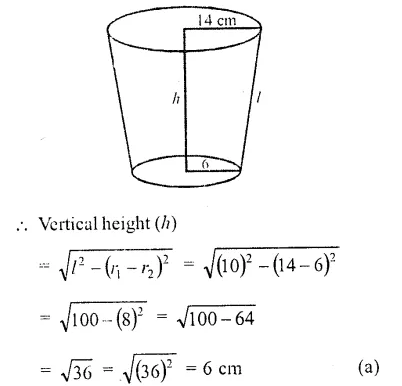
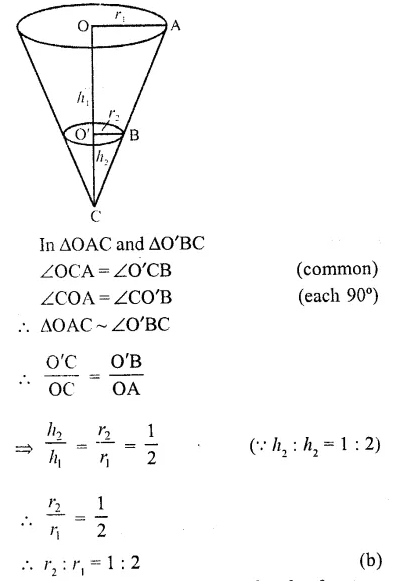
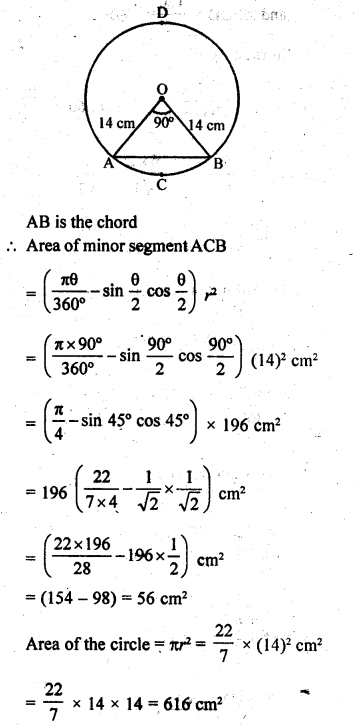
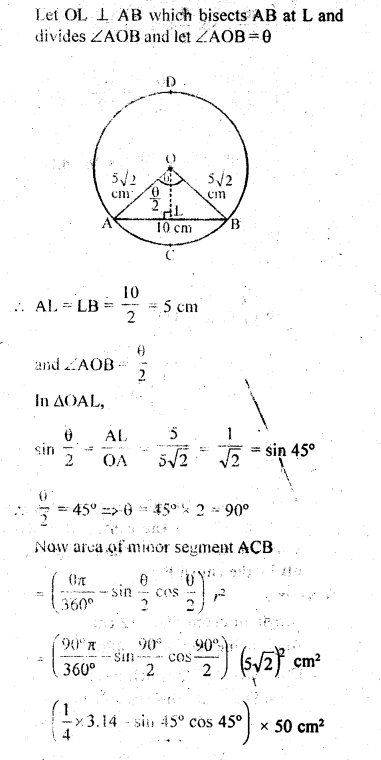
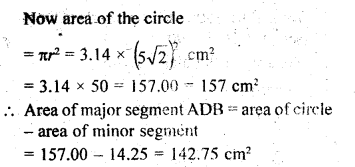
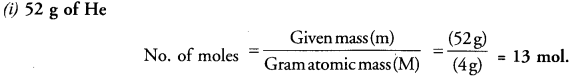
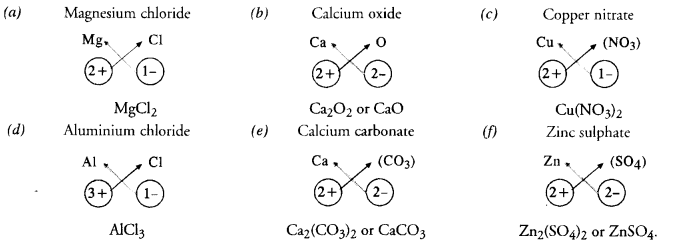
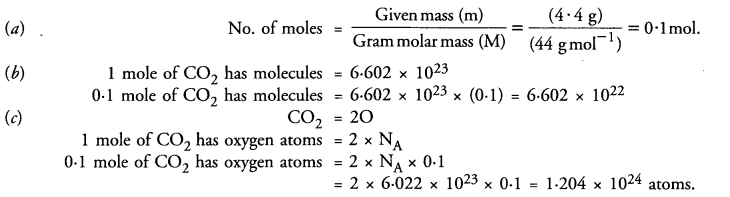
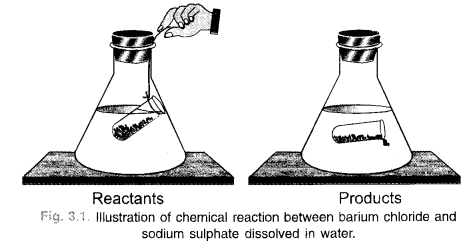
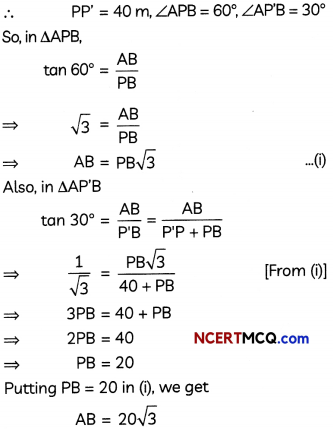
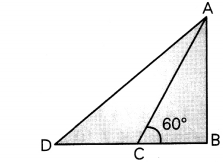
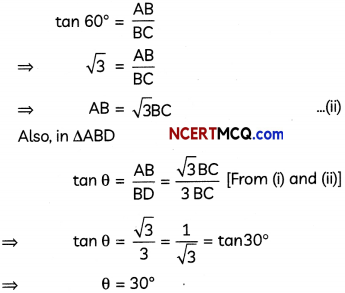
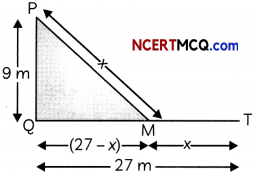
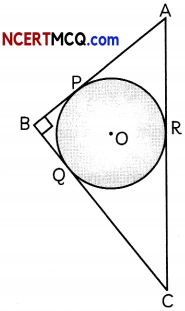
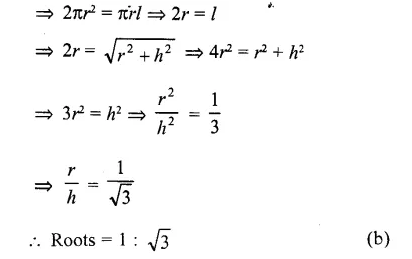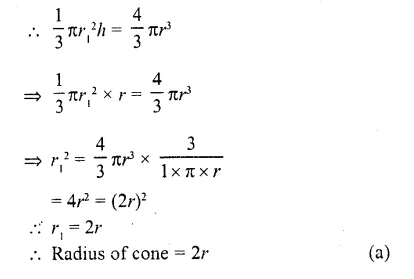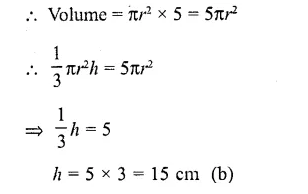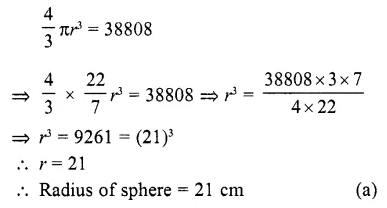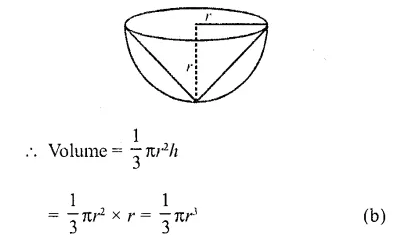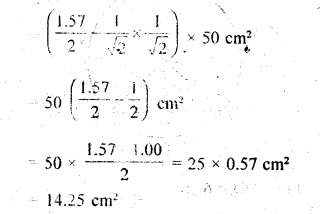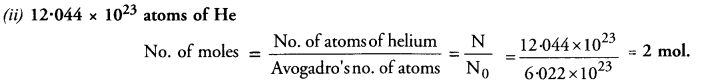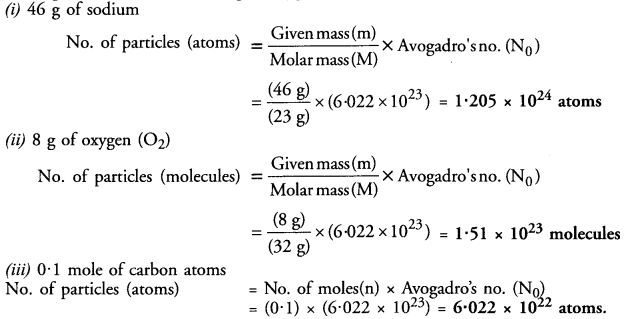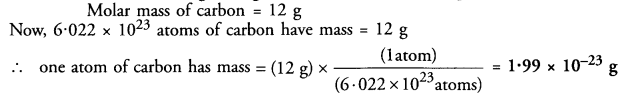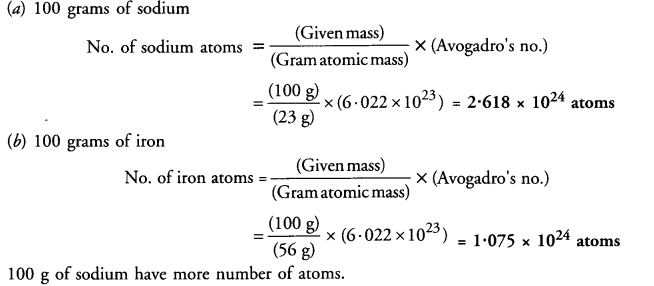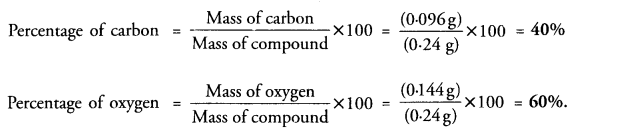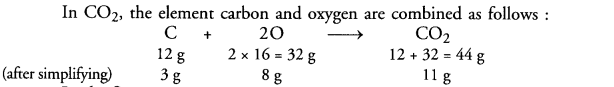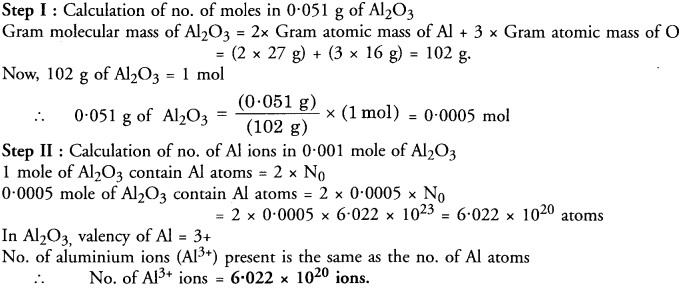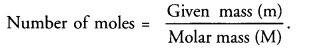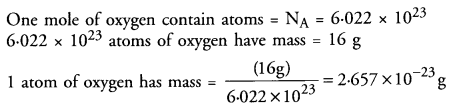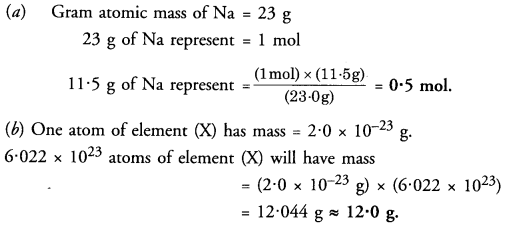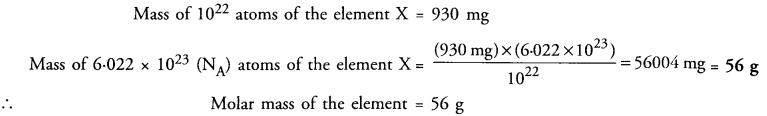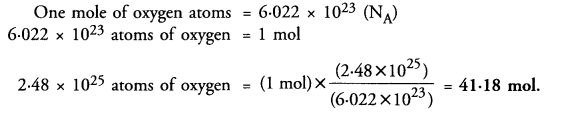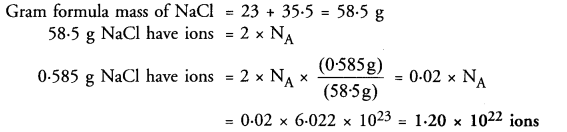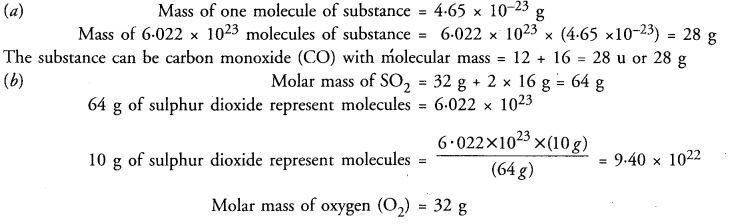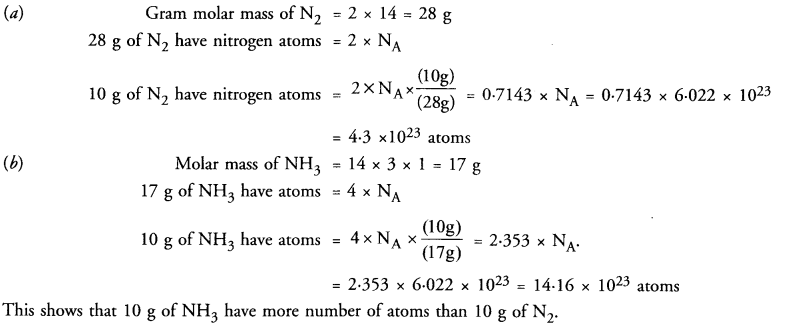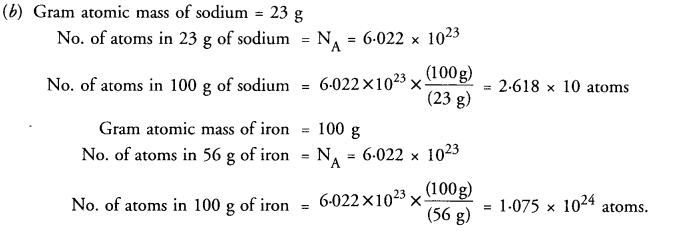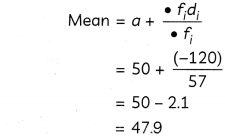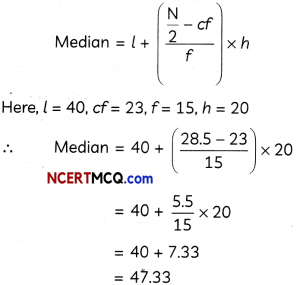This grammar section explains Online Education English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used.
Online Education Adverbs Worksheet Exercises for Class 3 CBSE with Answers PDF
- Words that tells us more about the doing words are called How Words.
- They show how an action is done.
These how words are called Adverbs. Adverbs end in-ly. For example: slow – slowly, loud – loudly, brave – bravely, sweet – sweetly, sad – sadly - We can often convert a describing word into a how word by adding -ly.
- An adverb is generally placed after the verb it is describing. For example: Arun ran swiftly.
- An adverb can also be placed away from the verb. For example: Arun ran to the door swiftly.
Adverbs Worksheet Exercises for Grade 3 with Answers CBSE PDF
A. Underline the adverbs that describe the verbs in the following sentences.
1. My grandpa snored loudly. 
2. My sheepdog sat lazily in the pool. so 
3. Nitin placed a card slowly on the house of cards.
4. Naveen stamped his feet angrily. 
5. Neerja waited patiently for the computer to load.
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable adverbs from the word bank.
1. The lion roared ___________
2. I am tired. Let’s walk ___________
3. I woke up because the phone rang ___________
4. She does not complain about the food. Angrily She eats ___________
5. The children are reading ___________
6. He finished his homework ___________
C. Change the adjectives into adverbs. Then write a sentence about each picture using the adverb.
1. strong – strongly

The boy kicked the ball strongly.
2. happy – ___________

______________________
3. beautiful – ___________

______________________
4. loud – ___________

______________________
5. soft – ___________

______________________