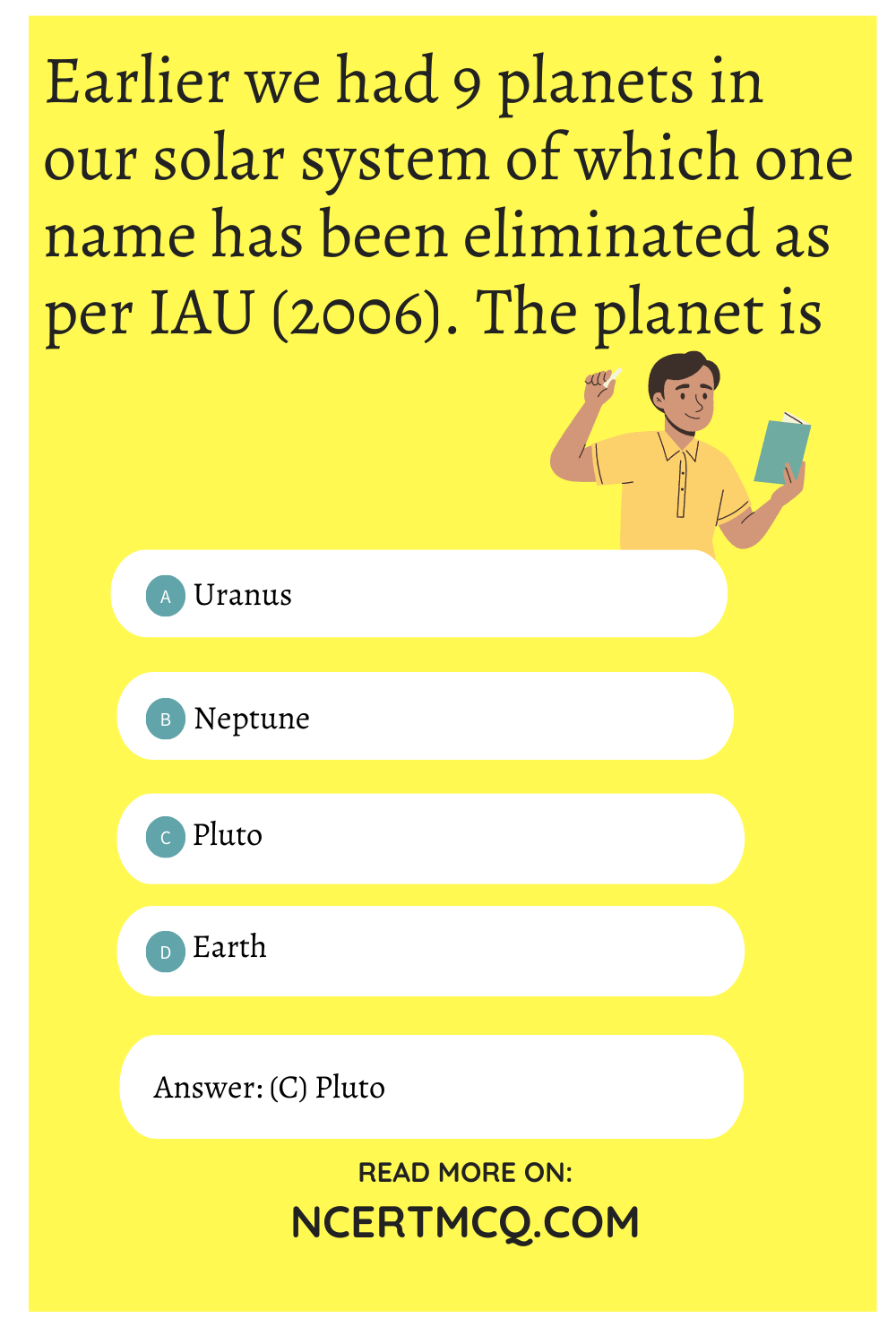
Check the below Online Education NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Sound Class 8 Science MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well. https://ncertmcq.com/mcq-questions-for-class-8-science-with-answers/
You can refer to NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound to revise the concepts in the syllabus effectively and improve your chances of securing high marks in your board exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 13 MCQ With Answers
Science Class 8 Chapter 13 MCQs On Sound
Choose the correct option.
Sound Class 8 MCQ Question 1.
The voice box is also called as
(a) stomach
(b) heart
(c) larynx
(d) mouth
Answer
Answer: (c) larynx
Sound MCQ Class 8 Question 2.
Sound is a kind of
(a) work
(b) energy
(c) force
(d) pressure
Answer
Answer: (b) energy
Class 8 Science Chapter 13 MCQ Question 3.
The hearing range of human ear is
(a) 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
(b) less than 20 Hz
(c) more than 20,000 Hz
(d) 20 Hz to 25,000 Hz
Answer
Answer: (a) 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
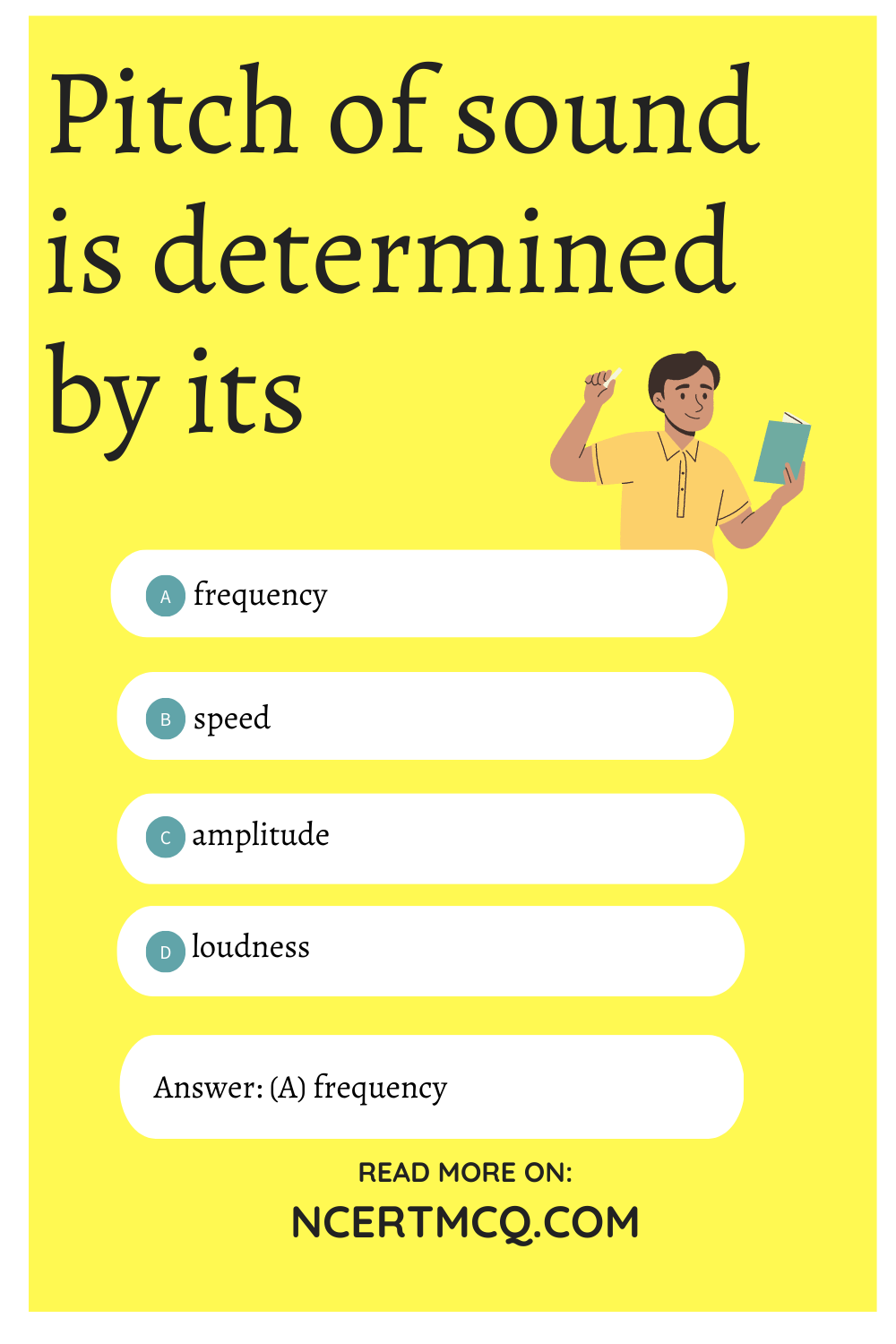
Class 8 Sound MCQ Question 4.
Pitch of sound is determined by its
(a) frequency
(b) speed
(c) amplitude
(d) loudness
Answer
Answer: (a) frequency
MCQ On Sound Class 8 Question 5.
The frequency of subsonic sound is
(a) more than 20 Hz
(b) 100 Hz
(c) less than 20 Hz
(d) more than 20,000 Hz
Answer
Answer: (c) less than 20 Hz
MCQ Of Sound Class 8 Question 6.
Cochlea is a part of
(a) hearing organ
(b) sound producing organ
(c) muscular organ
(d) air pollution
Answer
Answer: (a) hearing organ
Class 8 Science Sound MCQ Question 7.
1 hertz is equal to
(a) 1 vibration per minute
(b) 10 vibrations per minute
(c) 60 vibrations per minute
(d) 600 vibrations per minute
Answer
Answer: (c) 60 vibrations per minute
MCQ Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Question 8.
Sound cannot travel through
(a) air
(b) water
(c) air
(d) vacuum
Answer
Answer: (d) vacuum
Sound Chapter Class 8 MCQ Question 9.
The sound in the audible range is called
(a) ultrasonic sound
(b) sonic sound
(c) subonic sound
(d) light sound
Answer
Answer: (b) sonic sound
Class 8 Science Ch 13 MCQ Question 10.
Speed is
(a) \(\frac{Distance travelled}{Time}\)
(b) \(\frac{Time}{Distance travelled}\)
(c) Distance travelled × Time
(d) Time + Distance travelled
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{Distance travelled}{Time}\)
Ch 13 Science Class 8 MCQ Question 11.
A pendulum oscillates 20 times in 4 seconds. Find its time period.
(a) 0.05 sec.
(b) 0.001 sec.
(c) 0.2 sec.
(d) 0.1 sec
Answer
Answer: (c) 0.2 sec.
MCQ Sound Class 8 Question 12.
Loudness of sound is determined by
(a) pitch
(b) frequency
(c) amplitude
(d) time period
Answer
Answer: (c) amplitude
Class 8 Science Chapter Sound MCQ Question 13.
The number of vibrations made by a vibrating body in one second is
(a) frequency
(b) noise
(c) loudness
(d) pitch
Answer
Answer: (a) frequency
MCQs On Sound Class 8 Question 14.
The maximum displacement of a body from its mean position is called
(a) amplitude
(b) oscillation
(c) periodic motion
(d) frequency
Answer
Answer: (a) amplitude
MCQ Questions On Sound Class 8 Question 15.
The velocity of sound at 20°C is approximately
(a) 3400 m/sec.
(b) 340 m/sec.
(c) 430 m/sec
(d) 304 m/sec.
Answer
Answer: (b) 340 m/sec.
Question 16.
Sound is produced by
(a) Non-Vibrating objects only
(b) Vibrating and non- vibrating objects
(c) Vibration has no relation to sound
(d) Vibrating objects only
Answer
Answer: (d) Vibrating objects only
Question 17.
Sound cannot travel through
(a) vacuum
(b) air
(c) water
(d) solids
Answer
Answer: (a) vacuum
Question 18.
Vibration is also known as
(a) Vibratory motion
(b) Translatory motion
(c) Oscillatory motion
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Oscillatory motion
Question 19.
Frequency is expressed in
(a) Kilometer
(b) Hertz
(c) gram
(d) Degree centigrade
Answer
Answer: (b) Hertz
Question 20.
The number of oscillations per second is called
(a) Amplitude of oscillation
(b) Pitch of oscillation
(c) Frequency of oscillation
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Frequency of oscillation
Question 21.
Above _____ dB the sound becomes physically painful
(a) 60
(b) 40
(c) 120
(d) 80
Answer
Answer: (d) 80
Question 22.
When the amplitude of vibration is large, sound produced is
(a) No sound
(b) feeble
(c) loud
(d) No relation between amplitude and sound
Answer
Answer: (c) loud
Question 23.
Human can hear sound in the range of
(a) 200-2000 Hz
(b) 20-20,000 Hz
(c) 2-20000 Hz
(d) 2000-200000 Hz
Answer
Answer: (b) 20-20,000 Hz
Question 24.
An ultrasound equipment works at frequency
(a) Higher than 20,000 Hz
(b) Higher than 10,000 Hz
(c) Lower than 20,000 Hz
(d) Lower than 10,000 Hz
Answer
Answer: (a) Higher than 20,000 Hz
Question 25.
Voice of man is heavy compared to a woman because
(a) Female vocal cord is longer
(b) Male vocal cord is shorter
(c) Male vocal cord is longer
(d) The concept is not related
Answer
Answer: (c) Male vocal cord is longer

Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Audible frequencies | (a) 10 dB |
| 2. Length of vocal cords in man | (b) 30 dB |
| 3. Ultrasound | (c) 20 mm long |
| 4. Normal breathing | (d) 20 to 20,000 Hz |
| 5. Soft whisper (At 5 m) | (e) Hertz |
| 6. Frequency | (f) Percussion instrument |
| 7. Unpleasant sound | (g) Music |
| 8. Pitch | (h) Produced by bats |
| 9. Tabla | (i) Noise |
| 10. Pleasant sound | (j) Higher frequency |
Answer
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Audible frequencies | (d) 20 to 20,000 Hz |
| 2. Length of vocal cords in man | (c) 20 mm long |
| 3. Ultrasound | (h) Produced by bats |
| 4. Normal breathing | (a) 10 dB |
| 5. Soft whisper (At 5 m) | (b) 30 dB |
| 6. Frequency | (e) Hertz |
| 7. Unpleasant sound | (i) Noise |
| 8. Pitch | (j) Higher frequency |
| 9. Tabla | (f) Percussion instrument |
| 10. Pleasant sound | (g) Music |
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
1. human beings sound is produced by __________.
Answer
Answer: larynx
2. Sound of frequency lower than 20 Hz is called the __________.
Answer
Answer: infrasonic
3. The __________ nerve is also present in the inner ear.
Answer
Answer: auditory
4. Sounds which are unpleasant to the ear is called __________.
Answer
Answer: noise
5. Too much noise in our surroundings that causes discomfort is called __________.
Answer
Answer: noise pollution
6. The speed of sound is maximum in __________.
Answer
Answer: solids
7. Sounds of frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz are called the __________ sound.
Answer
Answer: ultrasonic
8. __________ is the time taken by a vibrating body for one complete vibration.
Answer
Answer: Time period
9. Above __________ the noise becomes physically painful.
Answer
Answer: 80 dB
10. Plantation on the roadside can reduce __________.
Answer
Answer: noise pollution
11. The hearing range of human ears is __________.
Answer
Answer: 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
12. The loudness of normal breathing of human is __________.
Answer
Answer: 10 dB
13. Vibration is a repeated __________ and __________ motion.
Answer
Answer: to, fro
14. The loudness of sound is determined by the __________ of vibration.
Answer
Answer: amplitude
15. The human voice box is called __________.
Answer
Answer: larynx
State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. All human beings can hear sounds of frequencies upto 60,000 Hz.
Answer
Answer: False
2. The sound in a sitar is produced by plucking its strings.
Answer
Answer: True
3. Sound cannot travel through vacuum.
Answer
Answer: True
4. Sound does not need a medium for its propagation.
Answer
Answer: False
5. The loudness is expressed in a unit called decibel.
Answer
Answer: True
6. Loud sounds have high frequencies.
Answer
Answer: False
7. Sound travel faster in air, slower in iron.
Answer
Answer: False
8. Light travels much faster than sound.
Answer
Answer: True
9. Man cannot hear sound of bats.
Answer
Answer: True
10. The time taken to complete one oscillation is called frequency.
Answer
Answer: False
11. Shriller sound has more frequency.
Answer
Answer: True
12. Tabla is a musical instrument.
Answer
Answer: True
13. The sound could not travel in solid.
Answer
Answer: False
14. The pitch of a sound depends in the frequency of the waves.
Answer
Answer: True
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Sound with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding Sound CBSE Class 8 Science MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 8 Science MCQ:
- Crop Production and Management Class 8 MCQ
- Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 MCQ
- Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Class 8 MCQ
- Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Class 8 MCQ
- Coal and Petroleum Class 8 MCQ
- Combustion and Flame Class 8 MCQ
- Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 MCQ
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 MCQ
- Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 MCQ
- Force and Pressure Class 8 MCQ
- Friction Class 8 MCQ
- Sound Class 8 MCQ
- Chemical Effects of Electric Current Class 8 MCQ
- Some Natural Phenomena Class 8 MCQ
- Light Class 8 MCQ
- Stars and the Solar System Class 8 MCQ
- Pollution of Air and Water Class 8 MCQ