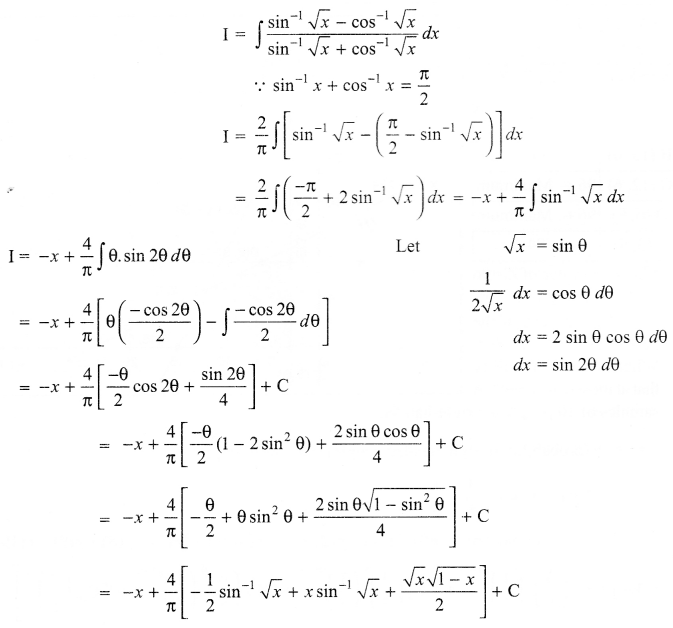
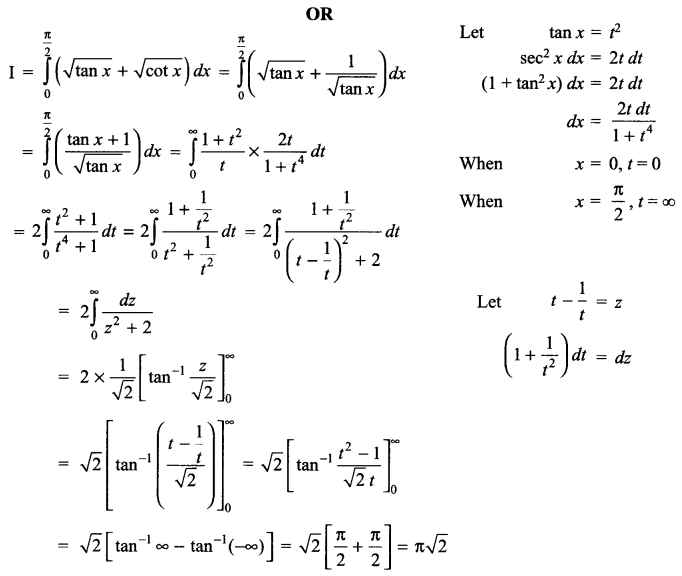
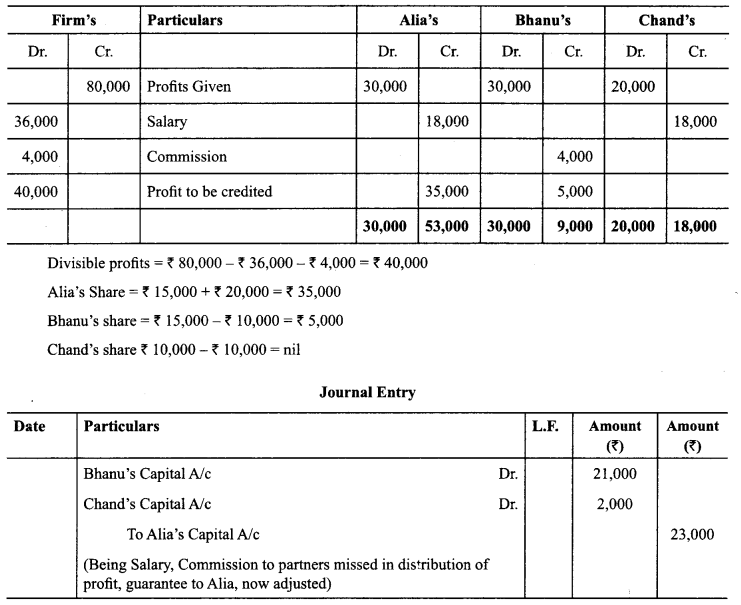
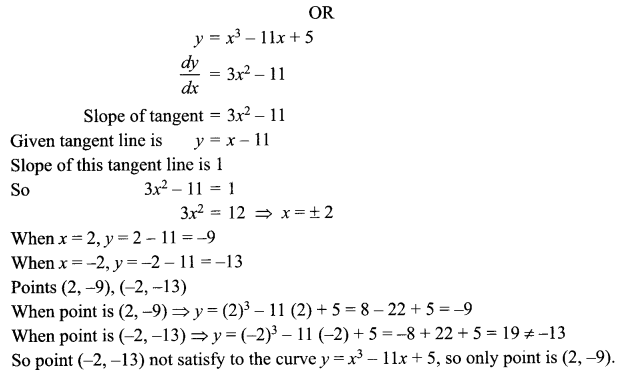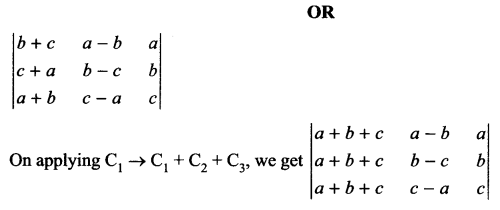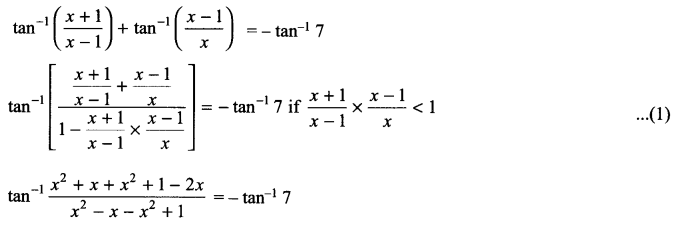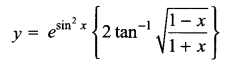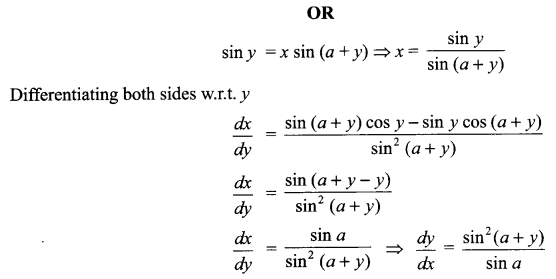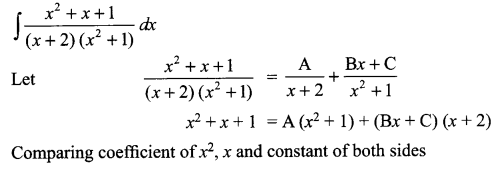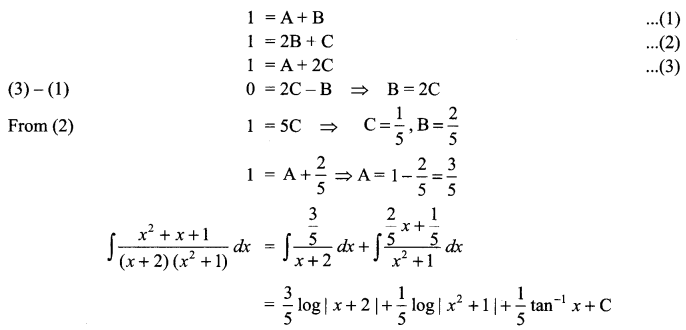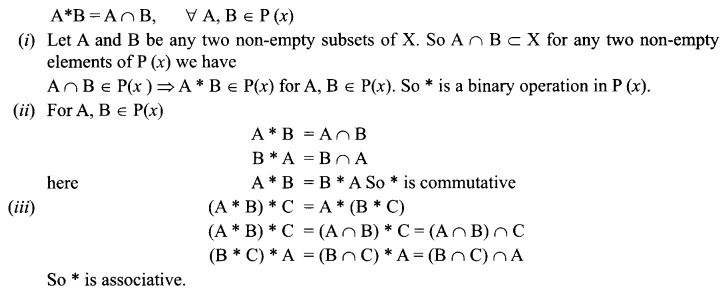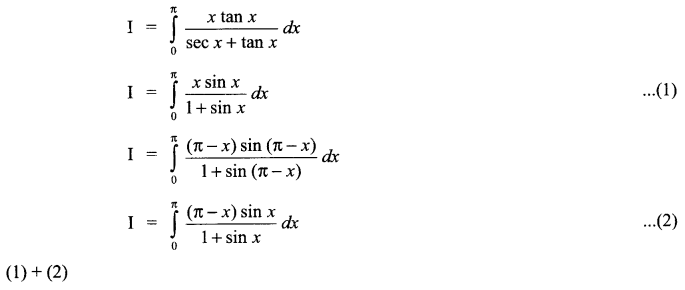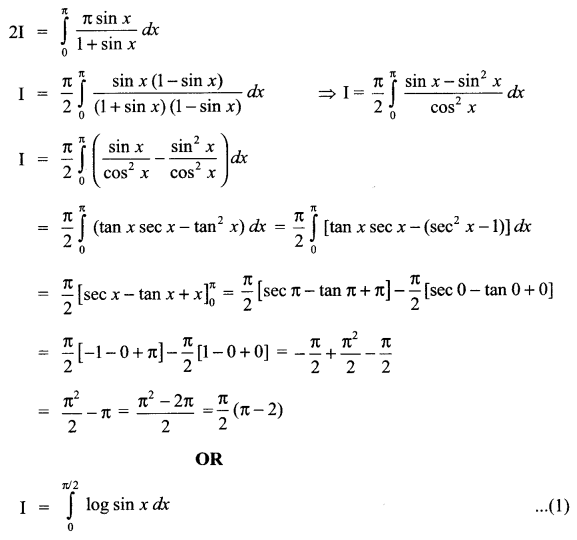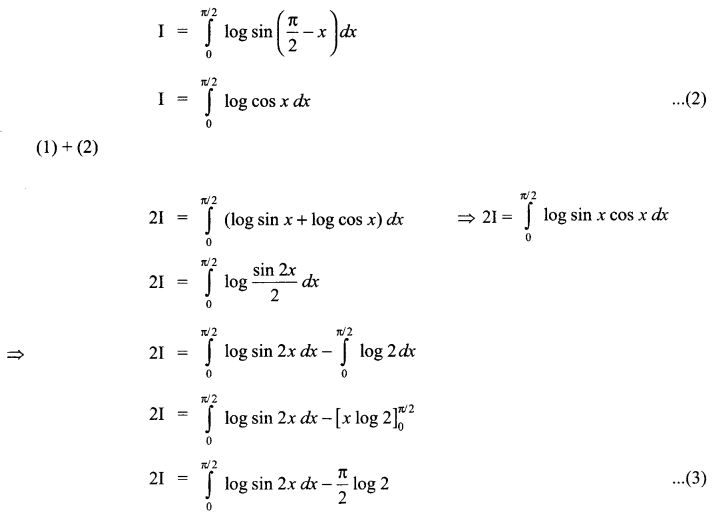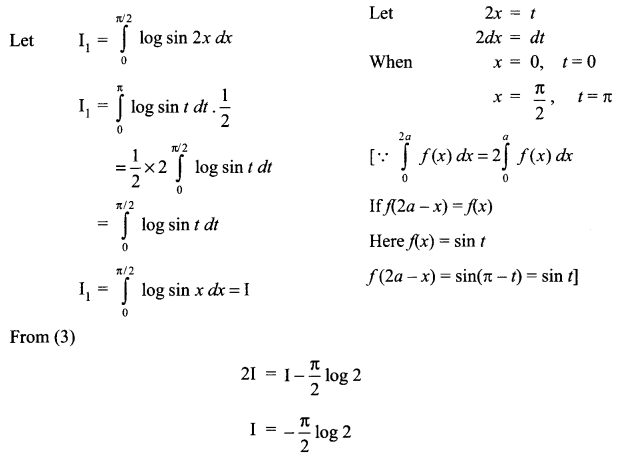CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 English Core Paper 1 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 English Core. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 English Core Paper 1.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 English Core Paper 1
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | English Core |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 1 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 1 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Englsih Core is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed : 3 hours
Maximum Marks : 100
General Instructions
- This paper is divided into three sections: A, B and C. All the sections are compulsory.
- Separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary. Read these instructions very carefully and follow them faithfully.
- Do not exceed the prescribed Word limit while answering the questions.
SECTION A
READING (30 MARKS)
Question 1.
Read the following passage carefully. (12 Marks)
Cycle of change: Biking communities making the bicycle popular again
1. In 1976, six-year-old Anil Uchil started cycling by renting a bicycle at 25 paise an hour. He got his own road bike when he turned 13, and he cycled everywhere: to school, college and even to work in 1993. He still cycles to work. “It’s healthy, environment-friendly and economical. But the real reason I cycle is because it’s sheer fun,” he says.
2. Earlier this year, PM Narendra Modi, in a speech on environmental crisis, said, “Why don’t we make Sunday cycle day? I am saying that only one day a week; don’t use fuel- driven vehicles.” Internationally, a lot has been done to encourage people to use the bicycle as a primary means of transport. UK’s Cycle to Work scheme offers tax-free bicycles to employees. 45% of people in Copenhagen cycle to work/college. In Brussels (Belgium), Geneva (Switzerland), or San Francisco (USA), it is not uncommon to see top rung corporate executives in three-piece suits cycling their way to office.
3. Cycling, though, has been a part of Indian culture for decades. Apart from people across strata in smaller towns and villages, in cities, mill workers, newspaper delivery boys, milk vendors and bread sellers have always used the bicycle. Today, the resurgent popularity of the bicycle isn’t so much as a practical mode of commuting as it is a way towards fitter lifestyles and eco-friendliness.
4. Around the late 2000s, as the middle and affluent classes took to cycling, internet penetration also grew in India. Many made use of social media to create awareness. Numerous groups on Facebook today help cyclists connect to fellow riders. The shared passion for cycling brings together absolute strangers, building friendships and a sense of community.
5. Jose George, an avid cycling enthusiast and the owner of the cycling store, Haybren Adventures, says, “Riding in a group is always more enjoyable. And you end up riding a lot more.” Usually, the ride distances range from 20 to 80 km, and are held mostly on weekends. Apart from the environmental benefits, cycling is also an effective way to break away from a sedentary lifestyle. “It’s a low-impact exercise where you don’t carry your body weight. The machine does. It’s great stress buster too,” George says.
6. But (while there are eager riders, the lack of infrastructure is a deterrent. Dedicated cycling lanes are still a distant dream. And if the traffic and questionable driving skills of many don’t discourage you, the potholes and gaps between concrete segments might. Another sore point is the derisive attitude of motorists and drivers. Banker and cycling enthusiast Ninad Waghule, 28, says, “Most drivers aren’t considerate towards cyclists. However, if you’re on an expensive cycle and wearing a helmet, you get more respect compared to a regular person commuting to work. It’s a pity.”
7. The cycling culture has also given birth to adventure travel companies that organise cycling trips. From short weekend trips to longer and more arduous (but rewarding) journeys, cycling tours are gaining popularity. CEO Prateek Deo Gupta, a cycling enthusiast, says, “Travelling by cycle, as opposed to a car, shows you know more of the local culture”. Nitin Yadav, co-founder of Delhi-based Cycle It, which focuses solely on cycling trips, says the past four to five months have particularly seen a rise in numbers. Launched last year, Cycle It offers trips on the picturesque Manali to Leh route, and Kumaon, Uttarakhand.
8. American science educator Bill Nye famously said, “There’s something wrong with a society that drives a car to work out in a gym.” Thankfully, in spite of potholed roads and our despicable habit of honking cyclists out of the way, things are changing.
(Source: Manali Shah, Hindustan Times, Mumbai, Oct 08, 2015)
I. On the basis of your understanding of the passage, answer the following questions by choosing the most appropriate option. (1 × 4 = 4 Marks)
(a) Cycling is becoming popular again due to
- traffic jams.
- request of the Prime minister.
- health benefits.
- reviving Indian culture.
(b) Riding in groups is more beneficial because it helps to :
- restrict friendships.
- inculcate sense of kinship.
- follow the routine of everyday life.
- none of the above.
(c) Cycling tours are becoming popular because:
- they are discussed on facebook.
- they are more satisfying.
- one can experience more of regional traditions.
- all the above.
(d) The deterrents to cycling include:
- Co-operation of the motorists.
- stress while cycling.
- non availability of allocated lanes for cyclists.
- going to the gym regularly.
II. Answer the following questions as briefly as possible. (1 × 6 = 6 Marks)
(e) How has cycling been a part of Indian culture?
(f) What is the difference between the attitude of people of Brussels or Geneva and India to cyclists?
(g) How has the spread of internet helped in promoting cycling?
(h) How have the travel companies benefitted from cycling?
(i) There is a difference in attitude of the drivers to the different cyclists. Explain.
(j) Why does the columnist say that the things are changing?
III. Find words from the passage which mean the same as: (1 × 2 = 2 Marks)
(a) chief (para 2)
(b) sarcastic (para 6)
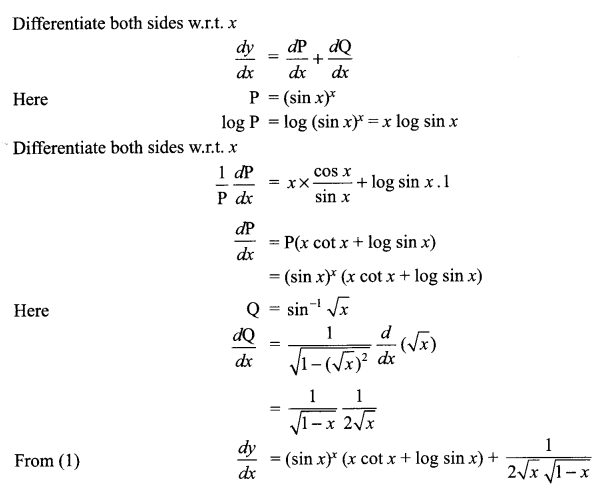
Question 2.
Read the following passage carefully. (10 Marks)
Don’t be snobbish! Teach your folks the latest technology
1. Quite recently, I observed a young guy in the office cafeteria yelling at his mom because she had called him to ask how to send an audio message through Whatsapp. “Mom, you don’t need to try and be all savvy. Just leave it and make a normal call”, he said, after trying to teach her the commands once, and realising that she’s not getting it. I didn’t like what he said and his tone but it did make me realise and feel guilty about the several times that even I may have lost patience while helping my parents understand the new technologies. If you are, intentionally or unintentionally, fuelling insecurity and lack of confidence in an elderly person about use of new technologies, you are not doing yourself a favour, because you’ll soon reach that stage yourself.
2. It was not long ago that Orkut became Facebook and BBM became Whatsapp. So it’s not long when these two also become obsolete or die down. The same goes for the operating systems of the various phones and gadgets we use. The fact that most of you so easily adapt to a new platform or gadget is because you are constantly, almost 24X7, using these gadgets. But unlike most of you, people who did not have these gadgets in their hands as constant fixtures have to start from the scratch. Hence, they find it tough and intimidating, and often struggle with the basics. It’s like when they were teaching you ABC. Did they shout at you because you couldn’t frame sentences? So, now that the roles stand reversed and you get to be the teacher, you better treat them with the same love and patience that they showed for you.
3. For those of you who have never experienced the joy of seeing an old person discover the magic of internet, it is a wonderful thing when their eyes light up on discovering that they can message their friends or relatives anywhere in the world and get instant response, for free. They may take ages to type out a coherent sentence, but the moment they click ‘send’, their excitement is incomparable. They may make a lot of mistakes and you may get frustrated or embarrassed but it’s all worthwhile in the end. Remember, holding a smart-phone in your hand doesn’t make you smart. Being able to give back to someone who patiently taught you everything you know in life does.
4. Yes, life is hectic and teaching technology to parents or grandparents isn’t a priority but the little effort of spending an hour every week in making your elders proficient in technology goes a long way in making your own life much easier.
5. While for them, being on social media brings up a new universe to explore joyfully, it also opens several new avenues for you to communicate with your ageing parents. Many young people who were too busy to call their mom or dad often have now taken to regularly chatting with them on Whatsapp. Although I would never agree that chatting or talking on the phone is a sufficient replacement for spending actual, physical time with your elders, it’s still better than not being in touch for days together.
6. So, no more making faces, rolling eyes or being all sarcastic about an elder person struggling with the basics of technology. You may know the software more, but they’ve seen the world more. There’s no comparison.
(Source: Sonal Kalra, Hindustan Times, New Delhi, August 22, 2015)
I. On the basis of your understanding of the passage, answer the following questions by choosing the most appropriate option. (1 × 2 = 2 Marks)
(a) How does the writer suggest that we would be in the same position as the elderly?
- We will have impatient children
- Technology gets updated regularly
- The next generation will speak rudely to us
- Both (i) and (ii)
(b) The learning process for the elderly with reference to technology would include:
- taking time to type a understandable message
- being anxious at their attempts
- asking about it repeatedly
- all the above.
II. Answer the following questions as briefly as possible. (1 × 6 = 6 Marks)
(c) What realization did the columnist have after her observation at the cafeteria?
(d) Why does the younger generation pick up technology fast?
(e) What is fascinating about the internet for elderly?
(f) How should we respond to the queries of the elderly regarding technology?
(g) How can teaching technology to the elders in our family make our life easier?
(h) What is the final message of the writer?
III. Find words from the passage which are similar in meaning to the following. (1 × 2 = 2 Marks)
(a) increasing (para 1)
(b) unique (para 3)
Question 3.
Read the following passage carefully. (8 Marks)
In a very short period of time the internet has had a profound impact on the way we live. Since the internet was made operational in 1983, it has lowered both the costs of communication and the barriers to creative expression. It has challenged old business models and enabled new ones. It has provided access to information on a scale never before achievable.
It succeeded because we designed it to be flexible and open. These two features have allowed it to accommodate innovation without massive changes to its infrastructure. An open, borderless and standardized platform means that barriers to entry are low, competition is high, interoperability is assured and innovation is rapid.
The beauty of an open platform is that there are no gatekeepers. For centuries, access to and creation of information was controlled by the few. The internet has changed that and is rapidly becoming the platform for everyone, by everyone.
Of course, it still has a way to go. Today there are only about 2.3 billion internet users, representing roughly 30% of the world’s population. Much of the information that they can access online is in English, but this is changing rapidly. The technological progress of the internet has also set social change in motion. As with other enabling inventions before it, from the telegraph to television, some will worry about the effects of broader access to information—the printing press and the rise in literacy that it effected were, after all, long seen as destabilising. Similar concerns about the internet are occasionally raised, but if we take a long view, I’m confident that its benefits far outweigh the discomforts of learning to integrate it into our lives. The internet and the world wide web are what they are because literally millions of people have made it so. It is a grand collaboration.
It would be foolish not to acknowledge that the openness of the internet has had a price. Security is an increasingly important issue and cannot be ignored. If there is an area of vital research and development for the internet, this is one of them. I am increasingly confident, however, that techniques and practices exist to make the internet safer and more secure while retaining its essentially open quality.
After working on the internet and its predecessors for over decades, I’m more optimistic about its promise than I have ever been. We are all free to innovate on the net every day. The internet is tool of the people, built by the people and it must stay that way.
A. On the basis of your reading of the above passage make notes on it, using headings and sub-headings. Use recognizable abbreviations (wherever necessary—minimum four) and a format you consider suitable. Also supply an appropriate title to it. (5 Marks)
B. Write a summary of the passage in about 80 words. (3 Marks)
SECTION B
ADVANCE WRITING SKILLS (30 MARKS)
Question 4.
Every year on Children’s Day, an exhibition of Science projects is held at the Indira Gandhi Indoor Stadium. Your school has received an invitation from the Education Minister of Delhi inviting the students of your school to visit it. Write a notice in about 50 words informing the students about the display, advising them to go and enjoy it. You are Sunil/Sunita Sahoo, Head Boy/Head Girl Bright Minds Public School, New Delhi. (4 Marks)
OR
Draft a poster informing the readers about hazards of alcoholism in 50 words.
Question 5.
On the approaching Sports’ Day, you realise that many House Flags, batons, badminton racquets, high jump equipment, and many other required by the participants, are in a bad state because of wear & tear. Place an order for all these things along with their numbers to Akram Sports Goods, A-10, Sector-10 Noida, specifying the terms & conditions to get good bargain at a discounted rate for the school. Write this letter as Navtej/Navita, the Sport’s teacher, Navin Public School, 112 Taj Road, Agra. (6 Marks)
OR
Recently you travelled from Bangalore city to Vasco in Vasco Express. To your dismay, you found that the coach was infested with cockroaches. Write a letter to The General Manager, Southern Railways, complaining about the prevailing unhygienic conditions and asking for remedial action. You are Saroj/Saran, 5/31, Bangalore Cantt., Bangalore.
Question 6.
Recent rains and consequent water-logging have increased the risk of malaria and dengue. Write a speech in 150-200 words to be delivered in the morning assembly advising the students on prevention of and protection against these ailments and the steps that the school has taken to prevent mosquito breeding in and around the school. Imagine you are the Principal of the school. (10 Marks)
OR
More industrial production means availability of more goods, better life style, lower prices, more jobs, etc. However, a higher standard of living can be achieved only at a cost and that is, depletion of raw materials and air and water pollution. Write a debate in 150-200 words either for or against the motion—‘Standard of living can be raised, but only at a great cost.’ You are Aseem/Aashima.
Question 7.
Recently, a Car Free Day was organized in Gurgaon and Delhi to encourage the commuters to avail public transport. This was done as vehicles lead to traffic jams, air pollution, road rage and an unhealthy competition in the middle class to own more and newer cars. What are your views on the issue—Private cars or Public transport? Describe them in an article in 150-200 words. You are Sujit/ Sunaina. (10 Marks)
OR
Write a speech to be delivered in the morning assembly in 150-200 words on ‘Delhi: A City of Crime’.
SECTION C
TEXTBOOKS AND EXTENDED READING TEXT (40 MARKS)
Question 8.
Read the following extract carefully and answer the questions that follow : (1 × 4 = 4 Marks)
Those who prepare green wars,
Wars with gas, wars with fire, victory with no survivors,
Would put on clean clothes and walk about With their brothers in the shade, doing nothing.
(a) What are green wars?
(b) How will the few moments of introspection affect the people?
(c) Explain the irony in “Victory with no survivors”.
(d) Name the poem and the poet.
OR
Rich with sprinkling of fair musk rose blooms;
And such too is the grandeur of the dooms
We have imagined for the mighty dead;
All lovely-tales that we have heard or read;
An endless fountain of Immortal drink,
Pouring unto us from the heaven’s brink.
(a) What is the beautiful scene that one sees in the middle of the forest?
(b) Why does the poet call the dooms to be full of grandeur?
(c) Whom does the word ‘mighty dead’ refer to?
(d) Explain ‘Immortal drink’.
Question 9.
Answer any four of the following questions in about 30-40 words each: (3 × 4 = 12 Marks)
(a) Why do you think Aunt Jennifer’s hands are fluttering through her wool? Why is she finding the needle so hard to pull?
(b) Why were a large number of villagers seated on the back benches?
(c) How did the Maharaja manage to save his throne?
(d) Why did Evans drape a blanket round his shoulder?
(e) Why did Bama take half hour to an hour to cover the distance to her home that would normally take only ten minutes?
(f) How did the wizard help Roger Skunk?
Question 10.
Why did Gandhiji consider ‘freedom from fear‘ and a realization that in their own country they can fight for justice was more important than legal and monetary justice for the poor peasants of Champaran? Answer in about 120-150 words. (6 marks)
OR
“The absence of essential value of human compassion, dignity of human life and consideration can be clearly visualized in the ‘Memories of Childhood’.” How far has the meaning of this statement been exemplified in the stories of the two women? Are they close to Malala’s fight for right to education?
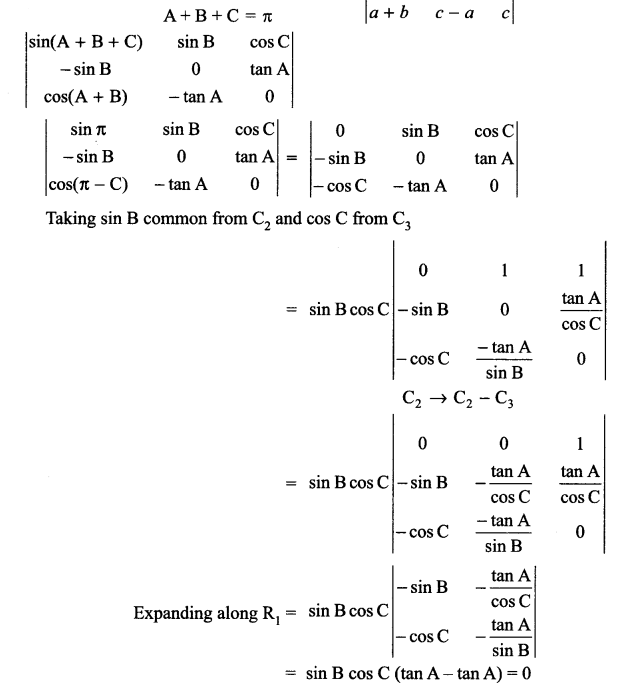
Question 11.
How did Dr. Sadao, rise above narrow prejudices of race and country for assisting a human being in need? Discuss. (Word limit 120-150) (6 marks)
OR
By looking at Zitkala-Sa and Bama’s life, one can say that it may take a long time for oppression to be resisted but seeds of rebellion are sowed early in life. Additionally, injustice in any form can have a permanent impact on children too. Justify. (Word limit 120-150) (NCERT)
Question 12.
What forced Griffin to become a bandaged caricature of a man? (Word Limit 120-150) (6 Marks)
OR
What kind of life did Silas lead before coming to Raveloe?
Question 13.
Excessive ambition is behind all that happens in the story. Griffin, devoid of all traces of humanity has become blind in his pursuit. Justify in context of the novel ‘The Invisible Man’. (Word limit 120-150) (6 Marks)
OR
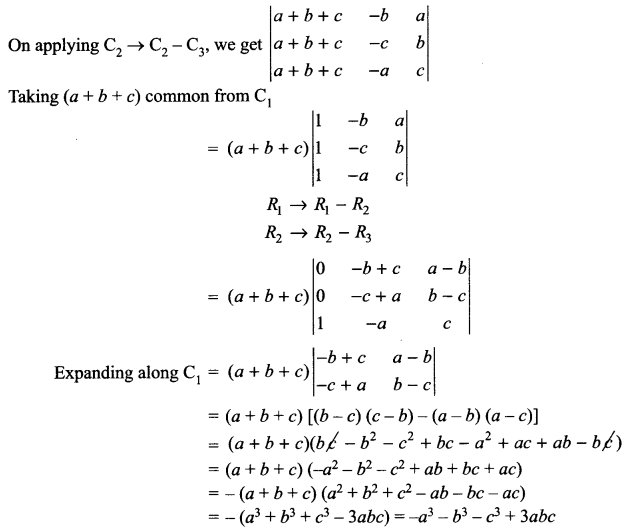
Describe Nancy’s character and her outlook to life in Silas Marner.
ANSWERS
Answer 1.
I.
(a) (iii) health benefits
(b) (ii) none of the above
(c) (iv) all of the above
(d) (iii) non availability of allocated lanes for cyclists.
II. (e) Cycling has always been a part of Indian culture especially among the less affluent in smaller towns and villages. In cities it is used by mill workers, milk vendors newspaper delivery boys and bread sellers. Today it is used as a way to fitter and eco-friendly lifestyles.
(f) In Brussels even the top rung corporate executives prefer cycling to their offices. This is not the case in India.
(g) Spread of Internet has given rise to numerous groups on Facebook that help cyclists connect to fellow riders. Thus a shared passion builds a friendship and a sense of community.
(h) Adventure travel companies have taken to organising short weekend cycling trips to longer and more arduous trips.
(i) Most drivers display derisive attitude towards cyclists unless they are in an expensive cycle with a helmet.
(j) Things are slowly changing as despite the odds more and more people are opting for cycling to keep fit. Social media has proved to be a boon in promoting the culture of cycling.
III. (a) primary (b) derisive
Answer 2.
I. (a) (iv) Both (i) and (ii) (b) (iv) all of the above
II. (c) The columnist realised that she herself may have been impatient with her parents while helping them with new technologies and felt guilty for such treatment.
(d) The younger generation is faster in learning new technologies since they are using them 24 × 7.
(e) The internet opens up a new universe which the elderly explore joyfully. They also love the newer and easier ways of communicating that internet offers.
(f) If elders ask us about the use of technology, we should teach it to them patiently and respectfully.
(g) If we teach technology to the elders of our family, we will be able to have regular chatting or talking with them on phone as we have no time to talk with them regularly face to face.
(h) The final message of the writer is that wre should not make any sarcastic comments if our elders ask us to teach them to use technology, instead we should teach them calmly and respectfully.
III. (a) fuelling (b) incomparable
Answer 3.
A. TITLE: Internet—A Game Changer
NOTES :
1. Features Of Internet
(a) Flexible & open
(b) Standardised platform
(c) High Compttn.
(d) Rapid innovation.
2. Global Penetration
(a) Used by 30% of populn.
(b) English-major language.
3. Positive Impact
(a) Agent of social change
(b) Enable new busi. models
(c) Lowered commun. costs
(d) Aids creative innovation
4. Areas of concern
(а) Insecure platform v open
(b) Need to put checks for greater safety.
| Key to Abbreviations | |
| compttn. | : competition |
| populn. | : population |
| busi. | : business |
| commun. | : communication |
| ∵ | : as |
B. SUMMARY
Internet is an open and flexible platform. It is standardised. The competition is high and is open to rapid innovation. About 30% of the world population is internet user. Though the access is in English but this is also changing. It has positively impacted society as it has triggered great social change. It has also enabled new business models. Besides lowering communication costs it has aided creative innovation. Still it is not without drawbacks. The greatest one being that due to its openness it is too insecure. There is a need to create checks and practices which will lend it greater degree of safety.
Answer 4.

Answer 5.
Navin Public School
112 Taj Road, Agra
30th Sep, 20XX
The Manager
Akram Sports Goods
A-10, Sector 10, Noida
Sub: Order for Sports Goods
Dear Sir,
Our school is going to host its Annual Sports Day on 18 October, 20xx. With regard to this, we would like to place an order for certain sports equipment.
The set specifications of the order are as under :
| S. No. | Item | Brand | Quantity |
| 1. | Cricket Bats | Adidas | 5 |
| 2. | Tennis Racquets | Wilson | 6 |
| 3. | Shot put Balls | Mcsports | 7 |
| 4. | Tennis Balls | Wilson | 7 |
Since our association with you is a long one, we would like a discount of 25% on the above order. You are requested to arrange for the goods to be delivered by 8 October, 20xx. Kindly note that the damaged goods will be returned for replacement. Payment would be made by cheque at the time of delivery.
Yours sincerely
Navtej
H.O.D., Sports Department
OR
5/31, Bangalore Cantt.
Bangalore
7th September, 20xx
The General Manager
Southern Railways
Sub: Unhygienic Condition in Rail Coaches
Dear Sir/Madam
Last month I took the Vasco Express from Bangalore on a business related matter. After I settled myself and my luggage thinking of getting a good night’s rest, I was dismayed and disgusted to see cockroaches creeping out of the seat. I myself spotted not less than fifteen or twenty. I could not sleep the entire night fearing that they may crawl over me while I was sleep.
Sir, my mind is full of questions. Is it not the customer’s right to have clean and pest-free compartment as they pay for the travel? Railways need to improve the hygienic conditions of the coaches in order to improve their own reputation and the travel experience of their customers.
Yours sincerely
Saroj
Answer 6.
Good morning, respected principal, teachers and students! I take the opportunity in this morning assembly to address you on an important health issues. As you all are aware the recent heavy rains have caused widespread waterlogging and have increased the risk of malaria and dengue. I am sure you know that both these diseases are caused by mosquitoe bites and once contracted can take a toll on your health. Here are a few tips to keep mosquitoes at bay.
- Wear full sleeve clothes.
- Wear trousers instead of shorts and skirts.
- Use mosquito repellant creams and patches.
On our part we have arranged fumigation of all rooms, nooks and corners by professionals. One bottle of mosquito spray has been kept in each class to use as and when required. All drains in and around the school have been cleaned and disinfected.
I hope you will take care of your health and cooperate in creating mosquito-free surroundings.
Thank you.
OR
Esteemed judges I, Aseem stand before you to debate for the motion. Standard of living can be raised but only at a great cost. We are living in an era of consumerism, which dictates our definition of ‘standard of living’. In a nutshell if you have more goods and more and more of the same goods, you are perceived as having a high standard of living. For example, car owners are seen as having a higher standards than those who own scooters. Likewise a person owning three cars is seen with more respect and admiration than the one having just one. But raising of the so-called standard of living entails a great toll on our natural resources. More trees need to be cut to have bigger and better houses and furniture. More animals need to be butchered to satisfy our taste for exotic meats. These are but a few examples. Our consumerist attitude may deplete the earth in the near future. So the need of the hour is to adopt a minimalistic lifestyle thereby saving the earth’s resources.
Thank you.
Answer 7.
Private cars or public Transport? By: Sujit
The Delhi government recently announced Car-free days in a bid to decrease congestion on roads and encourage commuters to use public transport. The number of cars on Delhi roads is on the rise owing to the rising purchasing power of the middle class coupled with the desire to compete with others. Hardly do they realise that how much congestion and pollution is caused due to this trend.
The advantages of using private cars are that they are convenient and comfortable and give the users a great degree of autonomy. The disadvantages of using private card are that they result in traffic jams, air pollution and accidents. Though public transport has some drawbacks, yet we should try to use public transport as much as possible instead of our private cars. DTC buses are unreliable and unsafe especially for women who sometimes suffer eve-teasing while travelling in them. They are overcrowded too. Delhi Metro is a better alternative as it is punctual, safer for women and more secure. There is a need to increase the frequency of DTC buses and metro trains to make public transport more appealing. Autos should run only by the meter and not should not over charge.
OR
Respected Principal, teachers and my dear friends!
Today I am going to express my views on the topic ‘Delhi: A City of Crime’ and hope my views will be appreciated by you.
Delhi has become notorious for its crime rate—robberies in the day time, murders of senior citizens in crowded colonies, kidnappings from main roads and rapes in moving cars. With the police dragging its feet in catching the wrongdoers and the courts’ lackadaisical attitude in passing judgement, criminals are encouraged to continue their nefarious activities. Matters are not helped when highly placed officials and politicians use their influence upon the guilty. The contrast between the wealthy and the underprivileged is growing, and with the open display of wealth of the former, the latter feel crime is the shortest way to achieve the same goals. Movies romanticize the bad and the ugly side of life, adding fuel to the already growing fire. People themselves break laws by not verifying their servants or tenants or by turning a blind eye to wrongdoings.
The city has acquired a bad reputation. Where once only selected areas were considered unsafe, now the whole city is under attack.
The government needs to take strict action against recalcitrant police officers and those who block the course of justice. Judgement in criminal cases must be swift and harsh. People must realise that they also have the responsibility of keeping crime at bay. It is only when everyone works together that we can make Delhi a worthwhile place to live in.
Thank you.
Answer 8.
(a) ‘Green wars’ are all activities which harm nature and environment.
(b) While introspecting, the poet hopes that man will be able to see their mindless activities which are harming nature. They may change their goals and means to achieve their needs thus bringing more peace in their lives.
(c) It is ironical that when wars are won there are no survivors to celebrate the victory.
(d) The poem is ‘Keeping Quiet’. The poet is Pablo Neruda.
OR
(a) One sees the musk rose blooming in the middle of the forest.
(b) The stories of the death of the mighty heroes in the past have been described with great grandeur. Hence the poet speaks about them admiringly.
(c) ‘Mighty dead’ refers to the great and powerful inspiring heroes who are now dead.
(d) The things of beauty are a source of eternal pleasure and relaxation to man. Thus the immortal drink, an elixir, never dries up.
Answer 9.
(a) Aunt Jennifer’s fluttering fingers indicate her terrorised and tortured state of mind. The uncle’s wedding ring has burdened her soul and personality so much that she finds even a needle hard to handle.
(b) It was the last day of French lessons in M. Hamel’s classroom. The German order had forbidden the learning of French from the next day. Only German would be spoken in Alsace. The villagers had come to attend the last French lesson to pay their respect to their teacher who had spent forty years in teaching French.
(c) The Maharaja had refused the British official. In doing so he ran a great risk as his kingdom could be annexed. To make up to the British official he sent 50 rings to the official’s wife who instead of choosing one or two accepted all the 50 rings as a gift. The Maharaja paid a heavy sum but managed to save his throne.
(d) Evans draped on a blanket around his shoulder on the pretext of his cell being cold. In fact, beneath it he changed his clothes that McLeery brought for him.
(e) Ori her way back home Bama was captivated by the many entertaining people and activities of the market. She found the snake charmer, the performing monkey to name a few very engrossing. Hence the ten minute walk stretched to thirty minutes.
(f) The wizard helped Roger Skunk by substituting the awful smell of the skunk with the beautiful fragrance of roses. In doing so the wizard helped Roger Skunk immensely as now he was happily accepted by his friends.
Answer 10.
Gandhiji believed that the 25% refund amount was insignificant for the peasants. What was more vital was that for the first time the farmers had won a court case against the British. The farmers had gained confidence and courage while the British complacency had received a rude jolt. This episode released the farmer from the shackles of fear of the British. Hitherto the farmers had lived in complete subjection to the British but with losing the court case the British had to part with their prestige and also some of their money. Gandhiji saw this as a victory of truth. Also Gandhiji’s dream that Indians should live on their land freely and fearlessly was realized for the first time. He believed that if minds were freed of fear, independence would not be far behind.
OR
Both Zitkala-sa and Bama were victims of discrimination. While the farmer suffered racist discrimination, Bama suffered the caste-based discrimination in the form of untouchability. They suffered great atrocities. The whites in the Carlisle school sought to erase her identity by teaching her western ways and manners. Her long hair was shingled. This was forbidden in her Indian culture; She was made to wear tight dresses which she found immodest. Likewise Bama learnt from her brother that she was Dalit and hence untouchable. Bama and Zitkala-sa both experienced painfully how prejudice and discrimination can deprive human beings of compassion, consideration and humanity. Malala has fought for education for girls in her own country, Afghanistan. She too must have experienced the indignities humans can commit due to lack of education.
Answer 11.
After Sadao decided to help the wounded American soldier, he experienced a conflict between his sense of patriotism and sense of professional duty. He was in a dilemma—if he abandons the American he would be doing a disservice to his profession as a surgeon; if he helped him he would be betraying his country. He resolves this dilemma by choosing humanity over considerations of race. He also has to overcome his personal hatred of Americans whom he had come to loathe during his stay in America. In the end Sadao rises above all these narrow considerations and upholds humanity and his professional duty to serve humanity.
OR
The experiences and life of Bama and Zitkala-sa exemplify that oppression and injustice doesn’t go unnoticed even by children. Zitkala-sa experienced extreme blows to her sense of identity and self-esteem. Similarly a young Bama realized that she was an untouchable. Her anger at the upper caste who subjugated them and yet used them shamelessly is brought out in Bama’s account. In the throes of mental agony it is her brother who advises her to educate herself well so as to break the shackles of untouchability. Zitkala-sa and Bama grew up to be champions of equality. By writing about their experiences of societal discrimination they took to creating an equal, discrimination free society by creating awareness among their readers.
Answer 12.
Griffin was a genius, a student of science. He dreamed of becoming invisible so as to become all powerful. His untiring experiments made him realize this evil dream. Ironically invisibility proved very inconvenient to Griffin: People knocked into him on roads, the food and drink in his digestive tract could be spotted since it was visible. Moreover he could not bear the chill of England. Now he longed to reverse the experiment. To brave the cold he put on warm clothes, bandaged his face, stuck a fake pink nose on his face in order to appear normal. Thus his unnatural ambition reduced him to a caricature of a man physically but also degraded him morally and spiritually.
OR
Before coming to Raveloe, Silas Marner lived in a town called Lantern Yard. He was a weaver and a religious man. He was friendly and popular so that people loved him. He was engaged to Sara. William Dane was his trusted friend. Silas often suffered from epileptic fits. During these fits he lost all consciousness. His friend thought that he was possessed by Satan. During one such fit, William taking advantage of his unconscious state framed him as a thief. Silas was subsequently expelled on the charge of stealing money. He was embittered and lost all faith and trust. In such a mental state he arrived at Raveloe.
Answer 13.
In his pursuit of invisibility Griffin gradually loses all traces of humanity. He became isolated and hated people. His treatment with Marvel highlights his predilection for violence and abuse. He ill treats his father too by stealing his money. His father, commits suicide. Yet Griffin does not feel any remorse. He commits a burglary in Mr. Bunting’s house. He also harasses Mrs Hall many times by his rudeness and carelessness. Later he misuses Dr. Kemp who he sees as his enemy and declares to kill him. Thus Griffin is totally blinded by his pursuit of power and becomes a maniac.
OR
Nancy is a beautiful and charming girl from a rich family of Raveloe. She is caring. Godfrey loves and later marries. She has a strict moral upbringing and regards Godfrey’s flaws of character with disapproval. Yet she can’t help being flattered by Godfrey’s attention. Nancy carries herself gracefully in a lady like manner yet she is aware about her typical rural traits: her coarse hands betray her sophisticated manners. There is no denying her that physical beauty, height and upright posture and above all her moral sense were praiseworthy. After marriage, Nancy is stopped by her moral sense to adopt a child but she makes up to Godfrey for this lack in other ways. When she learns that Eppie is Godfrey’s daughter, she is moved by love and sympathy.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Englsih Core Paper 1 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 English Core Paper 1, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.