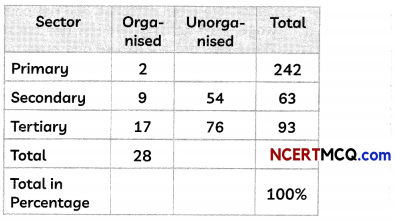
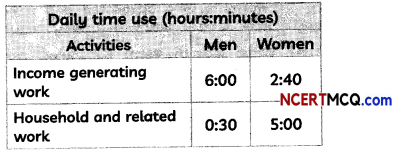
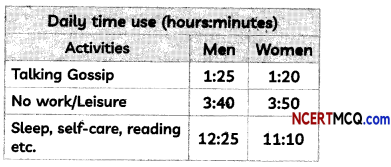
Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 9 Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Geography with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature Class 11 Geography MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Geography Chapter 9 Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature MCQ With Answers
Geography Class 11 Chapter 9 MCQs On Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature
Question 1.
The sun is vertically overhead at noon on 21st June at
(a) the equator
(b) 23.5 degree N
(c) 23.5 degree S
(d) 66.5 degree N
Answer
Answer: (b) 23.5 degree N
Question 2.
The days are longest at
(a) Thiruvananthapuram
(b) Hyderabad
(c) Chandigarh
(d) Nagpur
Answer
Answer: (a) Thiruvananthapuram
Question 3.
This process of vertical heating of the atmosphere is known as ________
(a) Psychrometer
(b) Convection
(c) Evaporation
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Convection
Question 4.
Differences in pressure on the earth surface causes:
(a) Winds
(b) Precipitation
(c) Hail
(d) Seasons
Answer
Answer: (a) Winds
Question 5.
______ are lines joining places having an equal temperature.
(a) Isotherms
(b) Evaporation
(c) Convection
(d) Pyrheliometer
Answer
Answer: (a) Isotherms
Question 6.
The heat energy absorbed by a known area in a fixed time is determined with the help of an instrument called
(a) Psychrometer
(b) Pyrheliometer
(c) Thermometric well
(d) Any instrument
Answer
Answer: (b) Pyrheliometer
Question 7.
What is Isotherm?
(a) The line joining the places of equal temperature
(b) The incoming short wave radiation
(c) The line joining the places of equal pressure
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) The line joining the places of equal temperature
Question 8.
The earth radiates energy to the atmosphere in:
(a) Long wavelengths
(b) Radiation
(c) Insolation
(d) Short wavelengths
Answer
Answer: (a) Long wavelengths
Question 9.
Maximum insolation is received over the ____________
(a) Equator
(b) Tropical areas
(c) Sub-tropical areas
(d) Poles
Answer
Answer: (c) Sub-tropical areas
Question 10.
Insolation refers to ________
(a) Wind direction
(b) Solar radiation
(c) Precipitation
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Solar radiation
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 9 Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Geography Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Geography with Answers MCQ:
- Geography as a Discipline Class 11 MCQ
- The Origin and Evolution of the Earth Class 11 MCQ
- Interior of the Earth Class 11 MCQ
- Distribution of Oceans and Continents Class 11 MCQ
- Minerals and Rocks Class 11 MCQ
- Geomorphic Processes Class 11 MCQ
- Landforms and their Evolution Class 11 MCQ
- Composition and Structure of Atmosphere Class 11 MCQ
- Solar Radiation, Heat Balance and Temperature Class 11 MCQ
- Atmospheric Circulation and Weather Systems Class 11 MCQ
- Water in the Atmosphere Class 11 MCQ
- World Climate and Climate Change Class 11 MCQ
- Water (Oceans) Class 11 MCQ
- Movements of Ocean Water Class 11 MCQ
- Life on the Earth Class 11 MCQ
- Biodiversity and Conversation Class 11 MCQ