Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-8-science-with-answers/
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 MCQ With Answers
Science Class 8 Chapter 2 MCQs On Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Class 8 Science Chapter 2 MCQ Question 1.
Alcohol is produced with the help of
(a) sodium chloride
(b) yeast
(c) nitrogen
(d) carbon dioxide
Answer
Answer: (b) yeast
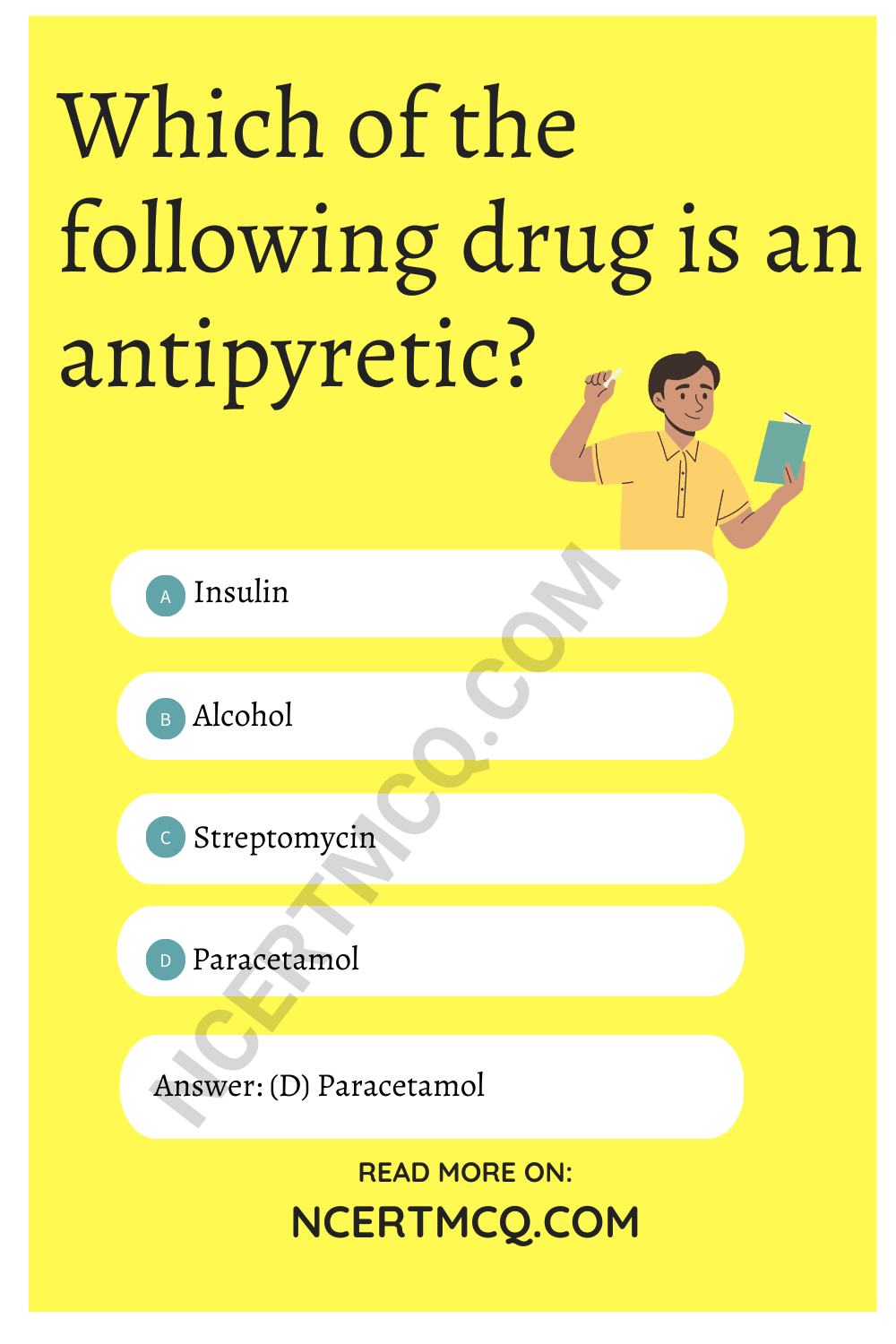
Microorganisms Friend And Foe Class 8 MCQ Question 2.
Which of the following drug is an antipyretic?
(a) Insulin
(b) Alcohol
(c) Streptomycin
(d) Paracetamol
Answer
Answer: (d) Paracetamol
Microorganisms Class 8 MCQ Question 3.
What helps in the rise of bread or dosa dough?
(a) Heat
(b) Grinding
(c) Growth of yeast cells
(d) Low pressure
Answer
Answer: (c) Growth of yeast cells
Class 8 Science Ch 2 MCQ Question 4.
The status of algae in the aquatic food chain is
(a) consumers
(b) producers
(c) host
(d) small in size
Answer
Answer: (b) producers
MCQ Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Question 5.
The rod shaped bacteria are called
(a) Bacillus
(b) Coccus
(c) Vibrio
(d) Spirillum
Answer
Answer: (a) Bacillus
Microorganisms Friend And Foe MCQ Question 6.
Bacteria present in root nodules of pea
(a) Coli
(b) Plasmodium
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Penicillin
Answer
Answer: (c) Rhizobium
Ncert Class 8 Science Chapter 2 MCQ Question 7.
The microorganism which contains chlorophyll
(a) Virus
(b) Fungus
(c) Algae
(d) All
Answer
Answer: (c) Algae
MCQ Questions For Class 8 Science With Answers Chapter 2 Question 8.
The disease caused by protozoa is
(a) tuberculosis
(b) polio
(c) typhoid
(d) malaria
Answer
Answer: (d) malaria
Class 8 Chapter 2 Science MCQ Question 9.
Which cannot fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Penicillin
Answer
Answer: (d) Penicillin
Ch 2 Science Class 8 MCQ Question 10.
The disease caused by fungi is
(a) measles
(b) chicken pox
(c) polio
(d) ringworm
Answer
Answer: (d) ringworm
Microorganisms MCQ Class 8 Question 11.
Which bacteria helps in settling of curd?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Lactobacillus
(c) Vibriocholarae
(d) Bacillus
Answer
Answer: (b) Lactobacillus
Science Class 8 Chapter 2 MCQ Question 12.
Which microorganism causes AIDS?
(a) A protozoa
(b) A bacteria
(c) A virus
(d) An algae
Answer
Answer: (c) A virus
Chapter 2 Science Class 8 MCQ Question 13.
Which of the following disease is spread due to bacteria?
(a) Tuberculosis
(b) Measles
(c) Chicken pox
(d) Polio
Answer
Answer: (a) Tuberculosis
MCQ For Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Question 14.
Which of the following is not used as food preservatives?
(a) Salt
(b) Sugar
(c) Vinegar
(d) Methane
Answer
Answer: (d) Methane
MCQ Of Microorganisms Class 8 Question 15.
The process by which amount of nitrogen remains the same in the atmosphere is known as
(a) fermentation
(b) carbon cycle
(c) nitrogen cycle
(d) photosynthesis
Answer
Answer: (c) nitrogen cycle

Match the following items given in Column ‘A with that in Column ‘B’:
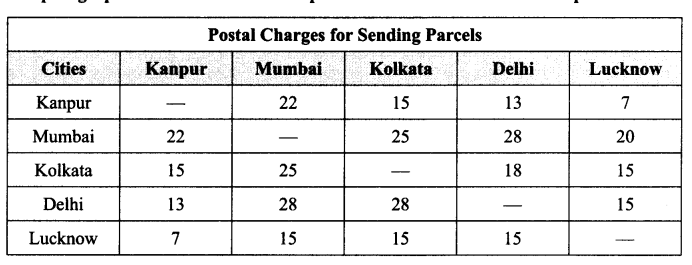
| Column A | Column B |
| Tuberculosis | Edward Jenner |
| Chicken pox | Fleming |
| Malaria | L. Pasteur |
| Rust of wheat | HIV |
| Pasteurization | Fungi |
| Antibiotic | Virus |
| Vaccination | Bacteria |
| AIDS | Protozoa |
Answer
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| Tuberculosis | Bacteria |
| Chicken pox | Virus |
| Malaria | Protozoa |
| Rust of wheat | Fungi |
| Pasteurization | L. Pasteur |
| Antibiotic | Fleming |
| Vaccination | Edward Jenner |
| AIDS | HIV |
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. ………….. are the smallest of all microorganisms.
Answer
Answer: Viruses
2. Fungi consist of two main groups of organisms ………….. and moulds.
Answer
Answer: yeast
3. Moulds are aerobic but some yeasts can survive in both aerobic and ………….. conditions.
Answer
Answer: anaerobic
4. The presence of ………….. and the warmth stimulate rapid growth of the yeast cells.
Answer
Answer: sugar
5. Algae are ………….. like organisms and contain chlorophyll.
Answer
Answer: plants
6. Agar is made from a type of red …………..
Answer
Answer: algae
7. Protozoa are ………….. just as algae are plant like.
Answer
Answer: animal like
8. Paramecium is slipper-shaped ………….. and possesses a ………….. for its transport.
Answer
Answer: protozoa, cilia
9. Viruses use the energy of the ………….. cells to reproduce themselves.
Answer
Answer: host
10. Cholera, chicken pox are some well-known examples of ………….. diseases.
Answer
Answer: communicable
11. Carriers of specific microorganisms are called …………..
Answer
Answer: Lactobacillus.
State whether the statements given below are True or False:
1. Microorganisms can be found only in air and water.
Answer
Answer: False
2. Protozoa cause diseases like dysentery and malaria.
Answer
Answer: True
3. Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by adding salt.
Answer
Answer: False
4. Some bacteria and blue green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen from atmosphere and convert into nitrogenous compounds.
Answer
Answer: True
5. Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
Answer
Answer: True.
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Microorganisms: Friend and Foe CBSE Class 8 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 8 Science MCQ:
- Crop Production and Management Class 8 MCQ
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 MCQ
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 MCQ
- Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 MCQ
- Coal and Petroleum Class 8 MCQ
- Combustion and Flame Class 8 MCQ
- Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 MCQ
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 MCQ
- Force and Pressure Class 8 MCQ
- Friction Class 8 MCQ
- Sound Class 8 MCQ
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current Class 8 MCQ
- Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 MCQ
- Light Class 8 MCQ
- Stars and the Solar System Class 8 MCQ
- Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 MCQ