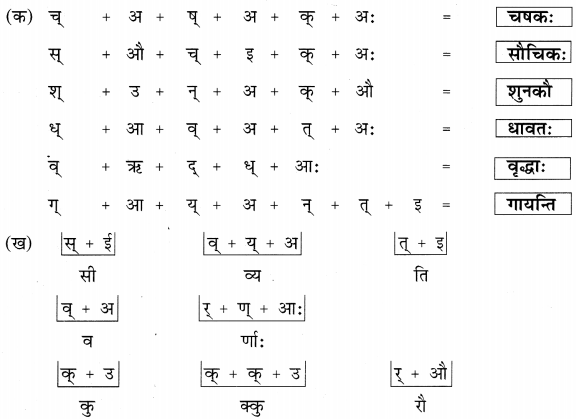
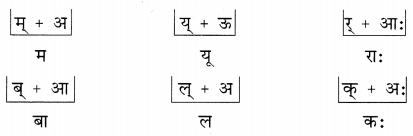
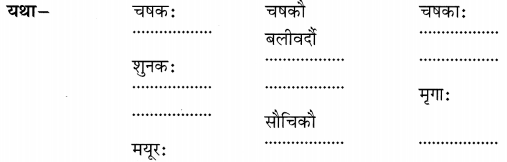
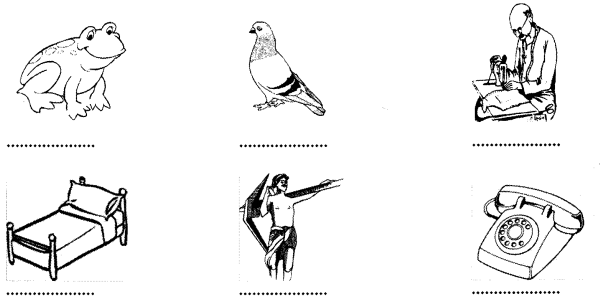
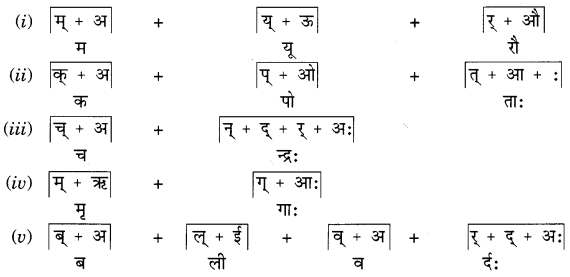
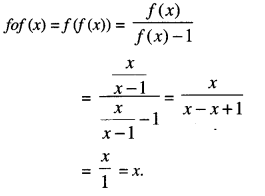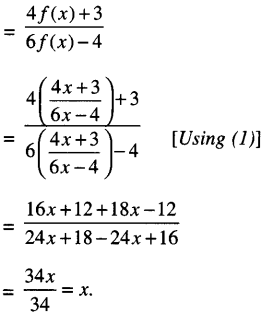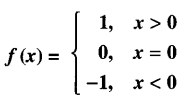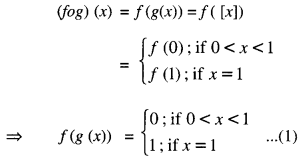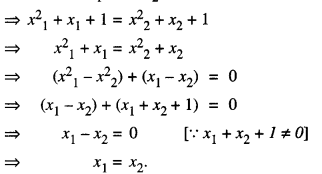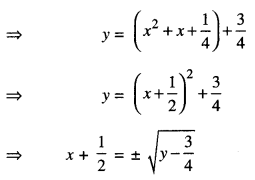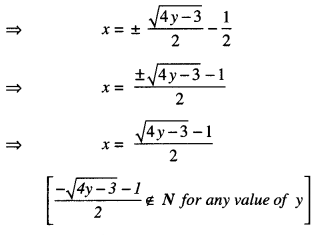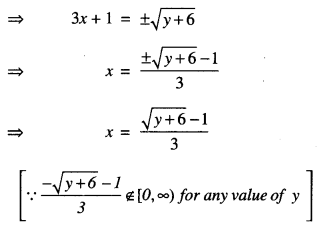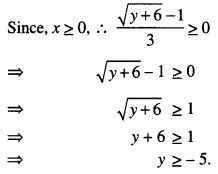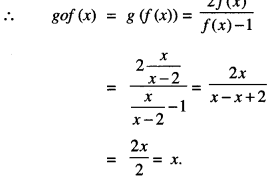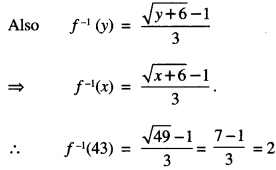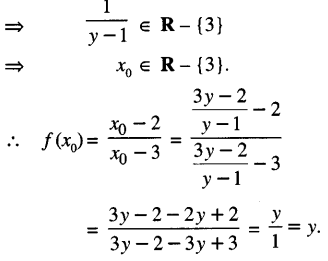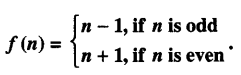Studying from CBSE Class 9 Sanskrit Notes helps students to prepare for the exam in a well-structured and organised way. Making NCERT Sanskrit Notes for Class 9 saves students time during revision as they don’t have to go through the entire textbook. In CBSE Notes, students find the summary of the complete chapters in a short and concise way. Students can refer to the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Sanskrit (Shemushi), to get the answers to the exercise questions.
NCERT Sanskrit Notes for Class 9
- भारतीवसन्तगीतिः Class 9 Notes
- स्वर्णकाकः Class 9 Notes
- गोदोहनम् Class 9 Notes
- कल्पतरूः Class 9 Notes
- सूक्तिमौक्तिकम् Class 9 Notes
- भ्रान्तो बालः Class 9 Notes
- प्रत्यभिज्ञानम् Class 9 Notes
- लौहतुला Class 9 Notes
- सिकतासेतुः Class 9 Notes
- जटायोः शौर्यम् Class 9 Notes
- पर्यावरणम् Class 9 Notes
- वाङ्मनःप्राणस्वरूपम् Class 9 Notes
We hope students have found these CBSE Class 9 Sanskrit Notes useful for their studies. If you have any queries related to NCERT Sanskrit Notes for Class 9, drop your questions below in the comment box.