Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have Provided Tissues Class 9 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-9-science-with-answers/
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Class 9 Science Biology Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers
Biology Class 9 Chapter 6 MCQs On Tissues
Tissues Class 9 MCQ Chapter 6 Question 1.
Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
Answer
Answer: (b) Sclerenchyma
Tissue Class 9 MCQ Chapter 6 Question 2.
Find out incorrect sentence.
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces.
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles.
Answer
Answer: (c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 MCQ Question 3.
Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
Answer
Answer: (b) lateral meristem
Class 9 Tissue MCQ Chapter 6 Question 4.
Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Answer
Answer: (b) Companion cells
Tissue MCQ Class 9 Chapter 6 Question 5.
Intestine absorbs the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Spindle fibres
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Answer
Answer: (b) Columnar epithelium
Tissues Class 9 MCQ With Answers Question 6.
A person met with an accident in which two long bones of the hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be the possible reason?
(a) Tendon break
(b) Break of skeletal muscle
(c) Ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue break
Answer
Answer: (c) Ligament break
MCQ Of Tissue Class 9 Chapter 6 Question 7.
While doing work and running, you move your organs Like hands, legs etc. Which among the following is correct?
(a) Smooth muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones.
(b) Smooth muscles contract and pull the tendons to move the bones.
(c) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones.
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones.
Answer
Answer: (d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones.
Class 9 Science Ch 6 MCQ Question 8.
Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muscles
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer
Answer: (b) (ii) and (iii)
Class 9 Tissues MCQ Chapter 6 Question 9.
Meristematic tissues in plants are
(a) localised and permanent
(b) not limited Lo certain regions
(c) localised and dividing cells
(d) growing in volume
Answer
Answer: (c) localised and dividing cells
Tissue MCQ Chapter 6 Question 10.
Which is not a function of epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
Answer
Answer: (c) Conduction of water
Ch 6 Science Class 9 MCQ Question 11.
Select the incorrect sentence.
(a) Blood has a matrix containing proteins, salts and hormones
(b) Two bones are connected by ligament
(c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
(d) Cartilage is a form of connective tissue
Answer
Answer: (c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
MCQ On Tissue Class 9 Chapter 6 Question 12.
Cartilage is not found in
(a) nose
(b) ear
(c) kidney
(d) larynx
Answer
Answer: (c) kidney
Tissues MCQs Class 9 Chapter 6 Question 13.
Fats are stored in human body as
(a) Cuboidal epithelium
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Bones
(d) Cartilage
Answer
Answer: (b) Adipose tissue
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 MCQ With Answers Question 14.
Bone matrix is rich in
(a) Fluoride and calcium
(b) Calcium and phosphorus
(c) Calcium and potassium
(d) Phosphorus and potassium
Answer
Answer: (b) Calcium and phosphorus
Class 9 Chapter 6 Science MCQ Question 15.
Contractile proteins are found in
(a) bones
(b) blood
(c) muscles
(d) cartilage
Answer
Answer: (c) muscles
Question 16.
Voluntary muscles are found in
(a) alimentary canal
(b) limbo
(c) iris of the eye
(d) bronchi of lungs
Answer
Answer: (b) limbo
Question 17.
Nervous tissue is not found in
(a) brain
(b) spinal cord
(c) tendons
(d) nerves
Answer
Answer: (c) tendons
Question 18.
Nerve cell does not contain
(a) axon
(b) nerve endings
(c) tendons
(d) dendrites
Answer
Answer: (c) tendons
Question 19.
Which of the following helps in repair of tissue and fills up the space inside the organ?
(a) Tendon
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Areolar
(d) Cartilage
Answer
Answer: (c) Areolar
Question 20.
The muscular tissue which function throughout life continuously without fatigue is
(a) skeletal muscle
(b) cardiac muscle
(c) smooth muscle
(d) voluntary muscle
Answer
Answer: (b) cardiac muscle
Question 21.
Which of the following cells is found in the cartilaginous tissue of the body?
(a) Mast cells
(b) Basophils
(c) Osteocytes
(d) Chondrocytes
Answer
Answer: (d) Chondrocytes
Question 22.
The dead element present in the phloem is
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) sieve tubes
Answer
Answer: (b) phloem fibres
Question 23.
Which of the following does not lose their nucleus at maturity?
(a) Companion cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Vessel
(d) Sieve tube cells
Answer
Answer: (a) Companion cells
Question 24.
In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to the presence of
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) lignin
(d) suberin
Answer
Answer: (a) cuticle
Question 25.
A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the side ways conduction of water in the branches is
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Answer
Answer: (d) xylem vessels
Question 26.
¡f the tip of sugar cane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. It is due to the presence of
(a) cambium
(b) apical meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) intercalary meristem
Answer
Answer: (d) intercalary meristem
Question 27.
A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3 years the nail will
(a) move downwards
(b) move upwards
(c) remain at the same position
(d) move sideways
Answer
Answer: (c) remain at the same position
Question 28.
Parenchyma cells are
(a) relatively unspecified and thin-walled
(b) thick walled and specialised
(c) lignified
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (a) relatively unspecified and thin-walled
Question 29.
Flexibility in plants is due to
(a) collenchyma
(b) scierenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) chiorenchyma
Answer
Answer: (a) collenchyma
Question 30.
Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
(a) cellulose
(b) lipids
(c) suberin
(d) lignin
Answer
Answer: (c) suberin
Question 31.
Survival of plants in terrestrial environment has been made possible by the presence of
(a) intercalary meristem
(b) conducting tissue
(c) apical meristem
(d) parenchymatous tissue
Answer
Answer: (b) conducting tissue

Question 32.
Choose the wrong statement.
(a) The nature of matrix differs according to the function of the tissue
(b) Fats are stored below the skin and in between the internal organs
(c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
(d) Cells of striated muscles are multinucle ate and unbranched
Answer
Answer: (c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
Question 33.
The water conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a) vessels
(b) sieve tube
(c) tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
Answer
Answer: (c) tracheids
Fill in the blanks:
1. Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the ……………. of the stem and the root.
Answer
Answer: Length
2. The ………….. meristem helps to increase the girth of the stem or root.
Answer
Answer: lateral
3. The process by which cells take up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called ……………..
Answer
Answer: specialisation
4. Large air cavities present in parenchyma of aquatic plants give ……………. to the plants to help them float.
Answer
Answer: buoyancy
5. Collenchyma is a …………… tissue present in plants which provides flexibility in plants.
Answer
Answer: simple permanent
6. The husk of a coconut is composed of …………… tissue.
Answer
Answer: sclerenchyrna
7. Two kidney-shaped cells called ……………… cells enclose the stomata.
Answer
Answer: guard
8. Cells of cork are dead and have a chemical called ……………. in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
Answer
Answer: suberin
9. The ……………. parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water.
Answer
Answer: xylem
10. An extracellular fibrous ……………. membrane separates all epithelium from the underlying tissue.
Answer
Answer: basement
11. The oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are covered with ……………… epithelium.
Answer
Answer: squamous
12. The …………….. epithelium is formed when the epithelial tissue folds inward and form a multicellular gland.
Answer
Answer: glandular
13. Blood has a fluid (liquid) matrix called …………….. in which red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs) and are suspended.
Answer
Answer: plasma, platelets
14. Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix that is composed of …………….. and ……………. compounds.
Answer
Answer: calcium and phosphorus
15. Tendon is a connective tissue which connects …………….. to bones.
Answer
Answer: muscles
16. Cartilage ……………. bone surfaces at joints and is also present in the nose, ear, trachea and larynx.
Answer
Answer: smoothens
17. The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow is called as ……………. tissue.
Answer
Answer: aerolar
18. The cells of ……………. muscular tissue are long, cylindrical, unbranched and multinucleate (having many nuclei).
Answer
Answer: striated
19. Heart muscle cells are cylindrical, …………… and uninucleate.
Answer
Answer: branched
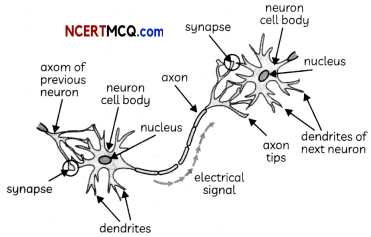
20. Each neuron has a single long part, called the ……………. and many short, branched parts called ………………
Answer
Answer: axon, dendrites
II. Match the following columns
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Adipocytes | (i) Blood |
| (b) Cartilage | (ii) Join bone to bone |
| (c) Tendon | (iii) Cambium |
| (d) Skin | (iv) Platelets |
| (e) Veins of leaves | (v) Fat containing cell |
| (f) Clotting of blood | (vi) Joins muscle to bones |
| (g) Fluid connective tissue | (vii) Stratified squamous epithelium |
| (h) Increases girth of stem | (viii) Composed of proteins and sugars |
| (i) Ligament | (ix) Sclerenchyma |
Answer
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Adipocytes | (v) Fat containing cell |
| (b) Cartilage | (viii) Composed of proteins and sugars |
| (c) Tendon | (vi) Joins muscle to bones |
| (d) Skin | (vii) Stratified squamous epithelium |
| (e) Veins of leaves | (ix) Sclerenchyma |
| (f) Clotting of blood | (iv) Platelets |
| (g) Fluid connective tissue | (i) Blood |
| (h) Increases girth of stem | (iii) Cambium |
| (i) Ligament | (ii) Join bone to bone |
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Tissues CBSE Class 9 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 9 Science Biology MCQ: