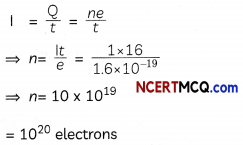
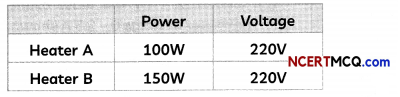
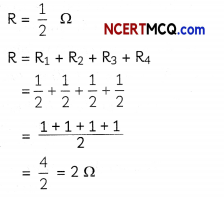Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of Motion with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 9 Physics Chapter 5 MCQ With Answers
Physics Class 9 Chapter 5 MCQs On Laws of Motion
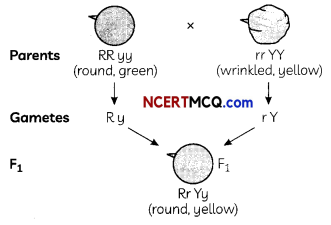
Laws Of Motion Class 11 MCQ With Answers Question 1.
The mass of a body which is equal to the ratio of the force acting on a body to the acceleration produced in the body is
(a) the gravitational mass
(b) the electromagnetic mass
(c) the internal mass
(d) the inertial mass
Answer
Answer: (d) the inertial mass
Laws Of Motion Class 11 MCQ Question 2.
A spherical ball of mass 10-6 kg hits a wall 1000 times per second normally with a velocity of 1000 m/s and rebounds with same velocity along the initial direction. The force experienced by the wall is
(a) 1 N
(b) 4 N
(c) 2 N
(d) 8 N
Answer
Answer: (c) 2 N
Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 MCQ Question 3.
The force required to produce an acceleration of 2 m/s² on a mass of 2 kg is
(a) 4 N
(b) 10 N
(c) 22 N
(d) 18 N
Answer
Answer: (a) 4 N
Laws Of Motion MCQ Class 11 Question 4.
A machine gun fires a bullet of mass 40 g with a velocity of 1200 ms-1. The man holding it can exert a maximum force on 144 N on the gum. How many bullets can he fire per second at the most?
(a) one
(b) four
(c) two
(d) three
Answer
Answer: (d) three
MCQ On Laws Of Motion Class 11 Question 5.
A passenger in a moving bus is thrown forward when the bus is suddenly stopped. This is explained
(a) by Newtons first law
(b) by Newtons second law
(c) by Newtons third law
(d) by the principle of conservation of momentum
Answer
Answer: (a) by Newtons first law
MCQ Questions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Question 6.
A passenger sitting in a bus moving at uniform speed, feels pushed backward whenever the bus is accelerated forward. This type of force is called
(a) Gravitational force
(b) real force
(c) fictitious force or pseudo force
(d) frictional force
Answer
Answer: (c) fictitious force or pseudo force
MCQ Of Laws Of Motion Class 11 Question 7.
A body of mass 5 kg is travelling with a uniform velocity of 2 m/s. Its momentum is
(a) 10 kg m/s
(b) 7 kg m/s
(c) 2 .5 kg m/s
(d) 3 kg m/s
Answer
Answer: (a) 10 kg m/s
Law Of Motion Class 11 MCQ Question 8.
Inside the nucleus, two protons are held together by a force which overcomes the repulsion. This force is called
(a) gravitational force
(b) electrostatic force
(c) weak force
(d) strong force
Answer
Answer: (d) strong force
Class 11 Laws Of Motion MCQ Question 9.
A block of wood is placed on a surface. A force is applied parallel to the surface to move the body. The frictional force developed acts
(a) normal to the surface upwards
(b) normal to the surface downwards
(c) along the direction of the applied force
(d) opposite to the direction of the applied force
Answer
Answer: (d) opposite to the direction of the applied force
Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 MCQ With Answers Question 10.
A bullet of mass 25 g moving with a velocity of 200 cm/s is stopped within 5 cm of the target. The average resistance offered by the target is
(a) 1 N
(b) 2 N
(c) 3 N
(d) 4 N
Answer
Answer: (a) 1 N
MCQ Questions On Laws Of Motion Class 11 Question 11.
The mass of a body is 2 kg. It weight is
(a) 19.6 N
(b) 20 N
(c) 30 N
(d) 40 N
Answer
Answer: (a) 19.6 N
Class 11 Physics Ch 5 MCQ Question 12.
A body is sliding down a rough inclined plane which makes an angle of 30 degree with the horizontal. If the coeffcient of friction is 0.26, the acceleration in m/s² is
(a) 1.95
(b) 2.78
(c) 3.47
(d) 4.6
Answer
Answer: (b) 2.78
Ch 5 Physics Class 11 MCQ Question 13.
A gun of mass 1000 kg fires a projectile of mass 1 kg with a horizontal velocity of 100 m/s. The velocity of recoil of the gun in the horizontal direction is
(a) 5 m/s
(b) 0.1 m/s
(c) 15 m/s
(d) 20 m/s
Answer
Answer: (b) 0.1 m/s
Chapter 5 Physics Class 11 MCQs Question 14.
A block of wood is placed on a surface. A force is applied parallel to the surface to move the body. The frictional force developed acts
(a) normal to the surface upwards
(b) normal to the surface downwards
(c) along the direction of the applied force
(d) opposite to the direction of the applied force
Answer
Answer: (d) opposite to the direction of the applied force
Class 11 Physics Laws Of Motion MCQ With Answers Question 15.
A block of mass 2 kg rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30 degree with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between he block and the plane is 0.7. The frictional force on the block is
(a) 9.8 N
(b) 0.7 × 9.8 × √3 N
(c) 9.8 × √3 N
(d) 0.7 × 9.8 N
Answer
Answer: (d) 0.7 × 9.8 N
MCQs On Laws Of Motion Class 11 Question 16.
A particle of mass 0.3 kg is subjected to a force F = -kx with k = 15 N/m. What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point 20 cm away from the origin?
(a) 15 m/s²
(b) 3 m/s²
(c) 10 m/s²
(d) 5 m/s²
Answer
Answer: (c) 10 m/s²
Laws Of Motion Class 11 MCQs Question 17.
Two bodies of masses 4 kg and 5 kg are acted upon by the same force. If the acceleration of lighter body is 2 m/s², the acceleration of heavier body is
(a) 1 m/s²
(b) 1.2 m/s²
(c) 1.6 m/s²
(d) 1.8 m/s²
Answer
Answer: (c) 1.6 m/s²
MCQ On Laws Of Motion Class 11 Pdf Question 18.
Out of the basic forces , gravitational force
(a) ranks first in strength
(b) ranks second in strength
(c) ranks third in strength
(d) ranks fourth in strength
Answer
Answer: (d) ranks fourth in strength
Question 19.
The frame of reference attached to a satellite of the earth is
(a) an inertial frame
(b) an absolute frame at rest with respect to the stars
(c) a non – inertial frame
(d) a gravitational frame
Answer
Answer: (c) a non – inertial frame
Question 20.
A block of mass M is placed on a flat surface. A force is applied to move it parallel to the surface. The frictional force f developed is proportional to the
(a) square of the mass of the body
(b) mass of the body
(c) reciprocal of the mass of the body
(d) reciprocal of the square of the body
Answer
Answer: (b) mass of the body
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 5 Laws of Motion with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Physics Laws of Motion MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Physics MCQ:
- Physical World Class 11 MCQ
- Units and Measurements Class 11 MCQ
- Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 MCQ
- Motion in a Plane Class 11 MCQ
- Laws of Motion Class 11 MCQ
- Work, Energy and Power Class 11 MCQ
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 MCQ
- Gravitation Class 11 MCQ
- Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 MCQ
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 MCQ
- Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 MCQ
- Thermodynamics Class 11 MCQ
- Kinetic Theory Class 11 MCQ
- Oscillations Class 11 MCQ
- Waves Class 11 MCQ