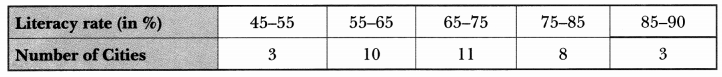
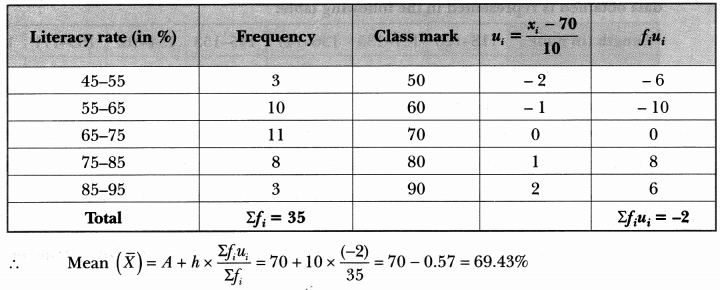
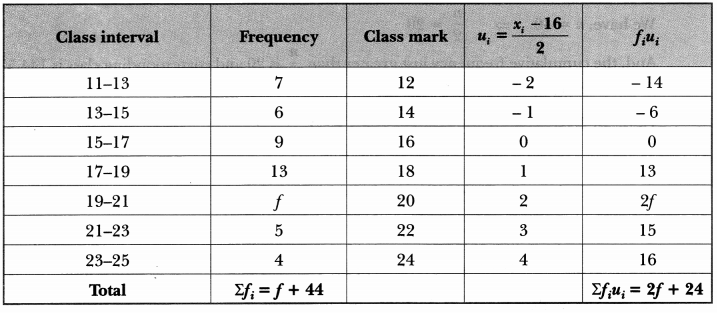
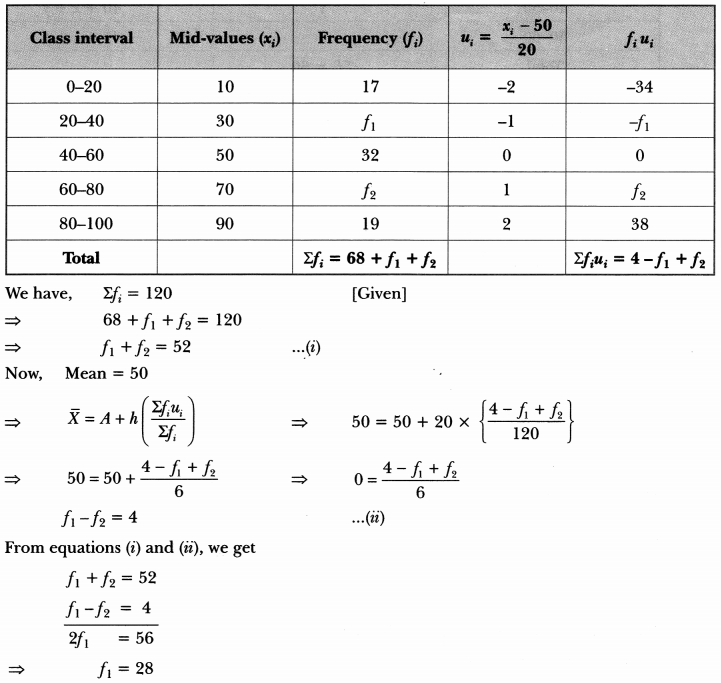
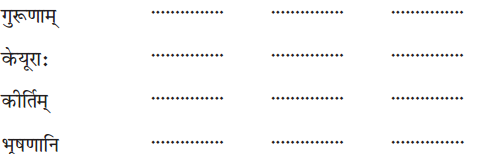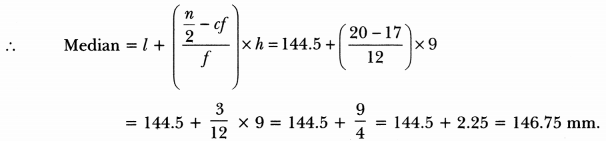We have given detailed Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 13 अमृतं संस्कृतम् Questions and Answers come in handy for quickly completing your homework.
Online Education NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Sanskrit Ruchira Chapter 13 अमृतं संस्कृतम्
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 13 अमृतं संस्कृतम् Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न: 1.
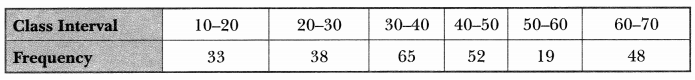
उच्चारणं कुरुत- (उच्चारण कीजिए- Pronounce these.)
उपलब्धासु
सङ्गणकस्य
चिकित्साशास्त्रम्
वैशिष्ट्यम्
भूगोलशास्त्रम्
वाङ्मये
विद्यमानाः
अर्थशास्त्रम्
उत्तराणि:
छात्र ध्यानपूर्वक शुद्ध उच्चारण करें।
प्रश्न: 2.
प्रश्नानाम् एकपदेन उत्तराणि लिखत- (प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक शब्द में लिखिए- Answer the following questions in one word.)
(क) का भाषा प्राचीनतमा?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतभाषा
(ख) शून्यस्य प्रतिपादनं कः अकरोत् ?
उत्तराणि:
भास्कराचार्यः
(ग) कौटिल्येन रचितं शास्त्रं किम्?
उत्तराणि:
अर्थशास्त्रम्
(घ) कस्याः भाषायाः काव्यसौन्दर्यम् अनुपमम्?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतभाषायाः
(ङ) काः अभ्युदयाय प्रेरयिन्ति?
उत्तराणि:
सूक्तयः।
प्रश्न: 3.
प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि एकवाक्येन लिखत। (प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक वाक्य में लिखिए। Answer the questions in one sentence.)
(क) सङ्गणकस्य कृते सर्वोत्तमा भाषा का?
उत्तराणि:
सङ्गणकस्य कृते संस्कृतमेव सर्वोत्तमा भाषा।
(ख) संस्कृतस्य वाङ्मयं कैः समृद्धमस्ति?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतस्य वाङ्मयं वेदैः, पुराणैः, नीतिशास्त्रैः चिकित्साशास्त्रादिभिः च समृद्धमस्ति ।
(ग) संस्कृतम् किं शिक्षयति?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतभाषा शिक्षयति यत् सर्वभूतेषु आत्मवत् व्यवहारः कर्त्तव्यः। अथवा संस्कृतभाषा आत्मवत् सर्वभूतेषु व्यवहारं कर्तुम् शिक्षयति।
(घ) अस्माभिः संस्कृतं किमर्थं पठनीयम्?
उत्तराणि:
अस्माभिः संस्कृतं मनुष्यस्य समाजस्य च परिष्कारार्थम् पठनीयम्।
प्रश्नः 4.
इकारान्त-स्त्रीलिङ्गशब्दरूपम् अधिकृत्य रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत- (इकारान्त-स्त्रीलिंग-शब्दरूप के आधार पर रिक्त स्थान भरिए- Fill in the blanks according to ‘इकारान्त’ feminine gender words.)
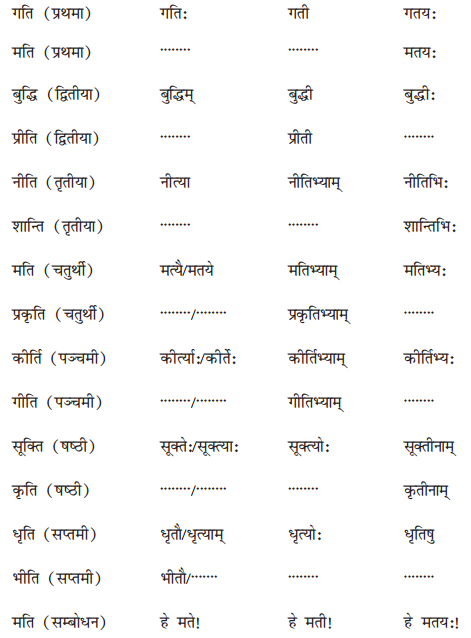
उत्तराणि:

प्रश्नः 5.
रेखाङ्कितानि पदानि अधिकृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत- (रेखांकित पदों के आधार पर प्रश्ननिर्माण कीजिए Frame questions based on the underlined words.)
(क) संस्कृते ज्ञानविज्ञानयोः निधिः सुरक्षितोऽस्ति ।
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृते ज्ञानविज्ञानयोः का सुरक्षितोऽस्ति?
(ख) संस्कृतमेव सङ्गणकस्य कृते सर्वोत्तमा भाषा।
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतमेव कस्य कृते सर्वोत्तमा भाषा?
(ग) शल्यक्रियायाः वर्णनं संस्कृतसाहित्ये अस्ति।
उत्तराणि:
शल्यक्रियायाः वर्णनं कस्मिन् अस्ति?
(घ) वरिष्ठान् प्रति अस्माभिः प्रियं व्यवहर्त्तव्यम्।
उत्तराणि:
कान् प्रति अस्माभिः प्रियं व्यवहर्त्तव्यम् ?
प्रश्नः 6.
उदाहरणानुसारं पदानां विभक्तिं वचनञ्च लिखत- (उदाहरण के अनुसार शब्दों के विभक्ति और वचन लिखिए- Write the inflexion and number of the words according to the example.)

उत्तराणि:

प्रश्न: 7.
यथायोग्यं संयोज्य लिखत- (यथा-उचित मिलाकर लिखिए- Match the following correctly.)
‘क’ – ‘ख’
कौटिल्येन – अभ्युदयाय प्रेरयन्ति।
चिकित्साशास्त्रे – ज्ञानविज्ञानपोषकम्।
शून्यस्य आविष्कर्ता – अर्थशास्त्रं रचितम्।
संस्कृतम् – चरकसुश्रुतयोः योगदानम्।
सूक्तयः – आर्यभटः।
उत्तराणि:
कौटिल्येन – अर्थशास्त्रं रचितम्।
चिकित्साशास्त्रे – चरकसुश्रुतयोः योगदानम्।
शून्यस्य आविष्कर्ता – आर्यभटः।
संस्कृतम् – ज्ञानविज्ञानपोषकम्।
सूक्तयः – अभ्युदयाय प्रेरयन्ति।
Class 7 Sanskrit Chapter 13 अमृतं संस्कृतम् Additional Important Questions and Answers
(1) पाठांशं पठत अधोदत्तान् च प्रश्नान् उत्तरत। (पाठांश को पढ़िए और निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए। Read the extract and answer the questions that follow.)
इयं भाषा अतीव वैज्ञानिकी। केचन कथयन्ति यत् संस्कृतमेव सङ्गणकस्य कृते सर्वोत्तमा भाषा। अस्याः वाङ्मयं वेदैः, पुराणैः, नीतिशास्त्रैः चिकित्साशास्त्रादिभिश्च समृद्धमस्ति। कालिदासादीनां विश्वकवीनां काव्यसौन्दर्यम् अनुपमम्। कौटिल्यरचितम् अर्थशास्त्रं जगति प्रसिद्धमस्ति । गणितशास्त्रे ह्यह्यह्यह्यशून्यस्य प्रतिपादनं सर्वप्रथमम् आर्यभटटः अकरोत् । चिकित्साशास्त्रे चरकसुश्रुतयोः योगदानं विश्वप्रसिद्धम्। संस्कृते यानि अन्यानि शास्त्राणि विद्यन्ते तेषु वास्तुशास्त्रं, रसायनशास्त्रं, खगोलविज्ञानं, ज्योतिषशास्त्रं, विमानशास्त्रम् इत्यादीनि उल्लेखनीयानि।
I. एकपदेन उत्तरत-(एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए- Answer in one word.)
(i) संस्कृतभाषा कीदृशी?
उत्तराणि:
वैज्ञानिकी
(ii) अर्थशास्त्रं कस्य रचना?
उत्तराणि:
कौटिल्यस्य
(iii) कालीदासादीनां काव्यसौन्दर्य कीदृशम्?
उत्तराणि:
अनुपमम्
(iv) चिकित्साशास्त्रे कयोः योगदानम् विश्वप्रसिद्धम्?
उत्तराणि:
चरकसुश्रुतयोः
II. पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत- (पूर्ण वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए- Answer in a complete sentence.)
(i) संस्कृतवाङ्मयम् कैः समृद्धम्?
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतवाङ्मयम् वेदैः, पुराणैः, नीतिशास्त्रैः, चिकित्साशास्त्रादिभिः च समृद्धम्।
(ii) आर्यभटः किमर्थं प्रसिद्धः?
उत्तराणि:
आर्यभटः गणितशास्त्रे शून्यस्य प्रतिपादनम् सर्वप्रथमम् अकरोत्, एतदर्थं सः प्रसिद्धः?
III. भाषिककार्यम्
यथानिर्देशम् उत्तरत- (निर्देशानुसार उत्तर दीजिए- Answer as directed.)
1. ‘कौटिल्यरचितम् अर्थशास्त्रं जगति प्रसिद्धम् अस्ति’- इति वाक्ये –
(i) ‘अस्ति’ क्रियापदस्य क: कर्ता? ……………. (कौटिल्यरचितम्, अर्थशास्त्रम्, प्रसिद्धम्)
उत्तराणि:
अर्थशास्त्रम्
(ii) पर्यायः कः? संसारे – …………….
उत्तराणि:
जगति
(iii) प्रसिद्धम् इति पदम् कस्य विशेषणम्?- …………….
उत्तराणि:
अर्थशास्त्रस्य/अर्थशास्त्रम् इति पदस्य
(iv) चरकसुश्रुतयोः- अत्र किं विभक्तिवचनम् (प्रथमा द्विवचनम्, षष्ठी द्विवचनम्, सप्तमी द्विवचनम्)
उत्तराणि:
षष्ठी द्विवचनम्
(2) परस्पर-मेलनं कृत्वा सूक्तीः पुनः लिखत- (परस्पर मेल करके सूक्तियाँ पुनः लिखिए Match the following quotes and rewrite them.)
(i) भारतस्य प्रतिष्ठे द्वे – जयते।
(ii) वसुधैव – कर्मसु कौशलम्।
(iii) योगः – अमृतमश्नुते।
(iv) सत्यमेव – संस्कृतं संस्कृतिः तथा।
(v) विद्यया – कुटुम्बकम्।
उत्तराणि:
(i) भारतस्य प्रतिष्ठे द्वे संस्कृतं संस्कृतिः तथा।
(ii) वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम्।
(iii) योगः कर्मसु कौशलम्।
(iv) सत्यमेव जयते।
(v) विद्ययाअमृतमश्नुते। (विद्यया + अमृतम् + अश्नुते)
(3) मञ्जूषातः उचितपदं चित्वा वाक्यानि पूरयत (मञ्जूषा से उचित पद चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए। Complete the sentences by picking out the appropriate word from the box.)
सूक्तयः, भाषाणाम्, प्राचीनतमा, संस्कृतम्, संस्कृतग्रन्थेषु |
(i) विश्वस्य उपलब्धासु भाषासु संस्कृतभाषा ।
(i) भाषा इयं अनेकासा . .जननी मता।
(iii) संस्कृते विद्यमानाः . अभ्युदयाय प्रेरयन्ति।
(iv) ……….. मानवजीवनाय विविधाः विषयाः समाविष्टाः।
(v) अस्माभिः ……… अवश्यमेव पठनीयम्।
उत्तराणि:
(i) प्राचीनतमा
(ii) भाषाणाम्
(iii) सूक्तयः
(iv) संस्कृतग्रन्थेषु
(v) संस्कृतम्।
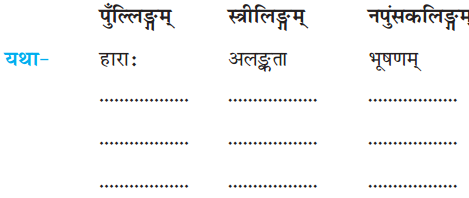
(4) इकारान्त-स्त्रीलिंग-शब्दरूपाणि यथानिर्देशं पूरयत। (इकारान्त स्त्रीलिंग शब्दरूप यथानिर्देश पूरे कीजिए। Complete the declcusion of इकारान्त words in feminine gender as directed.)

उत्तराणि:


(1) प्रदत्तविकल्पेभ्यः उचितं पदं चित्वा वाक्यानि पूरयत- (दिए गए विकल्पों से उचित पद चुनकर वाक्य पूरे कीजिए- Complete the sentences by picking out the appropriate word from the given options.)
(क) (i) प्राचीनयोः …………… निधिः संस्कृतभाषायाम् सुरक्षितः। (चरकसुश्रुतयोः, ज्ञानविज्ञानयोः, महापुरुषोः)
उत्तराणि:
ज्ञानविज्ञानयोः
(ii) संस्कृतेन मनुष्यस्य समाजस्य च …………… भवेत्। (कौशलम्, संस्कृतिः, परिष्कारः)
उत्तराणि:
परिष्कारः
(iii) ….. चरकसुश्रुतयोः योगदानं विश्वप्रसिद्धम्। (गणितशास्त्रे, चिकित्साशास्त्रे, वास्तुशास्त्रे)
उत्तराणि:
चिकित्साशास्त्रे
(vi) भारतस्य प्रतिष्ठे द्वे …………… संस्कृतिश्च। (ज्योतिषशास्त्रम्, साहित्यम्, संस्कृतम्)
उत्तराणि:
संस्कृतम्
(v) ………………. आत्मवत् व्यवहारं कुर्यात्। (महापुरुषेषु, संस्कृतग्रन्थेषु, सर्वभूतेषु)
उत्तराणि:
सर्वभूतेषु।
(ख)
(i) ……………… अमृतमश्नुते? (विद्याः, विद्यायाः, विद्यया)
उत्तराणि:
विद्यया
(ii) किं संस्कृतभाषायां केवलं ……………… साहित्यं वर्तते? (धार्मिक, धार्मिकम्, धार्मिक:)
उत्तराणि:
धार्मिकम्
(iii) ……………… रचितं अर्थशास्त्रं जगति प्रसिद्धम्। (कौटिल्यस्य, कौटिल्येन, कौटिल्यम्)
उत्तराणि:
कौटिल्येन
(vi) संस्कृते सूक्तयः……………… प्रेरयन्ति। (अभ्युदयः, अभ्युदये, अभ्युदयाय)
उत्तराणि:
अभ्युदयाय
(v) संस्कृतवाङ्मये ……………… विद्यन्ते। (अनेक शास्त्राणि, अनेकाः शास्त्राः, अनेकानि शास्त्राणि)
उत्तराणि:
अनेकानि शास्त्राणि।
 This grammar section explains Online Education
This grammar section explains Online Education