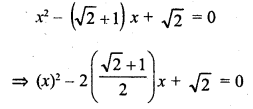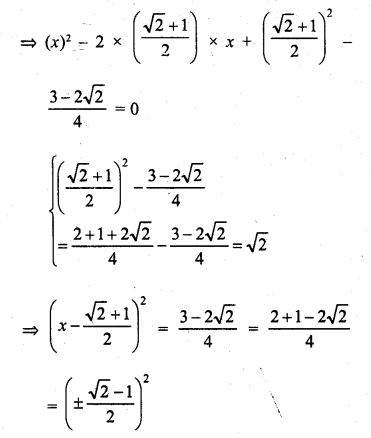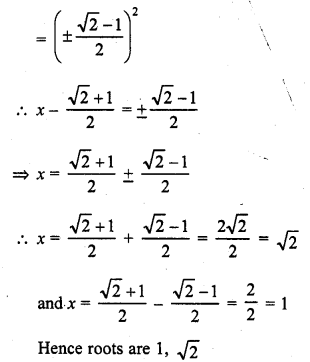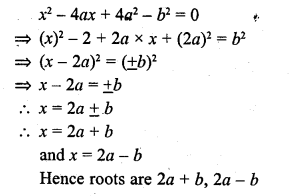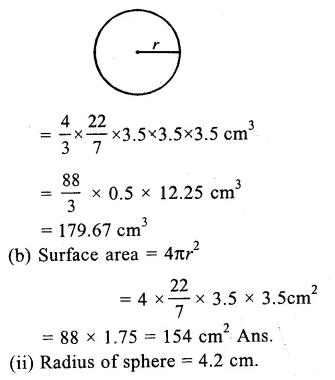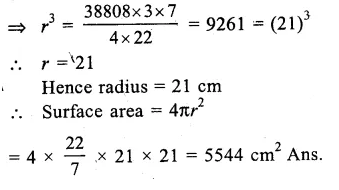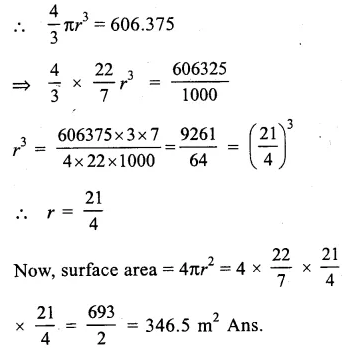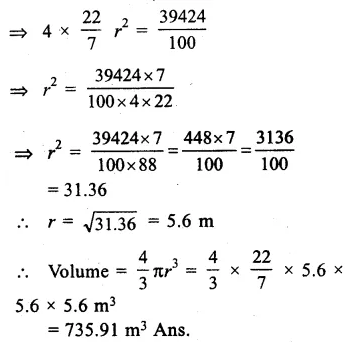Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit Chapter 10 जटायोः शौर्यम् with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided जटायोः शौर्यम् Class 9 Sanskrit MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-9-sanskrit-with-answers/
Students can also read NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Sanskrit Chapter 10 Questions and Answers at LearnInsta. Here all questions are solved with a detailed explanation, It will help to score more marks in your examinations.
निम्नलिखितेषु वाक्येषु रेखाङ्कितपदानां स्थाने समुचितं प्रश्नवाचकं पदं चित्वा लिखत
Question 1.
तदा सा सुदुःखिता गृघ्रं ददर्श।
(क) कः
(ख) किम्
(ग) काम्
(घ) कम्
Answer
Answer: (घ) कम्
Question 2.
आयतलोचना विलपन्ती सीता वनस्पतिगतं गृधं ददर्श।
(क) कीदृशी
(ख) का
(ग) कथम्
(घ) काम्
Answer
Answer: (क) कीदृशी
Question 3.
जटायो! माम् अनाथवत् ह्रियमाणाम् पश्य।
(क) कम्
(ख) काम्
(ग) किम्
(घ) कीदृशीम्
Answer
Answer: (ख) काम्
Question 4.
आर्य जटायो! अनेन पाकर्मणा राक्षसेन्द्रेण ह्रियमाणाम् मां पश्च।
(क) कम्
(ख) कथम्
(ग) केन
(घ) कीदृशेण
Answer
Answer: (ग) केन
Question 5.
अथ जटायुः तं शब्दं शुश्रुवे।
(क) किम्
(ख) काम्
(ग) कथम्
(घ) कम्
Answer
Answer: (घ) कम्
Question 6.
जटायुः क्षिप्रं रावणं निरीक्ष्य वैदेहीं च ददर्श।
(क) कम्
(ख) काम्
(ग) किम्
(घ) कीदृशीम्
Answer
Answer: (ख) काम्
Question 7.
अथ अवसुप्तः तु जटायुः तं शब्दं शुश्रुवे।
(क) कीदृशः
(ख) कः
(ग) काः
(घ) के
Answer
Answer: (क) कीदृशः
Question 8.
ततः तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः रावणं व्याजहार।
(क) कः
(ख) के
(ग) का
(घ) कीदृशः
Answer
Answer: (क) कः
Question 9.
अथ पर्वतशृङ्गाभः वनस्पतिगतः श्रीमान् शुभां गिरं व्याजहार।
(क) काम्
(ख) कथम्
(ग) कीदृशी
(घ) कीदृशीम्
Answer
Answer: (घ) कीदृशीम्
Question 10.
त्वं परदारा अभिमर्शनात् नीचां मतिं निवर्तय।
(क) कस्ममात्
(ख) कस्मै
(ग) कथम्
(घ) कदा
Answer
Answer: (क) कस्ममात्
Question 11.
धीरः तत् न समाचरेत्।
(क) कः
(ख) कम्
(ग) किम्
(घ) का
Answer
Answer: (ग) किम्
Question 12.
यत् परः अस्य विगर्हयेत्।
(क) कः
(ख) के
(ग) का
Answer
Answer: (क) कः
Question 13.
अहं वृद्धः अस्मि।
(क) कः
(ख) कीदृशः
(ग) कीदृशा
(घ) काः
Answer
Answer: (ख) कीदृशः
Question 14.
त्वं च युवा धन्वी सरथः च असि।
(क) का
(ख) कः
(ग) कथम्
(घ) के
Answer
Answer: (घ) के
Question 15.
त्व वैदेहीं मे आदाच कुशली न गमिष्यसि।
(क) कीदृशः
(ख) का
(ग) कथम्
(घ) केन
Answer
Answer: (क) कीदृशः
Question 16.
महाबलः पतगसत्तमः तस्य गात्रे बहुधाव्रणान् चकार।
(क) कः
(ख) कम्
(ग) काम्
(घ) कीदृशः
Answer
Answer: (घ) कीदृशः
Question 17.
पतगसत्तमः तु तीक्ष्णनखाभ्यां चरणाभ्यां बहुधा व्रणान् चकार।
(क) कः
(ख) काभ्याम्
(ग) कदा
(घ) किम्
Answer
Answer: (ख) काभ्याम्
Question 18.
ततः महातेजा अस्य महद्धनुः बभञ्ज।
(क) कीदृशीम्
(ख) कथम्
(ग) कम्
(घ) कः
Answer
Answer: (घ) कः
Question 19.
ततः जटायुः रावणस्य मुक्तामणिविभूषितं महद् धनुः बभञ्ज।
(क) कस्मात्
(ख) किम्
(ग) कः
(घ) का
Answer
Answer: (ख) किम्
Question 20.
सः रावणः भुवि पपात।।
(क) कुत्र/कस्याम्
(ख) कथम्
(ग) कम्
(घ) काम्
Answer
Answer: (क) कुत्र/कस्याम्
Question 21.
नतः सः रावणः वैदेहीम् अङ्केन आदाय भूवि पपात।
(क) केन
(ख) कः
(ग) कति
(घ) कम्
Answer
Answer: (ख) कः
Question 22.
क्रोधमूछितः रावणः वैदेहीं वामेन अकेन संपरिष्वज्य।
(क) कीदृशी
(ख) किम्
(ग) के
(घ) केन
Answer
Answer: (घ) केन
Question 23.
रावणः जटायुं तलेन आशु अभिजघान।
(क) काः
(ख) के
(ग) कः
(घ) केन
Answer
Answer: (घ) केन
Question 24.
तदा अरिन्दमः जटायुः तुण्डेन आक्राम्यत।
(क) कति
(ख) कः
(ग) कीदृशी
(घ) काम्
Answer
Answer: (ख) कः
Question 25.
ततः खगाधिपः जटायुः तुण्डेन अस्य दश बाहून् व्यपाहरत्
(क) कम्
(ख) काम्
(ग) कति
(घ) केन
Answer
Answer: (ग) कति
निम्नलिखितानि श्लोकानि पठित्वा तदाधारितानां प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि लिखत
सा तदा करुणा वाचो विलपन्ती सुदुःखिता।
वनस्पतिगतं गृधं ददर्शायतलोचना॥
Question 1.
आयतलोचना का आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सीता
Question 2.
सीता कं ददर्श?
Answer
Answer: गृध्रम्
Question 3.
का विलपन्ती आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सीता
Question 4.
सीता कीदृशी-वाचः विलपन्ती आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सीता करुणा-वाचः विलपन्ती आसीत्।
Question 5.
सीता कीदृशी आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सीता आयतलोचना आसीत्।
Question 6.
‘सा तदा करुणावाचो’। अत्र ‘सा’ पदं कस्यै प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: सीतायै
Question 7.
‘वनस्पतिगतं गृध्रम्’ अनयोः पदयोः विशेषणपदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: वनस्पतिगतम्
Question 8.
अत्र श्लोके ‘हसन्ती’ इति पदस्य कः विपर्ययः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: विलपन्ती
Question 9.
‘अपश्यत्’ इति अर्थ किम्. क्रियापदं प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: ददर्श
जटायो पश्य मामार्य ह्रियमाणामनाथवत्।
अनेन राक्षसेन्द्रेण करुणं पापकर्मणा॥
Question 1.
सीता जटायुं कः वदति?
Answer
Answer: आर्यः
Question 2.
सीता कथ/किंवत् ह्रियमाणा आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: अनाथवत्
Question 3.
रावणः कीदृशः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: पापकर्मः
Question 4.
केन सीता अनाथवत् ह्रियमाणा आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: पापकर्मणा राक्षसेन्द्रेण सीता अनाथवत् ह्रियमाणा आसीत्।
Question 5.
सीता केन ह्रियमाणा आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सीता राक्षसेन्द्रेण पापकर्मणा ह्रियमाणा आसीत्।
Question 6.
‘जटायो पश्य मामार्य ह्रियमाणा।’ अत्र क्रियापदं किमस्ति?
Answer
Answer: पश्य
Question 7.
श्लोके ‘पापकर्मणा’ पदं कस्मै आगतम्?
Answer
Answer: रावणाय
Question 8.
श्लोके ‘दानवपतिना’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: राक्षसेन्द्रेण
Question 9.
अत्र ‘आर्यपदं’ कस्मै प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: जटायोः कृते (जटायवे)
तं शब्दमवसुप्तस्तु जटायुरथ शुश्रुवे।
निरीक्ष्य रावणं क्षिप्रं वैदेहीं च ददर्श सः॥
Question 1.
कीदृशः जटायुः तं शब्दम् शुश्रुवे?
Answer
Answer: अवसुप्तः
Question 2.
जटायुः प्रथमं कं निरीक्षितवान्?
Answer
Answer: रावणम्
Question 3.
जटायुः कीदृशः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: सुप्तः
Question 4.
रावणं निरीक्ष्य सः जटायुः क्षिप्रं कां ददर्श?
Answer
Answer: रावणं निरीक्ष्य सः जटायुः क्षिप्रं वैदहीं ददर्श।
Question 5.
गृध्रः कम् निरीक्ष्य वैदेहीं ददर्श?
Answer
Answer: गृध्रः रावणम् निरीक्ष्य वैदेहीं ददर्श।
Question 6.
अत्र श्लोके ‘चिरम्’ इति पदस्य कः विपर्ययः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: क्षिप्रम्
Question 7.
‘ददर्श’ इत्यस्याः क्रियायाः श्लोके कर्तृपदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: सः
Question 8.
‘अवसुप्तः सः जटायु’ अनयोः पदयोः विशेषणं किमस्ति?
Answer
Answer: अवसुप्तः/सः
Question 9.
अत्र ‘शीघ्रम्’ इत्यर्थे किं पदं प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: क्षिप्रम्
ततः पर्वतशृङ्गाभस्तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः।
वनस्पतिगतः श्रीमान्व्याजहार शुभां गिरम्॥
Question 1.
खगोत्तमः कः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः
Question 2.
जटायोः तुण्डः कीदृशः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: तीक्ष्णः
Question 3.
कः व्याजहार?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः।
Question 4.
ततः कः शुभां गिरं व्याजहार?
Answer
Answer: ततः श्रीमान् पर्वतशृङ्गाभः, तीक्ष्णतुण्डः, वनस्पतिगतः खगोत्तमः शुभां गिरं व्याजहार।
Question 5.
तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः कः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः जटायुः आसीत्।
Question 6.
श्लोके ‘खगोत्तमः’ इति कर्तृपदस्य क्रियापदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: व्याजहार
Question 7.
श्लोके ‘वाणीम्’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: गिरम्
Question 8.
‘तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः’ अनयोः पदयोः विशेषणं किम् अत्र?
Answer
Answer: तीक्ष्णतुण्डः
Question 9.
श्लोके ‘अकथयत्’ इति पदस्य अर्थे किं पदं प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: व्याजहार।
निवर्तय मतिं नीचां परदाराभिमर्शनात्।
न तत्समाचरेद्धीरो यत्परोऽस्य विगर्हयेत्॥
Question 1.
रावणः कीदृशीं मतिं निवर्तयतु?
Answer
Answer: नीचाम्
Question 2.
जटायुः कस्याः अभिमर्शनात् निवर्तयितुं रावणं वदति?
Answer
Answer: परदारायाः
Question 3.
अयं श्लोकः कः वदति?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः।
Question 4.
धीरः किं न समाचरेत्?
Answer
Answer: धीरः तत् न समाचरेत् यत् परः अस्य विगर्हयेत्।
Question 5.
इदं श्लोकं कः कम् प्रति कथयति?
Answer
Answer: इदं श्लोकं जटायुः रावणम् प्रति कथयति।
Question 6.
अत्र ‘मतिं नीचाम्’ अनयोः पदयोः विशेषणं किमस्ति?
Answer
Answer: नीचाम्
Question 7.
‘यत्परोऽस्य विगर्हयेत्’ अस्मिन् वाक्ये क्रियापदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: विगर्हयेत्
Question 8.
श्लोके :प्रशंसेत्’ इति पदस्य कः विपर्ययः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: विगर्हयेत्
Question 9.
‘आचरणं कर्त्तव्यम्’ इत्यर्थे किं पदं प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: समाचरेत्।
वृद्धोऽहं त्वं युवा धन्वी सरथः कवची शरी।
न चाप्यादाय कुशली वैदेहीं मे गमिष्यसि॥
Question 1.
कः आत्मानं वृद्धः वदति?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः
Question 2.
कः सरथः अस्ति?
Answer
Answer: रावणः
Question 3.
युवा कः अस्ति?
Answer
Answer: रावणः।
Question 4.
कीदृशः रावणः वैदेहीं आदाय न गमिष्यति?
Answer
Answer: युवा, धन्वी, सरथः, कवची शरी च रावणः वैदेहीं आदाय न गमिष्यति।
Question 5.
रावणः कीदृशः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: रावणः युवा धन्वी सरथः कवची शरी आसीत्।
Question 6.
अस्मिन् श्लोके ‘वृद्धः’ पदस्य कः विपर्ययः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: युवा
Question 7.
श्लोके ‘त्वम्’ कर्तृपदस्य क्रियापदं किमस्ति?
Answer
Answer: गमिष्यसि
Question 8.
श्लोके ‘वाणधरः’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: शरी
Question 9.
अत्र ‘त्वम्’ पदं कस्मै प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: रावणाय।
तस्य तीक्ष्णनखाभ्यां तु चरणाभ्यां महाबलः।
चकार बहुधा गात्रे व्रणान्यतगसत्तमः॥
Question 1.
महाबलः कः आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः
Question 2.
कः पतगसत्तमः?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः
Question 3.
कुत्र व्रणान् अकरोत्?
Answer
Answer: गात्रे
Question 4.
महाबलः पतगसत्तमः जटायुः कथं किं च चकार?
Answer
Answer: महाबल: पतगसत्तमः जटायुः स्वतीक्ष्णनखाभ्यां चरणाभ्यां बहुधा व्रणान् चकार।
Question 5.
जटायुः कस्य गात्रे व्रणान् अकरोत्?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः रावणस्य गात्रे व्रणान् अकरोत्।
Question 6.
‘तीक्ष्णनखाभ्याम् चरणाभ्याम्’ अनयोः पदयोः अत्र विशेषणपदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: तीक्ष्णनखाभ्याम्
Question 7.
‘चकार बहुधा गात्रे व्रणान्पतगसत्तमः’। अस्मिन् वाक्ये क्रियापदं किम् वर्तते?
Answer
Answer: चकार।
Question 8.
श्लोके ‘रथविहीनः’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः अत्र आगतः?
Answer
Answer: पतगसत्तयः
Question 9.
‘शरीरे’ ‘इति अर्थे अत्र किं पदं आगतम्?
Answer
Answer: गात्रे।
ततोऽस्य सशरं चापं मुक्तामणिविभूषितम्।
चरणाभ्यां महातेजा बभञ्जास्य महद्धनुः॥
Question 1.
जटायुः कीदृशोऽस्मिन् श्लोके कथितः?
Answer
Answer: महातेजः
Question 2.
काभ्यां जटायुः महद् धनुः बभञ्ज?
Answer
Answer: चरणाभ्याम्
Question 3.
कः महातेजः अस्ति?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः
Question 4.
महातेजा जटायुः कीदृशं महद्धनुः स्वचरणाभ्यां बभञ्ज?
Answer
Answer: महातेजा जटायुः सशरं चापं मुक्तामणिविभूषितम् महद्धनुः स्वचरणाभ्यां बभञ्ज।
Question 5.
मुक्तामणिविभूषितम् किं आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: मुक्तामणिविभूषितम् महद्धनुः आसीत्
Question 6.
अत्र ‘महद्धनुः’ अनयोः पदयोः विशेषणं किम्?
Answer
Answer: महत्
Question 7.
श्लोके ‘अस्य’ पदं कस्मै आगतम्?
Answer
Answer: रावणाय
Question 8.
श्लोके ‘भग्नं कृतवान्’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: बभञ्ज
Question 9.
आसिन श्लोके ‘मुक्तामणिविभूषितम्’ अस्य पदस्य विशेष्यपदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: धनुः
स भग्नधन्वा विरथो हताश्वो हतसारथिः।
तलेनाभिजघानाशु जटायुं क्रोधमूर्छितः।
Question 1.
कः भग्नधन्वा अभवत्?
Answer
Answer: रावणः
Question 2.
रावणस्थ अश्वाः कीदृशाः अभवन्?
Answer
Answer: हताः
Question 3.
रावणः कम् अभिजघान?
Answer
Answer: जटायुम्
Question 4.
कीदृशः रावणः तलेन आशु जटायुम् अभिजघान?
Answer
Answer: क्रोधमूर्च्छितः रावणः तलेन आशु जटायुम् अभिजघान्।
Question 5.
रावणः कीदृशः अभवत्?
Answer
Answer: रावण हतसारिथः अभवत्।
Question 6.
‘शीघ्रम्’ इतस्य पदस्य की पर्यायः श्लोके आगतः?
Answer
Answer: आशु
Question 7.
श्लोके ‘सः’ इत्यस्य विशेष्यपदस्य विशेषणपदं किं वर्तते?
Answer
Answer: क्रोधमूर्च्छितः
Question 8.
‘मन्दम्’ इत्यस्य पदस्य कः विपर्ययः श्लोके आगतः?
Answer
Answer: आशु
Question 9.
श्लोके ‘तुरंगः’ इति पदस्य कः पर्यायः आगतः?
Answer
Answer: अश्वः
जटायुस्तमतिक्रम्य तुण्डेनास्य खगाधिपः।
वामबाहून्दश तदा व्यपाहरदरिन्दमः॥
Question 1.
श्लोके अरिन्दमः कः कथितः?
Answer
Answer: खगाधिपः (जटायुः)
Question 2.
रावणस्य कति बाहवः आसन्?
Answer
Answer: दश
Question 3.
रावणस्य वामबाहू कति आसीत्?
Answer
Answer: दश।
Question 4.
खगाधिपः अरिन्दमः जटायुः केन रावणस्य दशबाहून् व्यपाहरत्?
Answer
Answer: खगाधिपः अरिन्दमः जटायुः तुण्डेन रावणस्य दशबाहून् व्यपाहरत्।
Question 5.
जटायुः केन आक्रमणं अकरोत्?
Answer
Answer: जटायुः तुण्डेन आक्रमणम् करोत्?
Question 6.
‘तदा व्यपाहरदरिन्दमः’ अत्र श्लोके क्रियापदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: व्यपाहरत्
Question 7.
‘जटायुस्तमतिक्रम्य’ अत्र ‘तम्’ पदं कस्मै प्रयुक्तम्?
Answer
Answer: रावणाय
Question 8.
‘मुखेन’ इत्यस्य पदस्य कः पर्यायः श्लोके आगतः?
Answer
Answer: तुण्डेन
Question 9.
अत्र श्लोके ‘बाहून्’ इति पदस्य विशेषणपदं किम्?
Answer
Answer: दश।
अधोलिखित श्लोक अन्वयम् उचित पदक्रमेण पूरयत
सा तदा करुणा वाचो विलपन्ती सुदुःखिता।
वनस्पतिगतं गृधं ददर्शायतलोचना॥
अन्वयः- तदा करुणा (i) …………….. विलपन्ती सुदुःखिता (ii) ……………. .सा (सीता) (iii) ……………. गृध्रम् (iv) …………….. ।
मञ्जूषा- आयतलोचना, ददर्श, वाचः, वनस्पतिगतम् |
Answer
Answer:
(i) वाचः
(ii) आयतलोचना
(iii) वनस्पतिगतम्
(iv) ददर्श।
जटायो पश्य मामार्य ह्रियमाणामनाथवत्।
अनेन राक्षसेन्द्रेण करुणं पापकर्मणां॥
अन्वयः- आर्य (i) …………….. अनेन (ii) ………………… राक्षसेन्द्रेण (iii) ………………. ह्रियमाणाम् (iv) …………………… माम् पश्य।
मञ्जूषा- अनाथवत्, जटायो, सकरुणं, पापकर्मणा
Answer
Answer:
(i) जटायो
(ii) पापकर्मणा
(iii) अनाथवत्
(iv) सकरुणं।
तं शब्दमवसुप्तस्तु जटायुरथ शुश्रुवे।
निरीक्ष्य रावणं क्षिप्रं वैदेहीं च ददर्श सः॥
अन्वयः- अथ (i) …………….. जटायुः तु तं (ii) ………………. शुश्रुवे (iii) ……………….. निरीक्ष्य च सः क्षिप्रं (iv) ……………. ददर्श।
मञ्जूषा- रावणं, अवसुप्तः, वैदेहीम्, शब्दम्
Answer
Answer:
(i) अवसुप्तः
(ii) शब्दम्
(iii) रावणं
(iv) वैदेहीम्।
ततः पर्वतशृङ्गाभस्तीक्ष्णतुण्डः खगोत्तमः।
वनस्पतिगतः श्रीमान्व्याजहार शुमां गिरजम्॥
अन्वयः- ततः (i) …………… तीक्ष्णतुण्डः (ii) ………………… श्रीमान् (iii) ………………. (iv) …………………. व्यजहार।
मञ्जूषा- वनस्पतिगतः, पर्वतशृङ्गाभः, गिरम्, खगोत्तमः
Answer
Answer:
(i) पर्वतशृङ्गाभः
(ii) वनस्पतिगतः
(iii) खगोत्तमः
(iv) गिरम्।
निवर्तय मतिं नीचां परदाराभिमर्शनात्।
न तत्समाचारेद्वीरो यत्परोऽस्य विगर्हयेत्॥
अन्वयः- (त्वम्) परदारा (i) …………. (स्वां) नीचां (ii) ………….. निवर्तय, धीरः न (iii) …………….. समाचरेत् यत् परः (iv) …………………… विगर्हयेत्।
मञ्जूषा- अभिमर्शनात्, अस्य, तत्, मतिम्
Answer
Answer:
(i) अभिमर्शनात्
(ii) मतिम्
(iii) तत्
(iv) अस्य।
वृद्धोऽहं त्वं युवा धुन्वी सरथः कवची शरी।
न चाप्यादाय कुशली वैदेहीं ये गमिष्यासि॥
अन्वयः- अहं (i) ………………… त्वं युवा, धन्वी (ii) ……………….. कवची, शरी (चासि), न च (iii) ……………… मे वैदेहीम् आदाय अपि (iv) …………….. ।
मञ्जूषा- गमिष्यसि, कुशली, वृद्धः, सरथः।
Answer
Answer:
(i) वृद्धः
(ii) सरथः
(iii) कुशली
(iv) गमिष्यसि।
तस्य तीक्ष्णनखाभ्यां तु चरणाभ्यां महाबलः।
चकार बहुथा गात्रे व्रणान्यतगसन्तमः॥
अन्वयः- (ततः) पतगसत्तमः (i) ………………. (खगः) (ii) ……………. चरणाभ्याम् तस्य (iii) ………………… बहुधा (iv) ………….. चकार।
मञ्जूषा- गात्रे, महाबलः, व्रणान्, तीक्ष्णनखाभ्याम्
Answer
Answer:
(i) महाबलः
(ii) तीक्ष्णनखाभ्याम्
(iii) गात्रे
(iv) व्रणान्।
ततोऽस्य सशरं चापं मुक्तामणिविभूषितम्।
चरणाभ्यां महातेजा बभञ्जास्य महद्धनुः॥
अन्वयः- ततः अस्य (i) ………………. सशरं (ii) ……….. अस्य (iii) ………………. धनुः (iv) ………….
मञ्जूषा- चरणाभ्याम्, चापम्, महातेजा, मुक्तामणिविभूषितम्
Answer
Answer:
(i) महातेजा
(ii) चापम्
(iii) मुक्तामणिविभूषितम्
(iv) चरणाभ्याम्।
स भग्नधन्वा विरथो हताश्वो हतसारथिः।
तलेनाभिजघानाशु जटायुं क्रोधमूर्च्छितः॥
अन्वयः- (ततः) भग्नधन्वा (i) ………………. हताश्वः (ii) ………………… (सः) (iii) ……………. (iv) ……………….. अभिजघान।
मञ्जूषा- क्रोधमूर्च्छितः, विरथः, जटायुम्, हतसारथिः
Answer
Answer:
(i) विरथः
(ii) हतसारधिः
(iii) क्रोधमूच्छितः
(iv) जटायुम्
जटायुस्तमतिक्रम्य तुण्डेनास्य खगाधिपः।
वामबाहून्दश तदा व्यपाहरदरिन्दमः॥
अन्वयः- तदा (i) …………… अरिन्दमः जटायुः (ii) ………………. अरिन्दमः जटाय: (iii) ………………….. अतिक्रम्य अस्य (iv) ……………… व्यपाहरत्।
मञ्जूषा- खगाधिपः, बाहून्, तुण्डेन, वाम।
Answer
Answer:
(i) खगाधिपः
(ii) तुण्डेन
(iii) वाम
(iv) बाहून्
मञ्जूषायां दत्तानां पदानां सहायतया निम्न श्लोकस्य भावार्थं पूरयत
निवर्तय मतिं नीचां परदाराभिमर्शनात्।
न तत्समाचरेद्धीरो यत्परोऽस्य विगर्हयेत्॥
भावार्थ- हे विद्वन् रावण! त्वं परेषां स्त्रीहरणं रूपं (i) …………… स्व दुर्मतिं निवर्तय यतः (ii) ……………… जनाः तादृशाणि कर्माणि न (iii) ………………. यानि अन्यः जनः (iv) …………….. करोति।
मञ्जूषा- अपकीर्तिम्, पापात्, कुर्युः, धैर्यवन्तः।
Answer
Answer:
(i) पापात्
(ii) धैर्यवन्तः
(iii) कुर्युः
(iv) अपकीर्तिम्
निम्नलिखितानां ‘क’ वर्गीय पदानां ‘ख’ वर्गीय पदेषु पर्यायाः चीयन्ताम्
“क’ पदानि – ‘ख’ पर्यायाः
1. विलपन्ती – दृष्ट्वा
2. ददर्श – परस्त्रीस्पर्शात्
3. करुणा-वाचः – अकरोत्
4. आर्य – सबाण धनुः
5. करुणम् – धरायाम्
6. क्षिप्रम् – शोभायुक्तः
7. वैदेहीम् – अनेकशः
8. निरीक्ष्य – उत्तमाम्
9. अवसुप्तः – धैर्यवान्
10. खगोत्तमः – नीत्वा
11. श्रीमान् – पक्षीणाम् राजा
12. गिरम् – रोदन्ती
13. शुभाम् – सीताम्
14. मतिम् – दु:खम्
15. परदाराभिमर्शनात् – धनुर्धरः
16. धीरः – शरीरे
17. धन्वी – सदु:खवाण्याः
18. चकार – श्रेष्ठ/श्रीमान्
19. गात्रे – अत्रोटयत्
20. बहुधा – पक्षिषु श्रेष्ठः
21. सशरम्चापम् – रथहीनः
22. बभञ्ज – अपतत्
23. विरथः – बुद्धिम्
24. पपात – शीघ्रम्
25. भूवि – क्षिप्रम्
26. आदाय – आक्रमणं कृत्वा
27. आशु – वाणीम्
28. अतिक्रम्य – अनश्यत्
29. खगाधिपः – अपश्यत्
30. व्यपाहरत् – शयानः
Answer
Answer:
1. रोदन्ती
2. अपश्यत्
3. सदुःखवाण्याः
4. श्रेष्ठ/श्रीमान्
5. दु:खम्
6. शीघ्रम्
7. सीताम्
8. दृष्ट्वा
9. शयानः
10. पक्षिषुश्रेष्ठः
11. शोभायुक्तः
12. वाणीम्
13. उत्तमाम्
14. बुद्धिम्
15: परस्त्रीस्पर्शात्
16. धैर्यवान्
17. धनुर्धरः
18. अकरोत्
19. शरीरे
20. अनेकशः
21. सबाणधनुः
22. अनश्यत्
23. रथहीनः
24. अपतत्
25. धरायाम्
26. नीत्वा
27. क्षिप्रम्,
28. आक्रमणं कृत्वा
29. पक्षीणाम् राजा
30. अत्रोटयत्।
‘क’ स्तम्भे विशेषणानि ‘ख’ स्तम्भे विशेष्याणि दत्तानि। तानि समुचित योजयत
‘क’ स्तम्भः – ‘ख’ स्तम्भः
1. करुणा – सा
2. वनस्पतिगतम् – जटयो
3. सुदुःखिता – शब्दम्
4. आर्य – गिराम्
5. तम् – खगोत्तमः
6. शुभाम् – माम्
7. तीक्ष्णतुण्डः – मतिम्
8. करुणाम् – अहम्
9. नीचाम् – पतगसत्तमः
10. वृद्धः – चरणाभ्याम्
11. महाबलः – ग्रधम्
12. तीक्ष्णनखाभ्याम् – वाचः
Answer
Answer:
1. वाचः
2. गध्रम्
3. सा
4. जटयो
5. शब्दम्
6. गिराम्
7. खगोत्तमः
8. माम्
9. मतिम्
10. अहम्
11. पतगसत्तमः
12. चरणाभ्याम्
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit Chapter 10 जटायोः शौर्यम् with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 9 Sanskrit जटायोः शौर्यम् MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.