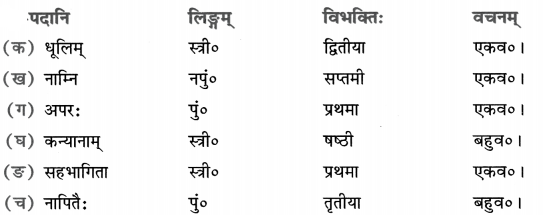
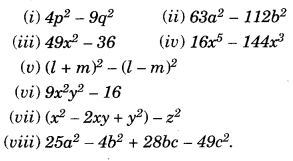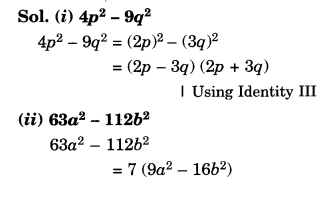Here we are providing Online Education Class 8 History Chapter 9 Extra Questions and Answers Women, Caste and Reform was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/class-8-history-chapter-9-extra-questions/
Online Education for Women, Caste and Reform Class 8 Extra Questions History Chapter 9
Question 1.
Till when is Indian National Congress said to be moderate in its objectives and methods?
Answer:
The Congress in the first twenty years was moderate in its objectives and methods.
Question 2.
What was the main objective of moderate leaders?
Answer:
The main objective of moderate leaders was to express their demands and make the government aware of the feelings of Indians.
Question 3.
Who were the main leaders of radicals?
Answer:
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Lala Lajpat Raj
- Bipin Chandra Pal.
Question 4.
What was the famous slogan of % Bal Gangadhar Tilak?
Answer:
Tilak raised the slogan, “Freedom is my birthright and I shall have it.”
Question 5.
When was Bengal partitioned?
Answer:
Bengal was partitioned in 1905.
Question 6.
Who was the Viceroy of India when Bengal was partitioned?
Answer:
Viceroy Curzon.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you mean by Swadeshi Movement?
Answer:
The struggle that unfolded after the partition of Bengal, came to be known as the Swadeshi movement.
Question 8.
What is Vandemataram Movement?
Answer:
The struggle that unfolded in deltaic Andhra after the partition of Bengal was known as the Vandemataram Movement.
Question 9.
When was the All India Muslim League established?
Answer:
The All India Muslim League was established at Dacca in 1906.
Question 10.
While the Congress opposed the partition of Bengal, which national organisation supported it?
Answer:
The All India Muslim League.
Question 11.
When did the Congress split?
Answer:
The Congress split in 1907.
Question 12.
When did the two groups of the Congress reunite?
Answer:
The two groups of the Congress reunited in December 1915.
Question 13.
Since when did the struggle against British rule become a mass movement?
Answer:
After 1919, the struggle against British rule gradually became a mass movement.
Question 14.
When did Gandhiji come in India from South Africa?
Answer:
Gandhiji arrived in India in 1915 from South Africa.
Question 15.
State the earliest interventions in the British rule by Mahatma Gandhi.
Answer:
His earliest interventions were in local movements in Champaran, Kheda and Ahmedabad.
Question 16.
What was the role of Gandhiji in Ahmedabad movement of 1918?
Answer:
In Ahmedabad, Gandhiji led a successful millworkers’ strike in 1918.
![]()
Question 17.
What is Rowlatt Satyagraha?
Answer:
In 1919, Gandhiji gave a call for a Satyagraha against the Rowlatt Act that is called the Rowlatt Satyagraha.
Question 18.
Which struggle is considered to be the first all-India struggle against the British government?
Answer:
The Rowlatt Satyagraha.
Question 19.
Why did Rabindranath Tagore renounce his Knighthood?
Answer:
On learning about the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, Rabindranath Tagore expressed the pain and anger of the country by renouncing his knighthood.
Question 20.
Who were the leaders of the Khilafat agitation?
Answer:
- Mohammad Ali,
- Shaukat Ali.
Question 21.
Which movement was fought for Hindu-Muslim unity?
Answer:
Khilafat-Non-Cooperation Movement.
Question 22.
What do you mean by Akali agitation?
Answer:
This was the agitation of Sikhs in Punjab which sought to remove corrupt mahants from their gurudwaras.
Question 23.
When did the Civil Disobedience Movement launch?
Answer:
In 1930.
Question 24.
Name the national organisations which came into existence in mid-1920s.
Answer:
- The Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS)
- The Communist Party of India.
Question 25.
When did the Congress resolve to fight for Purna Swaraj? Who was the president of the Congress at the time?
Answer:
- In 1929
- Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru.
Question 26.
What is the importance of 26 January 1930 in Indian freedom struggle?
Answer:
As the Congress resolved to fight for Purtia Swaraj in 1929, “Independence Day” was observed on 26 January 1930 all over the country.
Question 27.
Who led a march to break the salt law?
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi in 1930.
Question 28.
What was salt law?
Answer:
According to the law, the state had a monopoly on the manufacture and sale of salt.
Question 29.
Why did Gandhiji oppose the salt law?
Answer:
Gandhiji along with other nationalists reasoned that it was sinful to tax salt since it is such an essential item of our food.
Question 30.
Who was Ambabai?
Answer:
Ambabai was an active woman participant in the national movement.
![]()
Question 31.
Who persuaded Gandhiji to allow women to join the national movement?
Answer:
Sarojini Naidu.
Question 32.
Who was the first Indian woman to become president of the Indian National Congress?
Answer:
Smt. Sarojini Naidu in 1925.
Question 33.
What did the Congress do when the British refused to concede its demand of independence after the Second World War?
Answer:
The Congress ministries resigned in protest.
Question 34.
Who was Veer Lakhan Nayak?
Answer:
He was a legendary tribal leader who defied the British and later was hanged.
Question 35.
What was Quit India Movement?
Answer:
It was the movement initiated by Mahatma Gandhi in 1942 in which he told that the British must quit India immediately.
Question 36.
Who gave the famous slogan “do or die” during Quit India Movement?
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi.
Question 37.
Who founded the Azad Hind Fauj or the Indian National Army (INA)?
Answer:
Subhas Chandra Bose in 1941.
Question 38.
Who is called the father of Indian Constitution?
Answer:
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar is called the father of Indian Constitution.
Question 39.
What awareness came in the mind of Indians with the idea that India was the people of India?
Answer:
With this idea came the awareness that the British were exercising control over the resources of Indians and the lives of its people and until this control was ended India could not be for Indians.
Question 40.
What were the main motives of the British with regard to partition of Bengal?
Answer:
Though British argued for dividing Bengal for reasons of administrative convenience, but the main British motives were, perhaps, to curtail the influence of Bengali politicians and to split the Bengali people.
![]()
Question 41.
What were the objectives of the Swadeshi Movement?
Answer:
The main objectives of the Swadeshi Movement were to oppose British rule and encourage the ideas of self-help, Swadeshi enterprise, national education and use of Indian languages.
Question 42.
What is meant by Lucknow Pact?
Answer:
In 1916, the Congress and the Muslim League signed the historic Lucknow Pact and decided to work together for representative government in the country.
Question 43.
How did Gandhiji spend his first year in India?
Answer:
He spent his first year in India travelling throughout the country, understanding the people, their needs and the overall situation.
Question 44.
What was the Rowlatt Act?
Answer:
The Rowlatt Act was the Act passed by the British government in 1919 which curbed fundamental rights such as the freedom of expression and strengthened police powers.
Question 45.
Why did Gandhiji ask the Indian people to observe 6 April 1919 as a day of “humiliation and prayer”?
Answer:
Gandhiji asked the Indian people to observe 6 April 1919 as a day of “humiliation and prayer” and strike in order to do nonviolent opposition to this Act.
Question 46.
Why is Indian National Congress said to be moderate in its first twenty years?
Answer:
- The Congress SI the first twenty years was moderate in its objectives and methods.
- During this period, it was doing “politics of prayers”.
- It demanded a greater voice for Indians in the government and in administration.
- It demanded that Indians be placed in high positions in the government.
Question 47.
What were the economic demands of the Congress in its early years?
Answer:
The following were the economic demands of early leadership of the Congress :
- The Congress believed that the increase in the land revenue by the British government had impoverished peasants and zamindars. So, it demanded reduction of revenue.
- It demanded to cut in military expenditure.
- It also demanded more funds for irrigation.
- Moreover, it passed many resolutions on the salt tax, treatment of Indian labourers abroad and the sufferings of forest dwellers.
Question 48.
What was Swadeshi Movement? What were its objectives?
Answer:
- The struggle that unfolded after the partition of Bengal, came to be known as the Swadeshi Movement.
- The main objectives of the Movement were to oppose British rule and encourage the ideas of self-help, swadeshi enterprise, national education and use of Indian languages. To fight for Swaraj, the radicals advocated mass mobilisation and boycott of British institutions and goods.
![]()
Question 49.
How did Khilafat-Non- Cooperation alliance work?
Answer:
- The Muslim leaders and brothers Mohammad Ali and Shaukat Ali discussed the Khilafat issue with Gandhi and wished to initiate a full-fledged Non-Cooperation Movement.
- Gandhiji supported their call and urged the Congress to campaign against’ Punjab wrongs, the Khilafat wrong and demand swaraj.
Question 50.
What was Chauri Chaura incidence? Why did it happen?
Answer:
- In February 1922, a crowd of peasants set fire to a police station in which twenty-two policemen were killed.
- The peasants were provoked because the police had fired on their peaceful demonstration.
Question 51.
Explain the term “The Simon Commission”.
Answer:
In 1927, the British government in England decided to send a commission headed by Lord Simon to decide India’s political future. The Commission had no Indian representative. The decision created an outrage in India.
Question 52.
Who threw a bomb in the Central Legislative Assembly on 8 April 1929? What was the aim behind this act?
Answer:
1.
- Bhagat Singh,
- B.K. Dutt.
2. The aim of this act was not to kill but, “to make the deaf hear”, to remind the foreign government of its callous exploitation.
Question 53.
Where and how did Gandhiji break the salt law?
Answer:
- Gandhiji and his followers marched for over 240 miles from Sabarmati to the coastal town of Dandi where they broke the salt law on 6 April 1930.
- They broke the law by gathering natural salt found on the seashore, and boiling seawater to produce salt.
Question 54.
What were the result of the combined struggles of salt satyagraha?
Answer:
- The Government of India Act of 1935 came into existence.
- The Act prescribed provincial autonomy.
- The government announced elections to the provincial legislatures in 1937.
- The Congress formed governments in 7 out of 11 provinces.
![]()
Question 55.
Why did the Congress support the British in the Second World War? What did it demand in return?
Answer:
- Congress leaders were critical of Hitler, so they became ready to support the British war effort.
- In return, they wanted that India be granted independence after the war.
Question 56.
Explain the British repression during Quit India Movement.
Answer:
- The first response of the British was severe repression.
- Over 90,000 people were arrested by the end of 1943.
- Around 1,000 were killed in police firing.
- In many areas, orders were given to machine-gun crowds from aeroplanes.
Question 57.
What were the main demands of the Congress in its first twenty years?
Answer:
- The Congress demanded that Indians be placed in high positions in the government since most important jobs at that time were monopolised by British officials. It called for civil service examinations to be held in India as well as in London.
- It also demanded the separation of the judiciary from the executive.
- There should be repeal of the Arms Act.
- It demanded the freedom of speech and expression.
- Since, the increase in the land revenue had impoverished peasants and zamindars, the Congress demanded reduction of revenue.
- Moreover, it demanded to cut in military expenditure and more funds for irrigation.
Question 58.
What political impact did the First World War have on India?
Answer:
The First World War had the following political impact on India :
- The First World War led to a huge rise in the defence expenditure which, in turn, increased taxes on individual incomes and business profits. This agitated the people.
- Increased military expenditure and the demands of war supplies led to a sharp rise in prices which created great difficulties for the common people.
- The war created a demand for industrial goods such as jute bags, cloth, rails, etc. So, Indian industries expanded during the war and Indian business groups began to demand greater opportunities for development.
- A large number of Indian soldiers were sent to serve abroad. Many returned after the war with an understanding that the British were exploiting the peoples of Asia and Africa and with a desire to oppose colonial rule in India.
- As a result of Russian Revolution in 1917, the ideas of socialism circulated widely and inspired Indian nationalists.
Question 59.
Why did the League ask for an autonomous arrangement for the Muslims of the subcontinent?
Answer:
This had the following reasons :
- From the late 1930s, the League began viewing the Muslims as a separate nation from the Hindus.
- It may have been influenced by the history of tension between some Hindu and Muslim groups in the 1920s and 1930s.
- The provincial elections of 1937 convinced the League that Muslims were a minority and they would always have to play second fiddle in any democratic structure.
- It feared that Muslims may even go unrepresented.
- The Congress’s rejection of the League’s. desire to form a joint Congress-League government in the United Provinces in 1937 also annoyed the League.
Question 60.
In which circumstances did the Indian National Congress establish?
Answer:
People were dissatisfied with British rule in the 1870s and 1880s :
- The Arms Act, 1878 disallowed Indians from possessing arms.
- The Vernacular Press Act, 1878 was also enacted in an effort to silence the critics.
- The government withdrew Ilbert Bill as a result of white opposition.
- The need for an all-India organisation of educated Indians had been felt since 1880, but the Ilbert Bill controversy deepened this desire.
The Indian National Congress was established when 72 delegates from all over the country met at Bombay in December 1885. A retired British official, A.O. Hume became its first president.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Which of the following political associations was an all-India organisation of educated Indians?
(a) The Poona Sarvajanik Sabha
(b) The Indian Association
(c) The Madras Mahajan Sabha
(d) the Indian National Congress.
Answer:
(d) the Indian National Congress.
2. The early leadership of the Indian National Congress was largely from:
(а) Bombay and Delhi
(b) Bombay and Calcutta
(c) Calcutta and Madras
(d) Delhi and Madras.
Answer:
(b) Bombay and Calcutta.
3. Which of the following pairs is not correct?
(a) The Arms Act – 1878
(b) The Vernacular Press Act -1878
(c) Partition of Bengal – 1906
(d) The Ilbert Bill -1883.
Answer:
(c) Partition of Bengal – 1906.
![]()
4. The Congress in the first twenty years was moderate in its objectives and methods. What did it not demand in the following?
(a) It wanted the Legislative Councils to be made more representatives.
(b) It demanded that Indians be placed in high positions in the government.
(c) It wanted the separation of judiciary from the executive.
(d) They argued that people must rely on their own strength and fight for swaraj.
Answer:
(d) They argued that people must rely on their own strength and fight for swaraj.
5. Who said, “Freedom is my birthright and I shall have it”?
(а) Lala Lajpat Rai
(b) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
(c) Bipin Chandra Pal
(d) Mahatma Gandhi
Answer:
(b) Bal Gangadhar Tilak.
Glossary:
→ Sovereign -This is the capacity to act independently without outside interference.
→ Publicist- It refers to someone who publicises an idea by circulating information, writing reports, speaking at meetings.
→ Repeal – This is to undo law; to officially end the validity of something such as a law.
→ Revolutionary violence – This means the use of violence to make a radical change within society.
→ Council -An appointed or elected body of people with an administrative advisory or representative function.
→ Knighthood – This was an honour granted by the British Crown for exceptional personal achievement or public service.
→ Picket – People protesting outside a building or shop to prevent others from entering,
→ Mahants – This refers to religious functionaries of Sikh gurudwaras.
→ Illegal eviction – It means forcible and unlawful throwing out of tenants from the land they rent.
→ Provincial autonomy-Capacity of the provinces to make relatively independent decisions while remaining within a federation.