. Pearson was ___________ about Mrs. Fitzgerald’s plan.
(a) excited
(b) hesitant
(c) sure
(d) envious
Answer
Answer: (b) hesitant
Question 11.
How would you describe Mrs. Pearson?
(a) Dominating
(b) Considerate
(c) Compliant
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer
Answer: (d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 12.
How does Mrs. Pearson describe her family members?
(a) Thoughtless and selfish
(b) Pleasant and helpful
(c) Hardworking
(d) Mindful
Answer
Answer: (a) Thoughtless and selfish
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 English Snapshots Chapter 5 Mother’s Day with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 English Mother’s Day MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.