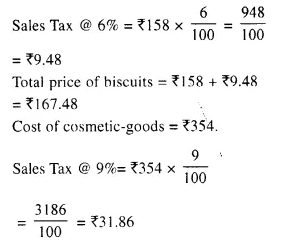
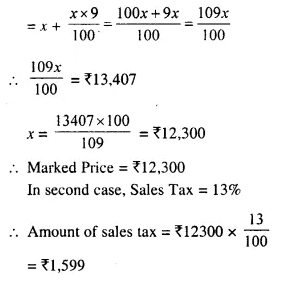
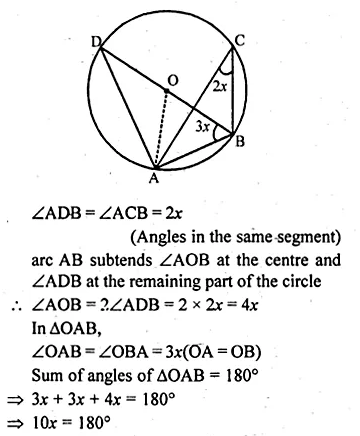
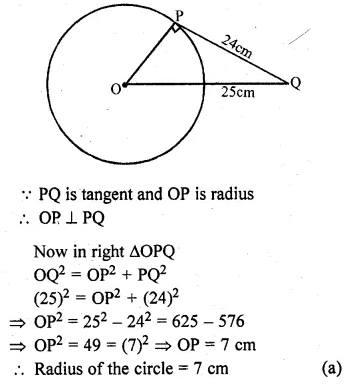
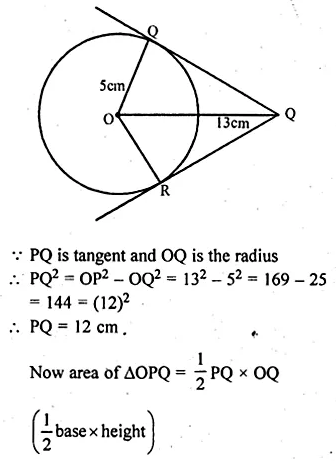
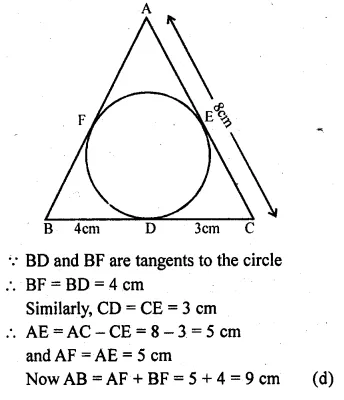
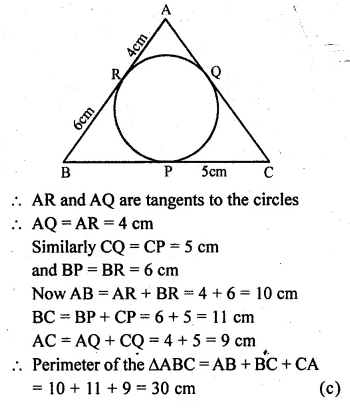
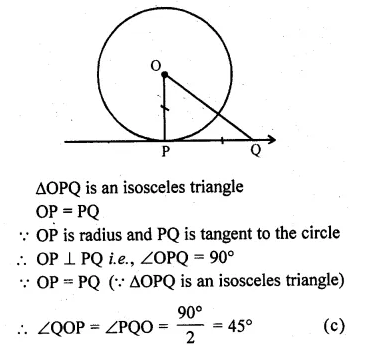
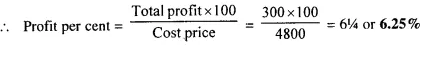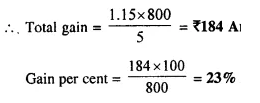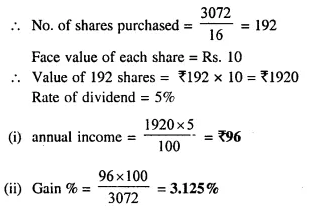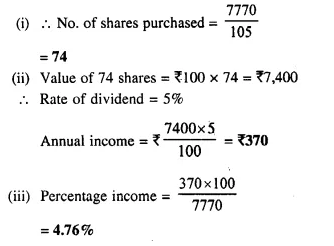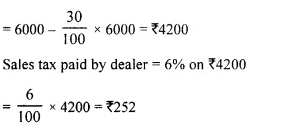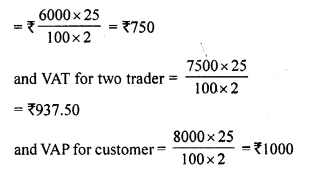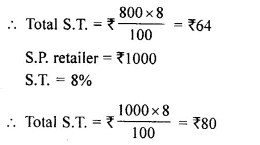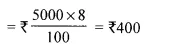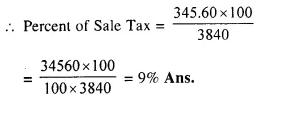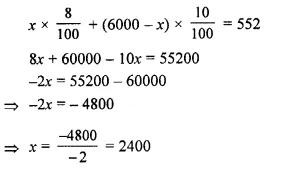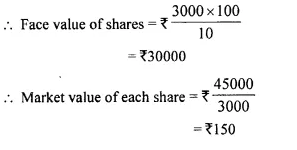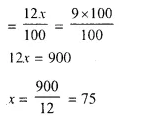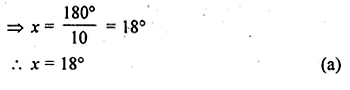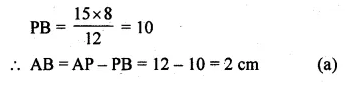Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions 2020-21 Edition
Learninsta.com provides step by step solutions for Selina Concise ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics. You can download the Selina Concise Mathematics ICSE Solutions for Class 10 with Free PDF download option. Selina Publishers Books of Concise Mathematics for Class 10 ICSE Solutions all questions are solved and explained by expert mathematic teachers as per ICSE board guidelines. By studying these Selina ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Maths you can easily get good marks in ICSE Class 10 Board Examinations.
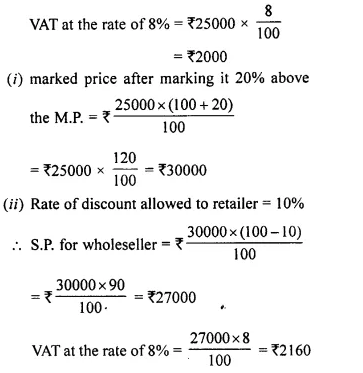
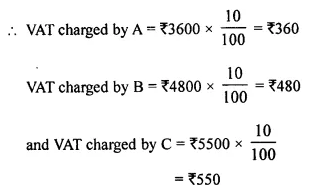
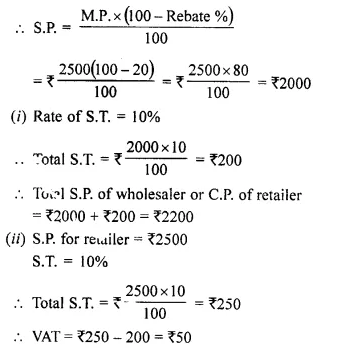
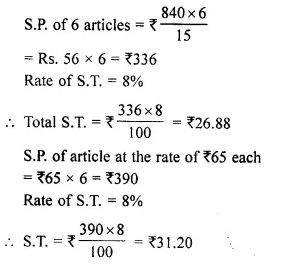
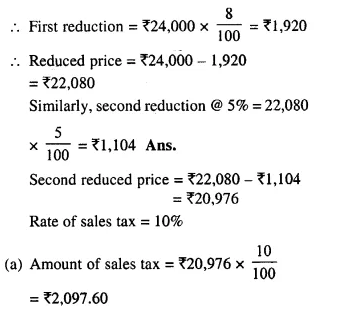
- Chapter 1 Value Added Tax Ex 1A Ex 1B Ex 1C
- Chapter 2 Banking (Recurring Deposit Accounts) Ex 2A Ex 2B
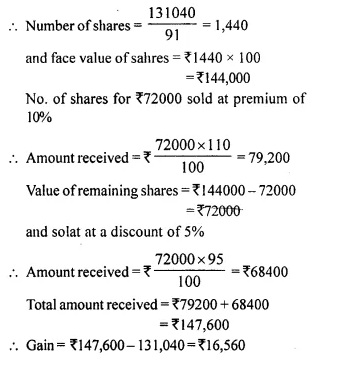
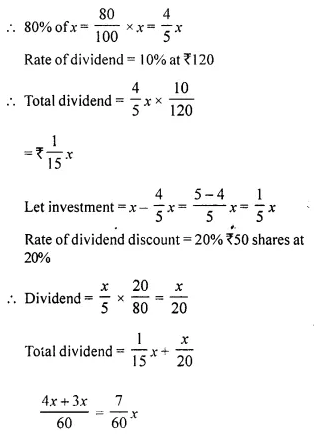
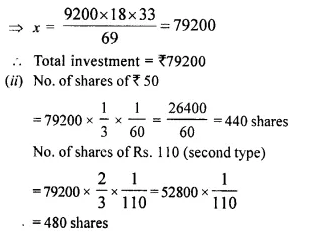
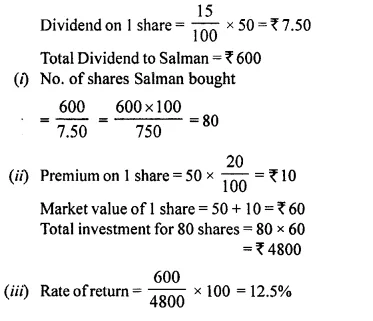
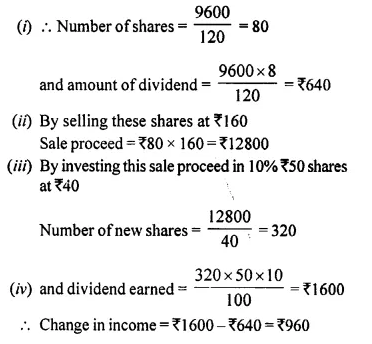
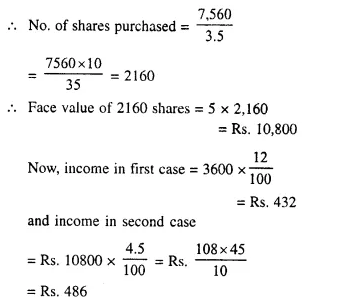
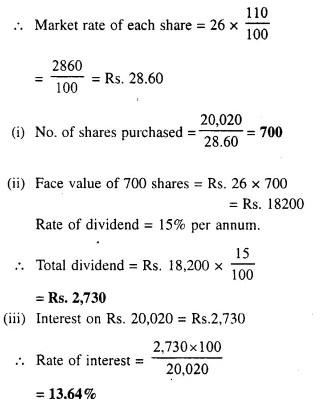
- Chapter 3 Shares and Dividend Ex 3A Ex 3B Ex 3C
- Chapter 4 Linear Inequations (In one variable) Ex 4A Ex 4B
- Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations Ex 5A Ex 5B Ex 5C Ex 5D
- Chapter 6 Solving Problems (Based on Quadratic Equations) Ex 6A Ex 6B Ex 6C Ex 6D Ex 6E
- Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion (Including Properties and Uses) Ex 7A Ex 7B Ex 7C Ex 7D
- Chapter 8 Remainder and Factor Theorems Ex 8A Ex 8B Ex 8C
- Chapter 9 Matrices Ex 9A Ex 9B Ex 9C Ex 9D
- Chapter 10 Arithmetic Progression Ex 10A Ex 10B Ex 10C Ex 10D Ex 10E Ex 10F
- Chapter 11 Geometric Progression Ex 11A Ex 11B Ex 11C Ex 11D Additional Questions
- Chapter 12 Reflection (In x-axis, y-axis, x=a, y=a and the origin ; Invariant Points) Ex 12A Ex 12B
- Chapter 13 Section and Mid-Point Formula Ex 13A Ex 13B Ex 13C
- Chapter 14 Equation of a Line Ex 14A Ex 14B Ex 14C Ex 14D Ex 14E
- Chapter 15 Similarity (With Applications to Maps and Models) Ex 15A Ex 15B Ex 15C Ex 15D Ex 15E
- Chapter 16 Loci (Locus and Its Constructions) Ex 16A Ex 16B
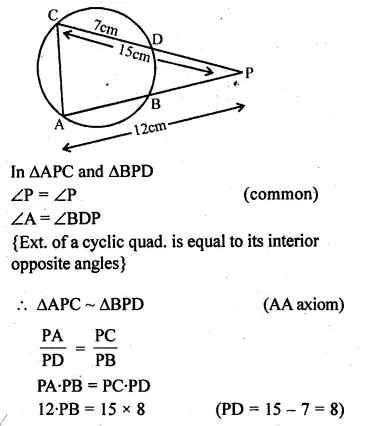
- Chapter 17 Circles Ex 17A Ex 17B Ex 17C
- Chapter 18 Tangents and Intersecting Chords Ex 18A Ex 18B Ex 18C
- Chapter 19 Constructions (Circles) Ex 19
- Chapter 20 Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)
- Chapter 21 Trigonometrical Identities (Including Trigonometrical Ratios of Complementary Angles and Use of Four Figure Trigonometrical Tables)
- Chapter 22 Heights and Distances Ex 22A Ex 22B Ex 22C
- Chapter 23 Graphical Representation (Histograms, Frequency Polygon and Ogives) Ex 23
- Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency (Mean, Median, Quartiles and Mode) Ex 24A Ex 24B Ex 24C Ex 24D Ex 24E
- Chapter 25 Probability Ex 25A Ex 25B Ex 25C
- Chapterwise Revision Exercises
Follow For More: