Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-8-science-with-answers/
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers
Science Class 8 Chapter 4 MCQs On Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Class 8 Science Chapter 4 MCQ Question 1.
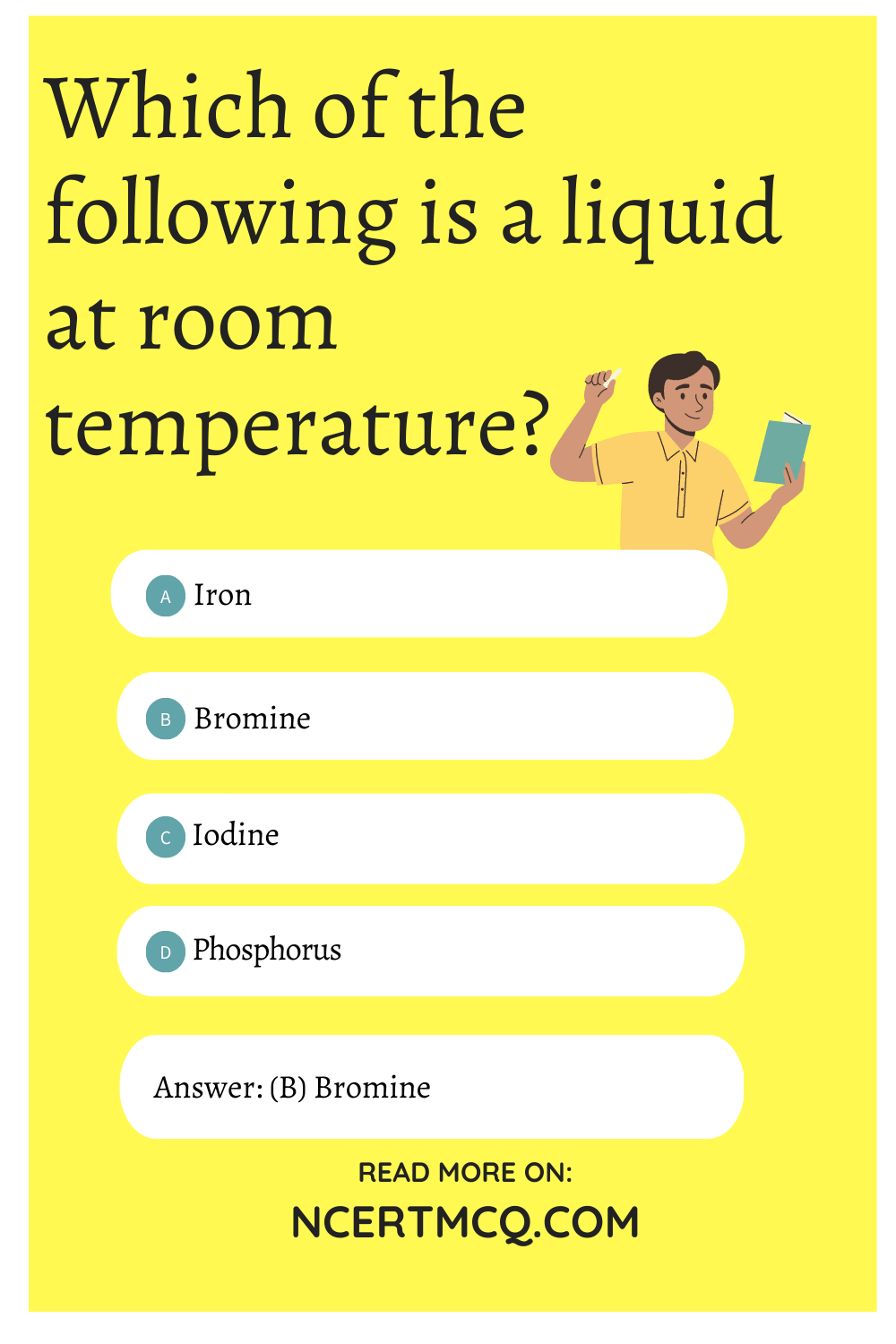
Which of the following is a liquid at room temperature?
(a) Iron
(b) Bromine
(c) Iodine
(d) Phosphorus
Answer
Answer: (b) Bromine
Metals And Non Metals Class 8 MCQ Question 2.
The most reactive metal is
(a) copper
(b) silver
(c) potassium
(d) calcium
Answer
Answer: (c) potassium
Class 8 Science Ch 4 MCQ Question 3.
The metal which is liquid at room temperature is
(a) sodium
(b) bromine
(c) calcium
(d) mercury
Answer
Answer: (d) mercury
Metal And Non Metals Class 8 MCQ Question 4.
Which one of the following metals is the most ductile?
(a) Aluminium
(b) Copper
(c) Silver
(d) Gold
Answer
Answer: (d) Gold
Metals And Non Metals MCQ Class 8 Question 5.
Which one of the following metals is the most reactive and stored in kerosene?
(a) Iron
(b) Gold
(c) Copper
(d) Potassium
Answer
Answer: (d) Potassium
Class 8 Metals And Non Metals MCQ Question 6.
Name the gas evolved when magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid
(a) Chlorine
(b) Oxygen
(c) hydrogen
(d) Nitrogen
Answer
Answer: (c) hydrogen
MCQ Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Question 7.
The metal which is not corroded by air, water and acid is
(a) copper
(b) zinc
(c) aluminium
(d) gold
Answer
Answer: (d) gold
Metals And Nonmetals Class 8 MCQ Question 8.
Metals are
(a) soft and brittle
(b) hard and solid
(c) liquid
(d) generally liquid
Answer
Answer: (b) hard and solid
Ch 4 Science Class 8 MCQ Question 9.
Materials having qualities of both metals and non-metals are
(a) alloys
(b) metalloids
(c) noble metals
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (b) metalloids
Class 8 Chapter 4 Science MCQ Question 10.
Which metal reacts readily with cold water?
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Magnesium
(d) Calcium
Answer
Answer: (d) Calcium
Chapter 4 Science Class 8 MCQ Question 11.
The best electrical conductor is
(a) gold
(b) copper
(c) silver
(d) aluminium
Answer
Answer: (c) silver
MCQ For Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Question 12.
Iron is galvanised by coating it with
(a) chromium
(b) sodium
(c) magnesium
(d) zinc
Answer
Answer: (d) zinc
MCQ On Metals And Non Metals Class 8 Question 13.
Out of these, which one is more reactive with water?
(a) Sodium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Iron
(d) Copper
Answer
Answer: (a) Sodium
Science Class 8 Chapter 4 MCQ Question 14.
Boron is
(a) metal
(b) metalloid
(c) non-metal
(d) alkali
Answer
Answer: (b) metalloid
Class 8 Science Chapter 4 MCQ With Answers Question 15.
A mineral from which. a metal can be extracted on the commercial scale, economically is called
(a) ore
(b) metalloid
(e) corrosion
(d) metal
Answer
Answer: (a) ore

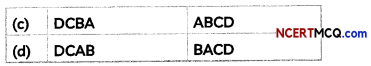
Match the following items given in Column ‘A’ with that in Column ‘B’:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| Zinc | Non-metal |
| iodine | Mercury |
| Liquid | Carbon |
| Graphite | Silver |
| Silicon | Water purification |
| Malleability | Metalloid |
| Chlorine | Bad conductor of heat |
| Non-metal | Metal |
Answer
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| Zinc | Metal |
| iodine | Non-metal |
| Liquid | Mercury |
| Graphite | Carbon |
| Silicon | Metalloid |
| Malleability | Silver |
| Chlorine | Water purification |
| Non-metal | Bad conductor of heat |
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
1. …………. is used in making mirrors.
Answer
Answer: Silver
2. …………. foils are used as packing material.
Answer
Answer: aluminium
3. …………. is used to prepare sulphuric acid.
Answer
Answer: Sulphur trioxide
4. A solution of …………. in alcohol has antiseptic properties.
Answer
Answer: iodine
5. Both …………. and …………. find extensive use in the native form as well as compounds.
Answer
Answer: metal, non-metal
6. Nitrates of …………. find use in photography.
Answer
Answer: silver
State whether the statements given below are True or False:
1. Sodium is more reactive than magnesium.
Answer
Answer: True
2. Magnesium reacts with cold water.
Answer
Answer: False
3. All înetal exist in solid form at room temperature.
Answer
Answer: False
4. Gallium has a low melting point.
Answer
Answer: True
5. Gold is allayed with copper to make it hard.
Answer
Answer: True
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Materials: Metals and Non-Metals CBSE Class 8 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 8 Science MCQ:
- Crop Production and Management Class 8 MCQ
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 MCQ
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 MCQ
- Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 MCQ
- Coal and Petroleum Class 8 MCQ
- Combustion and Flame Class 8 MCQ
- Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 MCQ
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 MCQ
- Force and Pressure Class 8 MCQ
- Friction Class 8 MCQ
- Sound Class 8 MCQ
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current Class 8 MCQ
- Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 MCQ
- Light Class 8 MCQ
- Stars and the Solar System Class 8 MCQ
- Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 MCQ