Students can also read MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources Questions with Answers hope will definitely help for your board exams. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-10-science-with-answers/
Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 16 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 10 Chapter 16 MCQs On Management of Natural Resources
Management Of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ Question 1.
Which one of the following is responsible for the ……………… water?
(a) Loss of vegetation cover
(b) Diversion for high water demanding crops
(c) Pollution from urban wastes
(d) Afforestation
Answer:
Class 10 Science Chapter 16 MCQ Question 2.
Which of the following are water-intensive crops?
(a) Wheat and rice
(b) Wheat and sugarcane
(c) Sugarcane and rice
(d) Wheat and gram
Answer:
(c) Sugarcane and rice.
Related Theory:
The construction of large dams leads to some problems.
People close to the source grow water-intensive crops like sugarcane and rice whereas people farther downstream do not get sufficient water to grow these crops. This causes social problems resulting due to unequal distribution of water. Other problems related to the construction of dams are economic and environmental problems.
Class 10 Science Chapter 16 MCQ With Answers Question 3.
Consider the following criticisms that are generally addressed when a new project is launched:
(I) Displacement of peasants and local tribals without compensation.
(II) Swallowing up large amount of public money without any benefits.
(Ill) Deforestation and loss of biodiversity. The criticisms about large dams in particular are:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (III)
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer:
Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ Question 4.
The Reni village of Garhwal is famous for:
(a) Monoculturesofpine,teakand eucalyptus.
(b) Chipko Movement.
(c) Extensive biodiversity.
(d) Participation of local people inefficient management of forests.
Answer:
![]()
Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ Question 5.
Which one of the following stakeholders of forests causes the maximum damage to forest?
(a) People who live in or around the forest
(b) The forest department of the government
(c) The wildlife and native enthusiasts
(d) The industrialists
Answer:
(d) The Industrialist
Ch 16 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 6.
Several factories were pouring their wastes in rivers A and B. Water samples were collected from these two rivers. It was observed that sample collected from river A was acidic while that of river B was basic. The factories located near A and B are:
(a) Soaps and detergents factories near A and alcohol distillery near B.
(b) Soaps and detergents factories near B and alcohol distillery near A.
(c) Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near A and soaps and detergents factories near B.
(d) Lead storage battery manufacturing factories near B and soaps and detergents factories near A.
Answer:
Chapter 16 Science Class 10 MCQ Question 7.
A diagram of traditional water harvesting system is given below:
The statement which defines the system and its parts is:

(a) This is an ideal setting of the Khadin system and A = Catchment area; B = Saline area and C = Shallow dug well:
(b) This is an ideal setting of the Shallow dug well system and A = Catchment area; B = Saline area and C = Khadin.
(c) This is an ideal setting of Catchment area and A = Khadin, B = Saline area, and C = Shallow dug well.
(d) This is showing the Saline area and A = Catchment area; B = Khadin and C = Shallow dug well.
Answer:
(a) This is an ideal setting of the Khadin system and:
A = catchment area
B = Saline area
C = Shallow dug well
Explanation: Khadin is a traditional rainwater haversting system in Rajasthan. The main feature of Khadin system of rainwater harvesting is a very long earthen embankment called ‘bund’ built across the lower edge of the sloping farmland. The rainwater from catchment area flows down the slopes and stopped by the bund to form a reservoir the excess water flows through pathwalls (made for this purpose) and filLs the shallow well dug behind the bund. This area is subsequently used for growing crops.
Management Of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ Questions And Answers Question 8.
The major ill effect of monoculture practice in forests is on the:
(a) biodiversity which faces large destruction
(b) local people whose basic needs can no longer be met from such forests
(c) industries
(d) forest department
Answer:
![]()
Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources Class 10 MCQ With Answers Question 9.
Which of the following are not responsible for failure to sustain water availability underground:
(I) Afforestation
(II) Loss of vegetation cover
(III) Diversion for high water demanding crops
(IV) Pollution from industrial effluents and urban wastes.
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) Both (I) and (III)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Question 10.
Which among the following factors help in confirming the contamination of river water?
(I) Measurement of pH of river water
(II) Existence of diverse life forms in river water
(III) Presence of chlorine in river water
(IV) Presence of coliform bacteria in river water
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) (I) and (III)
(b) (II) and (III)
(c) (I) and (IV)
(d) (II) and (IV)
Management Of Natural Resources MCQ Question 11.
Choose the correct statements among the following that are a consequence of raising the height of dams
(I) Deforestation and the loss of biological diversity.
(II) Displacement of large number of peasantsand tribals without adequate compensation or rehabilitation
(III) Loss of valuable agricultural land.
(IV) Generation of permanent employment for local people
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (IV)
(c) (I), (II) and (III)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
MCQ On Management Of Natural Resources Class 10 Question 12.
Which of these practices can be adopted to save the environment?
(a) Refuse the use of single-use plastic bags
(b) Reduce the use of paper bags
(c) Recycle single-use bags
(d) Reuse waste food
Answer:
(a) Refuse the use of single-use plastic bags Explanation: The 5R’s to save the environment are: Refuse, Reduce, Reuse, repurpose and Recycle. The best way to save the environment is by refusing to use products that may harm the environment.
MCQ Questions For Class 10 Science Management Of Natural Resources Question 13.
How does switching off unnecessary electrical appliances help the environment?
(a) It generates electricity when switched off
(b) It reduces wastage of energy
(c) It recycles the amount of energy used
(d) It increases the efficiency of the electrical appliances
Answer:
![]()
MCQ On Management Of Natural Resources Question 14.
Which of these is an example of sustainable development in order to conserve natural resources for the future generation?
(a) Cleaning water resources
(b) Finding additional fuel reserves
(c) Clearing forests to set up new industries
(d) Planning for safe disposal of wastes after mining
Answer:
Class 10 Management Of Natural Resources MCQ Question 15.
Which of the following industries would be identified as a stakeholder involved in a forest?
(a) That manufacture ceramic products using clay
(b) That make papers using wood products
(c) That make clothes using synthetic materials
(d) That manufacture device that generate electricity using solar energy
Answer:
Class 10 Science Ch 16 MCQ Question 16.
Which of the following practices will help to conserve the forest?
(a) Deforestation
(b) Banning deforestation
(c) Increased use of firewood by local people
(d) Increased use of timber by industries
Answer:
MCQ On Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources Question 17.
Which of these explains the use of dams?
(a) To replenish underground water resources
(b) To produce steady supply of water in hilly regions
(c) To provide irrigation and generate electricity
(d) To provide water for conservation of biological diversity
Answer:
Natural Resources MCQ Class 10 Question 18.
Which of the following steps should be adopted in order to save the environment?
(a) Replace coal to firewood for cooking food
(b) Replace petroleum to coal in vehicles for transportation
(c) Replace thermal power with solar power to generate electricity
(d) Replace the use of coal to petroleum for melting metals in a furnace
Answer:
Assertion Reasoning questions Class 10 Science Chapter 16
For the following questions, two statements are given – one labeled Assertion (A) and other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
MCQ Questions On Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources Question 19.
Assertion (A): Sustainable development implies a change in all aspects of life.
Reason (R): Economic development is linked to environmental conservation.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(Competency Based Questions (CBQs))
Question 1.
Find out about the international norms to regulate the emission of carbon dioxide. Have a discussion in class about how we can contribute towards meeting those norms.
There are a number of organisations that seek to spread awareness about our environment and promote activities and attitudes that lead to the conservation of our environment and natural resources. Find out about the organizations) active in your neighbourhood/ village/town/city.
(A) Which of the following greenhouses gas is present in very large quantities?
(a) Ozone
(b) Methane
(c) Carbon dioxide
(d) Propane
Answer:
(B) Select the incorrect statement from the statements given below:
(a) Increased emission of greenhouse gases is a natural process.
(b) Life on earth is possible due to presence of greenhouse gases.
(c) Greenhouse effect is a natural process that maintains earth’s temperature.
(d) More is the emission of greenhouse gases, more is the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere.
Answer:
(a) Increased emission of greenhouse gases is a natural process.

Explanation: The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the Sun’s energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases include water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and some artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth. This process maintains the Earth’s temperature at around 33 degrees Celsius warmer than it would otherwise be, allowing life on Earth to exist.
The problem we now face is that human activities – particularly burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), agriculture and land clearing – are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases. This is the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is contributing to warming of the Earth.
(C) Which of the following are the causes of increased emission of carbon dioxide in India?
(I) Burning of coal for power generation
(II) Increased vegetation cover during monsoon.
(III) Burning of agricultural wastes
(IV) Burning of fossil fuels for transportation
(a) Only (I)
(b) Only (II)
(c) (I), (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) Which one of the following cannot be a goal or an international norm to regulate the emission of carbon dioxide:
(a) To limit and reduce greenhouse gases (GHG) emissions in accordance with agreed individual targets.
(b) To monitor actual emission of greenhouse gases.
(c) To invest in technological development in the developing countries.
(d) To assist countries in adapting to the adverse effects of climate change.
Answer:
(c) To invest in technological development in the developing countries.
Explanation: The Kyoto Protocol is an international treaty which extends the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part one) global warming is occurring and (part two) that human-made CO2 emissions are driving it. Although it has scope of assisting countries in adapting to the adverse effects of climate change, it does not have scope for investing in technological development in the developing countries.
(E) One of the ways individuals can contribute towards conservation of environment and natural resources is:
(a) Recycling, reusing, and composting
(b) Making better transport choices
(c) Reducing your electricity usage
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation: Individuals can contribute towards conservation of the environment and natural resources by reusing, recycling of waste materials, composting of organic wastes, making better transport choices and using public transport as much as possible and reducing electricity usage.
![]()
Question 2.
Make a list of forest produce that you use. What do you think a person living near a forest would use? What do you think a person living in a forest would use? Discuss with your classmates how these needs differ or do not differ and the reasons for the same. Find out about any two forest produce that are the basis for an industry. Discuss whether this industry is sustainable in the long run. Or do we need to control our consumption of these products?
(A) Which of the following are not products derived directly or indirectly from forest produce used by most urban people?
(a) Paper
(b) Natural gas
(c) Timber
(d) Dyes
Answer:
(b) Natural gas
Explanation: Forests give us a lot of useful products such as paper, timber, dyes, medicines, fruits, spices, dyes and oils.
Natural gas on the other hand is a fossil fuel formed from the plants, animals, and microorganisms that lived millions of years ago.
(B) The table below lists the various stakeholders in forests. Select the row containing incorrect information:
| Stakeholders | Justification |
| (a) People who live in or around forests | Dependent on forest produce for various aspects of their life |
| (b) Forest Department of the Government | Owns land and controls the resources from forest |
| (c) Industrialists | Dependent on forests In any one area as they use various forest produce |
| (d) wild life and nature enthusiasts forests. | Want to conserve nature in its pristine form |
Answer:
(C) Which of the following forest produce are used by the persons Living in a forest?
(I) Firewood and small. timber
(II) Bamboo
(III) Various agricuLtural. Implements made of Iron and steel.
(IV) Fruits, nuts and medicines
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (IV)
(c) (II), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(D) For which of the following needs are people Living near forests dependent on forests?
(a) Fodder fruit and agricultural implements
(b) Fuel, fodder and monoculture
(c) Fuel, fodder and cuLtivation
(d) Minerals, fodder and fuel
Answer:
(E) We should conserve forests because:
(a) Forest provide us with oxygen and they cause rainfall.
(b) Forest prevents soil erosion.
(c) Various forest products are used as raw materials in industries.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation: Conservation of forests is the need of the jour as forests provide us with oxygen, they prevent soil erosion, various industries are dependent upon forests for their raw materials and medicines.
![]()
Question 3.
Usually we put recycling on top of everything, but today on the 5 R process, it comes in last. Five actions should respectively be taken if possible before recycling any products. These R’s include: refuse, reduce, reuse, repurpose and finally, recycle. This is an important methodology for businesses to follow to ensure they can reduce waste and boost their recycling efforts. This ultimately lessens the amount of waste that will end up in landfill and will optimise your recycling programs.
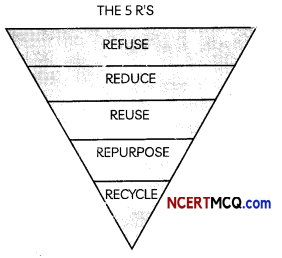
(A) The main items that can be recycled are:
(I) Lead-Acid Batteries
(II) Plastic (PET) bottles
(III) Egg cartons
(IV) Steel cans
Select the correct options from below:
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (1), (U) and (III)
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (II) and (IV)
Explanation: Among the items that can be recycled are lead acid batteries, plastic bottles, steel and aluminium cans, glass bottles, paper, cardboard boxes. Among the items that cannot be recycled are egg cartons, plastic shopping bags, drinking cups, plastic utensils and broken or sharp glass.
(B) The table below gives the meaning of the terms Reuse, reduce and reuse.
Select the row containing the correct meaning of the three terms
| Refuse | Reduce | Reuse |
| (a) Use less of something | Use something over and over again | Make something into something new |
| (b) Make something into something new | Use less of something | Use something over and over again |
| (c) Say no to things that can harm environment | Use less of something | Use something over and over again. |
| (d) Say no to things that can harm environment | Use something over and over again. | Use less of something |
Answer:
(C) How can organic waste be appropriately managed?
(a) Composting
(b) Recycling
(c) Burning
(d) Melting
Answer:
(D) Look at the figure below and suggest which out of the five ‘R’s is represented below:

(a) Reuse, as plastic bottle is being used again.
(b) Repurpose, as the plastic bottle is being used for a different purpose.
(c) Reduce, as less of the thing is being used.
(d) Recycle, as plastic bottle is being recycled.
Answer:
(E) The doorstep delivery of milk in glass bottles is an example of:
(a) Reduce
(b) Reuse
(c) Repurpose
(d) Recycle
Answer:
(b) Reuse
Explanation: Reuse is the action or practice of using an item by taking, but not reprocessing, previously used items and it helps save time, money, energy and resources. In the doorstep delivery of milk in glass bottles, the delivery person gives a bottle containing fresh milk and the empty bottle is returned to him the next day. In this way, the glass bottles are reused.
Question 4.
Fossil fuels Like coal, oil, and natural gas present environmental problems starting with their extraction and going all the wag through to their use. They are all different in their properties and uses, but they have some similarities.We use fossil fuels for most of our energy needs today. Coal, natural gas, and oil accounted for 87 percent of global primary energy consumption. Burning coal for electricity is in decline, while the use of natural gas, solar and wind power are on the rise.

Complete combustion of coal and petroleum:
(I) increases air pollution
(II) increases effciency of machines.
(III) reduces global warming.
(IV) produce poisonous gases.
The correct option is:
(a) (I) and (II)
(b) (II) and (IV)
(c) (II) and (III)
(d) (III) and (IV)
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
Half of Delhi’s school-going population (some 2.2 million children) suffers from some or the other form of irreversible lung damage from poor air quality in the city. Research is now showing that pollution can weaken a child’s immune system and increase the risk of cancer, epilepsy, diabetes and even adult- onset diseases like multiple sclerosis. In adults, poor air quality causes one’s lung capacity to decrease, more headaches, sore throats, coughs, fatigue, even lung cancer.
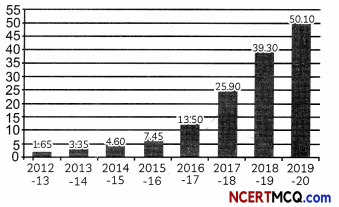
In 2017, air pollution was the fifth-highest mortality risk factor globally – linked to 4.9 million deaths and 147 million years of healthy life otherwise lost. Reducing global air pollution to levels recommended by the WHO would increase life expectancy worldwide as much as eradicating breast and lung cancer would, according to a Quartz report from earlier this year. Going by National Health Profile of India 2015 report, there were 3.5 million reported cases of acute respiratory infection nationwide last year – a 1,40,000 increase on the previous year, and a 30 percent increase since 2010. The pie chart below shows the average levels of fine particulate matter having diameter less than 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5) in Delhi in the month of Nov 2020.
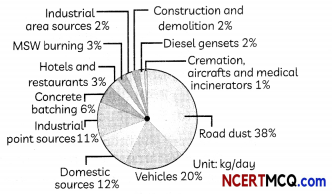
(A) According to the pie chart shown, the major contributors responsible for more than 80% of PM2.5 in air are:
(a) Road dust, Construction and demolition, hotels and restaurants, Industrial point sources
(b) Road dust, domestic sources, Diesel gensets, Industrial point sources
(c) Road dust, vehicles, Construction and demolition and Industrial point sources
(d) Road dust, vehicles, domestic sources and Industrial point sources
Answer:
(B) The major air pollutants are:
(I) Nitrogen dioxide
(II) Sulphur
(III) Particulate matter
(IV) Ozone
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) (I), (III) and (IV)
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
Answer:
(c) (I), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: The major air pollutants are: Ozone (O3), Nitrogen dioxide, Carbon Monoxide (CO), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) and Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5)
(C) Which of the following element is not present in coal and petroleum:
(a) Silicon
(b) Carbon
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(a) Silicon
Explanation: Coal and petroleum have been formed from biomass and contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulphur.
(D) The number of years our known petroleum and coal reserves will last as per the present estimates is given in the table below.
Select the row containing the correct values:
| Number of years our known petroleum reserves will last | Number of years our known coal reserves will last |
| (a) 100 | 300 |
| (b) 40 | 200 |
| (c) 400 | 300 |
| (d) 200 | 40 |
Answer:
(b) Number of years our known petroleum reserve will last: 40; Number of years our known coal reserves will last: 200.
Explanation: As per the present estimates, the number of years our known petroleum and coaL reserves will Last are 40 years and 200 years respectively. This estimate is based on the present rate of usage of these fuels.
(E) Select the incorrect option:
The main reason for using coal and petroleum judiciously is:
(a) These lead to global warming
(b) These pollute our environment
(c) These are not limited
(d) These are not inexhaustible
Answer:
Question 6.
When Sukanya visited her maternal grandparents during her school vacations, she observed that both her grandparents would switch off lights and fans when not in use. They would in fact encourage them also to use natural light as much as possible.
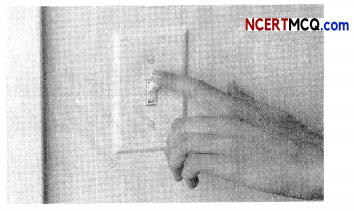
Switching off unnecessary lights and fans and repairing leaking taps correctly defines which term of 5R’s?
(a) Recycle
(b) Reuse
(c) Repurpose
(d) Reduce
Answer:
(d) Reduce

Explanation: We can reduce the voltage of electricity by switching off unnecessary lights and We can reduce the voltage of water by repairing the leaking taps.
- We can collect plastic, paper, glass and metal items and recycle these materials to make required things.
- Reuse means to use the same things again eq. Plastic bottles of same or pickles can be used for storing things in the kitchen.
- Repurpose: The object which can no more be used for the original purpose e.g. cups with broken handles can be used to grow small plants and as feeding vessels for birds.
- Refuse to take the things people offer you that you don’t need or are harmful to the environment, e.g., take your own cloth or jute bag for shopping and refuse to accept plastic bag.
![]()
Question 7.
Poachers, traffickers and highly-organised criminal gangs decimate already endangered wildlife species, reaping a deadly harvest in the pursuit of profits. To address the problem, in 1973 the United Nations General Assembly signed the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), aimed at stemming the illegal trade in wild animals and rare commodities. UN World Wildlife Day is held each year on the anniversary of the signing. The day helps raise awareness of the many challenges facing the world’s wild animals and plants and the efforts to stamp out illegal trading.
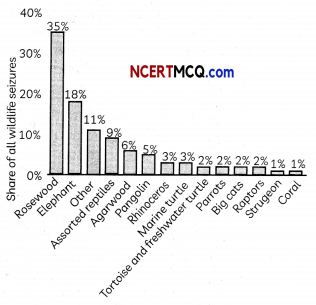
(A) The main objective of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) is that it:
(I) Ensures that some species entering into international trade is threatened with extinction.
(II) Promotes the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity
(III) Contributes to tangible benefits for poachers
(IV) Stops over exploitation of many endangered species
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (II) and (III)
(c) Both (III) and (IV)
(d) Both (II) and (IV)
Answer:
(B) Which of the following is a step taken by the government to protect the wildlife?
(a) Various Project to protect animals in forest
(b) Proper food facilities to the animals in forest
(c) Deforestation to provide space for urbanization
(d) Control the population of animals in forest
Answer:
(a) Various Project to protect animals in forest
Explanation: The Government of India has taken various steps to conserve the wildlife. The major among them is establishing of various projects in order to protect the wildlife. Some of the projects are Project Tiger, Project Rhino, Project Great Indian Bustard and many more.
(C) Which of the following is the most important human activity Leading to the extinction of wildlife?
(a) Increased pollution of air, water and land
(b) Alteration and destruction of the natural habitats.
(c) Hunting of wild animals for valuable wildlife products
(d) Afforestation
Answer:
(D) Which of the following will not be a result of uncovering half of the forest covering of the earth?
(a) Some wildlife species will become extinct
(b) Soil erosion will increase
(c) It will lead to climatic changes
(d) Forest dwelling people will be benefited.
Answer:
(E) Which of the following is the name given to a scheme to protect and conserve bio-diversity?
(a) Biosphere
(b) Biotechnology
(c) Bio-reserve
(d) Bio-ecology
Answer:
(c) Bio-reserve
Explanation: Bio-reserve is a scheme to protect and conserve bio-diversity. The central area preserves the flora and fauna. The surrounding zone is utilized for research and experiments regarding conservation of bio-diversity.
Question 8.
The first phase of the Ganga action plan was inaugurated by late Rajiv Gandhi at Rajendra prasad ghat of Banaras. The National Protection Agency was constituted for its implementation. During the first phase of Ganga Action Plan 256 schemes of 462 crores were undertaken in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal. Special stations have been created to check the quality of water. The experts from Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited and National Environment Engineering Research Institute were appointed to check the quality of the water.

The main purpose of the ‘Ganga Action Plan’ (GAP) project launched by the government in 1985 was to:
(a) Build new dams over the Ganga river
(b) Make its water pollution free
(c) Utilize the river water for irrigation purposes
(d) Promote the growth of water sports in the river
Answer:
![]()
Question 9.
India’s water situation is dire. There are no two ways around it. Around 2,00,000 people die every year due to inadequate access to safe water, 21 major cities will run out of groundwater by 2020, 75% of households do not have access to drinking water at home and 70% of India’s water is contaminated. Plus the problem is only going to get more severe, as the population grows, while water becomes even more scarce. It should be evident, then that India is facing a water crisis, one that whoever comes to power would be expected to help resolve.
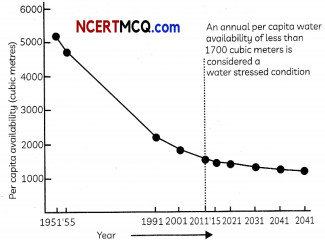
(A) The main causes of contamination of water are:
(I) Burning of fossil fuels
(II) Dissolved oxygen
(III) Untreated sewage
(IV) Agricultural runoff
(a) Both (I) and (II)
(b) Both (III) and (IV)
(c) (I), (II) and (IV)
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Answer:
(d) (I), (III) and (IV)
Explanation: Canals, rivers and lakes in India often serve as dumping grounds for sewage, solid and liquid wastes. Water pollution is a major environmental issue in India. The largest source of water pollution in India is untreated sewage. Other sources is of pollution include agricultural runoff and unregulated small-scale industry. Burning of fossil fuels releases harmful gases like carbon dioxide, oxides of suLphur and nitrogen which cause acid rain and pollute the water bodies. Dissolved oxygen, when released in water, helps aquatic plants and animals for respiration. So it does not cause pollution, but the removal of dissolved oxygen causes pollution.
(B) Which of the following is not the main cause of water scarcity in India?
(a) Climate change
(b) River pollution
(c) Natural disasters
(d) Groundwater extraction and irrigation
Answer:
(C) The main purpose of water harvesting is to:
(a) Use surface water for irrigation.
(b) Recharge ground water.
(c) Collect water directly for domestic use
(d) Refill lake water and other water bodies.
Answer:
(D) The aims of Watershed management is:
(a) To increase the biomass production.
(b) To develop primary resources of land and water
(c) To produce secondary resources of plants and animals.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Explanation: Through watershed manage¬ment, one can implement plans, projects that sustain and enhance watershed functions. Watershed functions include capturing, storing and recharging groundwater, filtering out water pollutants, and secure release of rainwater to avoid floods during heavy rainfalls. Watershed management emphasises scientific soil and water conservation in order to increase the biomass production. The aim is to develop primary resources of land and water, to produce secondary resources of plants and animals for use in a manner which will not cause ecological imbalance.
(E) Some of the ancient water harvesting alongwith states where these were built are listed in the table below. Select the row containing incorrect information:
| Ancient water harvesting | State where built |
| (a) Khadins | Uttar Pradesh |
| (b) Bandharas | Maharashtra |
| (c) Bundhis | Madhya Pradesh |
| (d) Ahars | Bihar |
Answer:
(a) Ancient water hervesting: Khadins State where buiLt: Utter Pradesh
Explanation: Water harvesting is an age-old concept in India. Khadins, tanks and nadis in Rajasthan, bandharas and tals in Maharashtra, bundhis in Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, ahars and pynes in Bihar, kulhs in Himachal Pradesh, ponds in the Kandi belt of Jammu region, and eris (tanks) in Tamil Nadu, surangams in Kerala, and kattas in Karnataka are some of the ancient water harvestings, including water conveyance, structures still in use today.
![]()
Question 10.
Groundwater, which can be used by people, constitutes only 0.8% of total water voLume while the rest Lies in the form of oceans and snow on mountains and glaciers. A growing population combined with huge demand of water for development purposes has put excessive stress on available water resources. The uneven distribution of water resources, artificial modification of natural flow of rivers and human abuse are the main reasons for the looming water crisis in India.The situation of groundwater is critical in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan. These states need urgent attention from the government and the implementation of proper water management techniques to prevent severe water crises.

In addition to low rainfall, what are the other reasons for non-availability of water in arid and semi-arid zones of our country?
Answer:
The reasons for the non-availability of water in arid and semi-arid zones of our country are:
- No proper rain water harvesting systems in these areas.
- Pollution of water due to mixing of industrial and domestic waste making it unfit for drinking purposes.
Question 11.
The Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is located in the state of Telangana. It is India’s largest Masonry Dams built till date. It is the largest manmade lake in the world. It has 26 gates and is 1.55 km in length. It is situated on the river Krishna.

Construction of a dam on a river often results in the reduction of fish catch. Why is it so?
Answer:
Fish populations are highly dependent upon the characteristics of their aquatic habitat which supports all their biological functions. The water stored by constructing dams is stagnant water whereas fishes breed in clean and running water due to which their population decreases and fish catch also reduces.
Question 12.
Sanjay visited a National park with his parents to observe wild life. As they were entered the forest area, they observed logs of teak wood being transported from the forest in big trucks by a contractor.
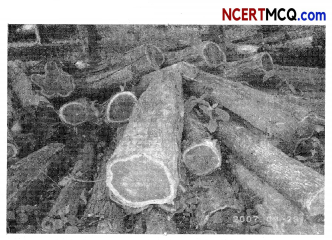
Will the local people also behave in a similar manner? Justify your answer.
Answer:
No, the local people will not behave in this manner. The reason is that the local people are dependent on the forest for their day to day sustenance since generations whereas for the contractor it is just a means of earning his livelihood. Once all the trees of a particular forest have been cut, the contractor will simply move on to a new forest.
![]()
Question 13.
You must be aware that the Indus valley civilization had been famous for its irrigation and water harvesting techniques and thus when it comes to Rain Water Harvesting, India has its pride. But why is it that despite having such an elaborate system and knowledge, the country is facing such extreme water shortage conditions? Bavaria are unique stepwells that were once a part of the ancient networks of water storage in the cities of Rajasthan. The irtle rain that the region received would be diverted to man-made tanks through canals built on the hilly outskirts of cities.The water would then percolate into the ground. raising the water table and recharging a deep and intricate network of aquifers. To minimise water loss through evaporation, a series of layered steps were built around the reservoirs to narrow and deepen the wells.

What are the advantages of water harvesting techniques?
Answer:
Rainwater harvesting is the process of accumulating and storing rainwater for on-site use instead of allowing it to run off Rainwater provides an independent and free water supply that offers several ways the water can be used. It reduces soil erosion arid flooding, reduces demand an ground warer. makes water available for non-drinking purposes and helps in plant growth
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Make a list of few industries that are dependent on forest products.
Answer:
Forest product-dependent industries are: Timber, paper, lac and sports equipment industries.
Question 2.
Is Water conservation necessary? Give reason.
Answer:
Water conservation is necessary as availability of water on Earth is more than enough for all but due to its uneven distribution, wide seasonal fluctuations in rainfall and majority of available water being saline, conservation is highly important for future generations.
![]()
Question 3.
How is the increase in demand for energy affecting atmosphere?
Answer:
Overconsumption and increase in demand of fossil fuels releases a huge amount of polluting gases into the atmosphere, which in turn causes global warming and also produces acid rain.